ASTM E557-12
(Guide)Standard Guide for Architectural Design and Installation Practices for Sound Isolation between Spaces Separated by Operable Partitions
Standard Guide for Architectural Design and Installation Practices for Sound Isolation between Spaces Separated by Operable Partitions
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Rooms formed by operable partitions often need to be isolated acoustically. Sound-isolating properties of operable partitions are specified by architects in terms of sound transmission class (STC) and so advertised by the manufacturer on the basis of laboratory tests in accordance with Test Method E90 and Classification E413.
Because normal building design and construction practices are not the same as those used in acoustical laboratories, actual field performance of partitions, including operable partitions, will probably be less than that of test specimens. Sound transmission between areas to be isolated will occur through all of the connecting building components in addition to the operable partition, that is, floor and ceiling slabs, ceiling plenums, common walls, etc. All possible paths between the areas being isolated should have a sound insulation performance at least equal to the operable partition. Unless good acoustical practice is followed in both building design and installation, there may be a significant discrepancy between the sound isolation expected and that achieved.
Because of the complex nature of the sound flanking paths adjacent to operable partitions, it is highly recommended that all related construction details be reviewed by a person qualified in acoustical design and construction.
This guide does not specify requirements. However, persons desiring to write installation and construction specifications may find the contents useful in developing requirements for the building design site preparation, and installation practices necessary to minimize leakage and flanking sound around the operable partition.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides design details that should be considered in the design of buildings that include operable partitions. Operable partitions are those that can be quickly put in place or removed and stored to provide flexibility in the size of spaces typically used for meetings or social functions.
1.1.1 The guide primarily discusses details in the building design required to limit leakage of sound around an operable partition.
1.1.2 The guide also discusses some factors that affect the performance of the partitions themselves.
1.1.3 This guide is neither a specification for operable partitions nor a document intended to be imposed as a requirement on manufacturers of operable partitions.
1.2 Excluded from this guide are those partitions that are classified by the building products industry as demountable. Demountable partitions are those that are designed and installed with the intent of later being taken down and re-erected by a crew over a period of time, with the components being reusable.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E557 − 12
Standard Guide for
Architectural Design and Installation Practices for Sound
1
Isolation between Spaces Separated by Operable Partitions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E557; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This guide provides design details that should be con-
E90 Test Method for Laboratory Measurement of Airborne
sidered in the design of buildings that include operable
Sound Transmission Loss of Building Partitions and
partitions. Operable partitions are those that can be quickly put
Elements
in place or removed and stored to provide flexibility in the size
E336 Test Method for Measurement of Airborne Sound
of spaces typically used for meetings or social functions.
Attenuation between Rooms in Buildings
1.1.1 The guide primarily discusses details in the building
E413 Classification for Rating Sound Insulation
design required to limit leakage of sound around an operable
E1155 Test Method for Determining F Floor Flatness and
partition.
F
F Floor Levelness Numbers
1.1.2 The guide also discusses some factors that affect the
L
E1155M TestMethodforDetermining F FloorFlatnessand
performance of the partitions themselves.
F
F Floor Levelness Numbers (Metric)
1.1.3 This guide is neither a specification for operable
L
partitions nor a document intended to be imposed as a
3. Significance and Use
requirement on manufacturers of operable partitions.
3.1 Rooms formed by operable partitions often need to be
1.2 Excluded from this guide are those partitions that are
isolated acoustically. Sound-isolating properties of operable
classified by the building products industry as demountable.
partitions are specified by architects in terms of sound trans-
Demountable partitions are those that are designed and in-
mission class (STC) and so advertised by the manufacturer on
stalled with the intent of later being taken down and re-erected
the basis of laboratory tests in accordance with Test Method
by a crew over a period of time, with the components being
E90 and Classification E413.
reusable.
3.2 Because normal building design and construction prac-
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
tices are not the same as those used in acoustical laboratories,
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
actual field performance of partitions, including operable
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
partitions, will probably be less than that of test specimens.
and are not considered standard.
Sound transmission between areas to be isolated will occur
through all of the connecting building components in addition
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the to the operable partition, that is, floor and ceiling slabs, ceiling
plenums, common walls, etc. All possible paths between the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- areas being isolated should have a sound insulation perfor-
mance at least equal to the operable partition. Unless good
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
acoustical practice is followed in both building design and
installation, there may be a significant discrepancy between the
sound isolation expected and that achieved.
