ASTM D5288-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Tracking Index of Electrical Insulating Materials Using Various Electrode Materials (Excluding Platinum)
Standard Test Method for Determining Tracking Index of Electrical Insulating Materials Using Various Electrode Materials (Excluding Platinum)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
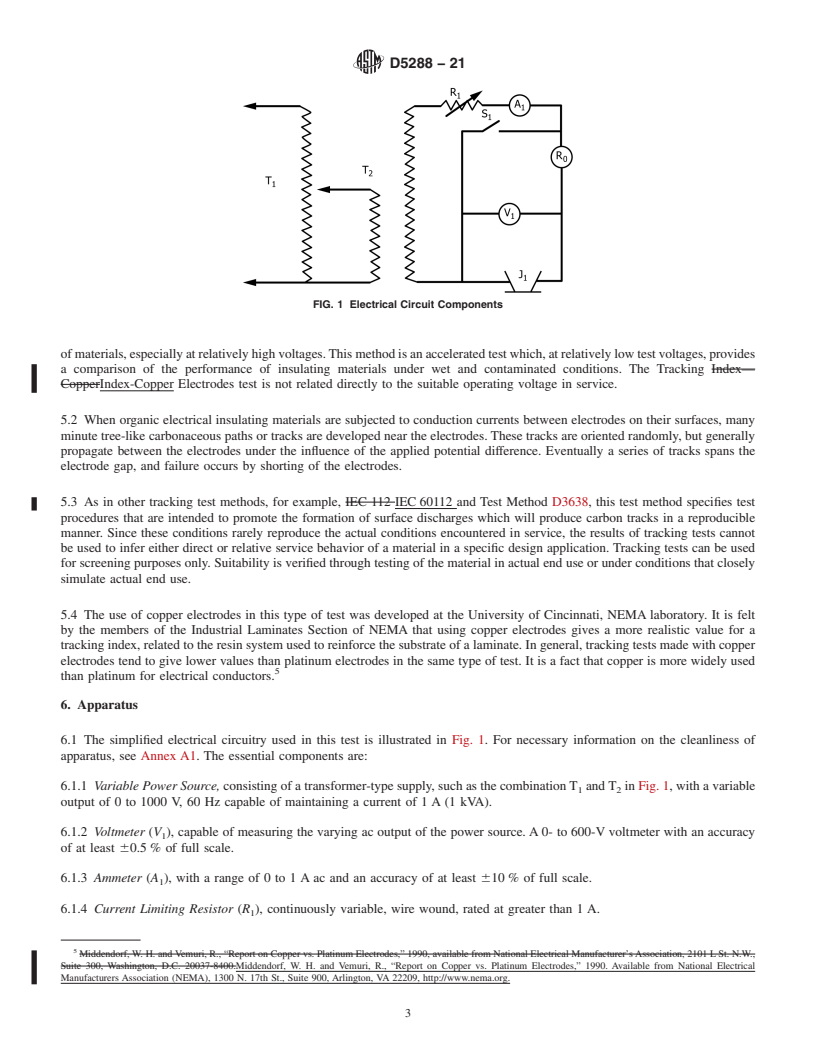
5.1 Electrical equipment has the potential to fail as a result of electrical tracking of insulating material that is exposed to various contaminating environments and surface conditions. A number of ASTM and other tests have been designed to quantify behavior of materials, especially at relatively high voltages. This method is an accelerated test which, at relatively low test voltages, provides a comparison of the performance of insulating materials under wet and contaminated conditions. The Tracking Index-Copper Electrodes test is not related directly to the suitable operating voltage in service.
5.2 When organic electrical insulating materials are subjected to conduction currents between electrodes on their surfaces, many minute tree-like carbonaceous paths or tracks are developed near the electrodes. These tracks are oriented randomly, but generally propagate between the electrodes under the influence of the applied potential difference. Eventually a series of tracks spans the electrode gap, and failure occurs by shorting of the electrodes.