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E33 on Building and
EnvironmentalAcousticsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeE33.04on
2
Application of Acoustical Materials and Systems. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2012. Published June 2012. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ε1
approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as E557 - 00(2006) . Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/E0557-12. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
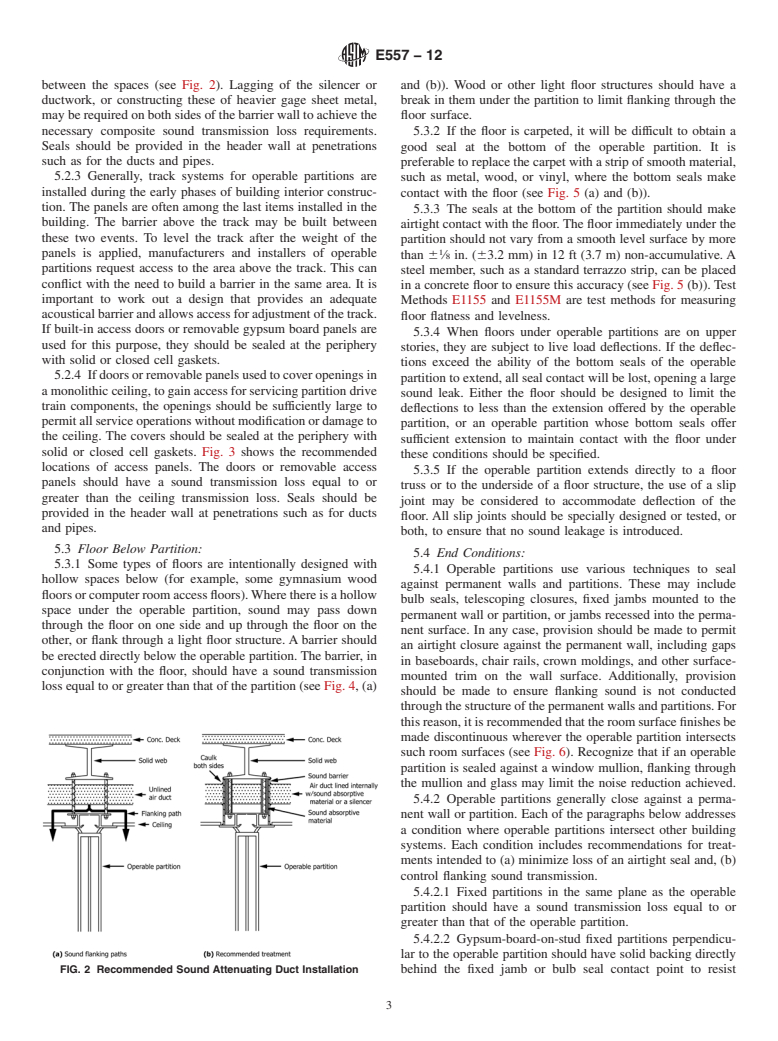
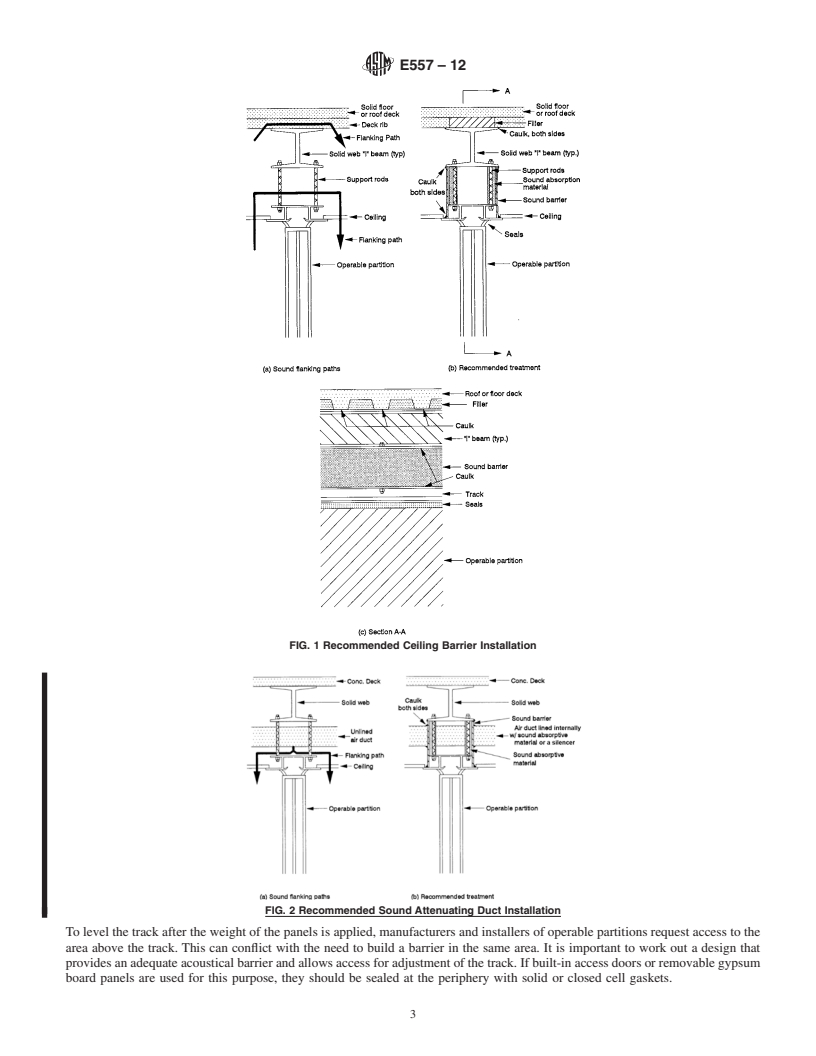
E557 − 12
3.3 Because of the complex nature of the sound flanking ceiling on the other.Abarrier should be erected directly above
paths adjacent to operable partitions, it is highly recommended the operable partitions. This barrier, in conjunction with the
that all related construction details
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation:E557–00(Reapproved 2006) Designation:E557–12
Standard Guide for
The Installation of Operable PartitionsArchitectural Design
and Installation Practices for Sound Isolation between
1
Spaces Separated by Operable Partitions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E557; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1
´ NOTE—1.3, units of measure statement, was editorially inserted and Fig. 3 and 5.3.3 and 5.4 were editorially revised in May
2010.
1. Scope
1.1This guide describes options of intructions recommended to be considered in preparation for, and application and installation
of, operable partitions and, to some extent, in the design of the building in which they are installed. Operable partitions are those
that are quickly movable.
1.1 This guide provides design details that should be considered in the design of buildings that include operable partitions.
Operable partitions are those that can be quickly put in place or removed and stored to provide flexibility in the size of spaces
typically used for meetings or social functions.
1.1.1 The guide primarily discusses details in the building design required to limit leakage of sound around an operable
partition.
1.1.2 The guide also discusses some factors that affect the performance of the partitions themselves.
1.1.3 This guide is neither a specification for operable partitions nor a document intended to be imposed as a requirement on
manufacturers of operable partitions.
1.2 Excluded from this guide are those partitions that are classified by the building products industry as demountable.
Demountable partitions are those that are designed and installed with the intent of later being taken down and re-erected by a crew
over a period of time, with the components being reusable.
1.3The1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E90 Test Method for Laboratory Measurement of Airborne Sound Transmission Loss of Building Partitions and Elements
E336 Test Method for Measurement of Airborne Sound Attenuation between Rooms in Buildings
E413 Classification for Rating Sound Insulation E497Practice for Installing Sound-Isolating Lightweight Partitions
E1155 Test Method for Determining F Floor Flatness and F Floor Levelness Numbers
F L
E1155M Test Method for Determining F Floor Flatness and F Floor Levelness Numbers (Metric)
F L
3. Significance and Use
3.1 Rooms formed by operable partitions must often need to be isolated acoustically. Sound-isolating properties of operable
partitions are specified by architects in terms of sound transmission class (STC) and so advertised by the manufacturer on the basis
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E33 on Building and Environmental Acoustics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E33.04 on
Application of Acoustical Materials and Systems.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2006. Published September 2006. Originally approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as E557-00. DOI:
10.1520/E0557-00R06E01.
´1
Current edition approved April 1, 2012. Published June 2012. Originally approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as E557 - 00(2006) . DOI:
10.1520/E0557-12.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E557–12
of laboratory tests in accordance with Test Method E90 and Classification E413.
3.2 Because normal building design
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.