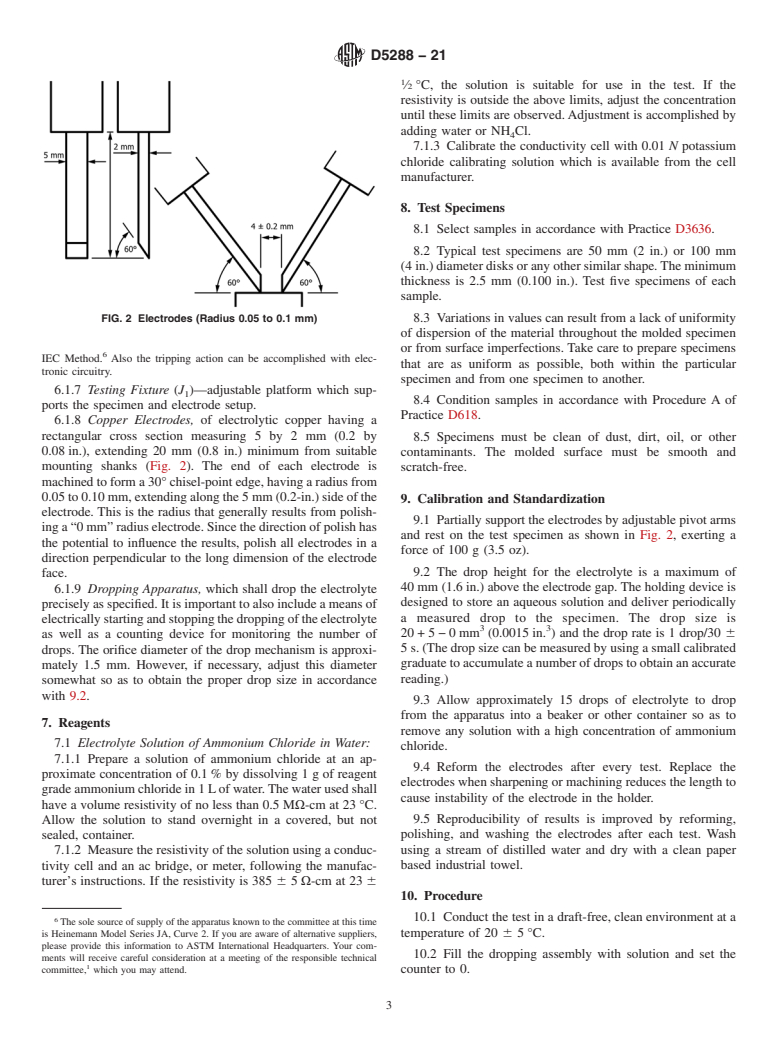
5.3 As in other tracking test methods, for example, IEC 60112 and Test Method D3638, this test method specifies test procedures that are intended to promote the formation of surface discharges which will produce carbon tracks in a reproducible manner. Since these conditions rarely reproduce the actual conditions encountered in service, the results of tracking tests cannot be used to infer either direct or relative service behavior of a material in a specific design application. Tracking tests can be used for screening purposes only. Suitability is verified through testing of the material in actual end use or under conditions that closely simulate actual end use.
5.4 The use of copper electrodes in this type of test was developed at the University of Cincinnati, NEMA laboratory. It is felt by the members of the Industrial Laminates Section of NEMA that using copper electrodes gives a more realistic value for a tracking...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method was developed using copper electrodes to evaluate the low-voltage (up to 600 V) tracking resistance of materials in the presence of aqueous contaminants.2
Note 1: At this time, only industrial laminates have been examined using this method, which was developed at the National Manufacturers Electrical Association (NEMA) laboratory located at the University of Cincinnati. It was found that a closer end point (less scatter) was obtained than with platinum electrodes, and materials tested tended to be ranked by resin system.
1.1.1 It is acceptable to consider other electrode materials for use with this test method depending upon the application of the insulating material.
1.2 This test method is similar to Test Method D3638, which determines the comparative tracking index of materials using platinum electrodes to produce the tracking on the specimen surface.
1.3 The values stated in metric (SI) units are the standard. The inch-pound equivalents of the metric units are approximate.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting these tests.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5288 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Determining Tracking Index of Electrical Insulating Materials
1
Using Various Electrode Materials (Excluding Platinum)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5288; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.1 Thistestmethodwasdevelopedusingcopperelectrodes
toevaluatethelow-voltage(upto600V)trackingresistanceof
2. Referenced Documents
2
materials in the presence of aqueous contaminants.
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NOTE 1—At this time, only industrial laminates have been examined
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
using this method, which was developed at the National Manufacturers
D1711Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
Electrical Association (NEMA) laboratory located at the University of
Cincinnati. It was found that a closer end point (less scatter) was obtained D3636Practice for Sampling and Judging Quality of Solid
thanwithplatinumelectrodes,andmaterialstestedtendedtoberankedby
Electrical Insulating Materials
resin system.
D3638Test Method for Comparative Tracking Index of
1.1.1 It is acceptable to consider other electrode materials
Electrical Insulating Materials
4
forusewiththistestmethoddependingupontheapplicationof
2.2 IEC Publication:
the insulating material.
IEC 60112Standard Method for the Determination of the
Proof and the Comparative Tracking Indices of Solid
1.2 This test method is similar to Test Method D3638,
Insulating Materials, 2003
which determines the comparative tracking index of materials
using platinum electrodes to produce the tracking on the
3. Terminology
specimen surface.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
1.3 The values stated in metric (SI) units are the standard.
method and associated with electrical and electronic insulating
The inch-pound equivalents of the metric units are approxi-
materials, use Terminology D1711.
mate.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.1 tracking index, TI, n—an index for electrical insulat-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ingmaterialswhichisarbitrarilydefinedasthenumericalvalue
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
of that voltage which will cause failure by tracking when the
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
number of drops of contaminant required to cause failure is
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
equal to 50.
1.5 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safe-
3.2.1.1 Discussion—This value is obtained from a plot of
guards for personnel and property shall be employed in
the number of drops required to cause failure by tracking
conducting these tests.
versus the applied voltage.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.2.2 tracking index-copper electrodes, TI-Cu, n—a track-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ing index test using copper electrodes.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.2.2.1 Discussion—This test is comparable to comparative
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
tracking index,Test Method D3638, with the following excep-
tions: (1) copper electrodes are used instead of platinum, and
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
3
Subcommittee D09.12 on Electrical Tests. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2021. Published October 2021. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D5288–14. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D5288-21. the ASTM website.
2 4
Mathes, K. N., “Surface Failure Measurements,” in Engineering Dielectrics Available from International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), 3, rue de
Volume IIB Electrical Properties of Solid Insulating Materials: Measurement Varembé, 1st floor, P.O. Box 131, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland, https://
Techniques, STP926, ASTM International, 1987. www.iec.ch.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this s
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5288 − 14 D5288 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Determining Tracking Index of Electrical Insulating Materials
1
Using Various Electrode Materials (Excluding Platinum)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5288; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method was developed using copper electrodes to evaluate the low-voltage (up to 600 V) tracking resistance of
2
materials in the presence of aqueous contaminants.
NOTE 1—At this time, only industrial laminates have been examined using this method, which was developed at the National Manufacturers Electrical
Association (NEMA) laboratory located at the University of Cincinnati. It was found that a closer end point (less scatter) was obtained than with platinum
electrodes, and materials tested tended to be ranked by resin system.
1.1.1 It is acceptable to consider other electrode materials for use with this test method depending upon the application of the
insulating material.
1.2 This test method is similar to Test Method D3638, which determines the comparative tracking index of materials using
platinum electrodes to produce the tracking on the specimen surface.
1.3 The values stated in metric (SI) units are the standard. The inch-pound equivalents of the metric units are approximate.
1.4 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under
controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the materials,
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with
its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting these
tests.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D09.12 on Electrical Tests.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2014Sept. 1, 2021. Published December 2014October 2021. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 20102014
as D5288 – 10.D5288 – 14. DOI: 10.1520/D5288-14.10.1520/D5288-21.
2
Mathes, K. N., Chapter 4, “Surface Failure Measurements,” Engineering Dielectrics, Vol IIB, Electrical Properties of Solid Insulating Materials, Measurement
Techniques, R. Bartnikas, Editor, ASTM STP 926, ASTM, Philadelphia, 1987.Mathes, K. N., “Surface Failure Measurements,” in Engineering Dielectrics Volume IIB
Electrical Properties of Solid Insulating Materials: Measurement Techniques, STP926, ASTM International, 1987.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5288 − 21
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
D3636 Practice for Sampling and Judging Quality of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials
D3638 Test Method for Comparative Tracking Index of Electrical Insulating Materials
4
2.2 IEC Publication:
IEC 60112 Standard Method for the Determination of the Proof and the Comparative Tracking Indices of Solid Insulating
Materials, 2003
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test method and associated with electrical and electronic insulating materials,
use Terminology D1711.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 track, n—a partially conducting path of localized deterioration on the surface of an insulating material.
3.2.2 tracking, n—the process
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.