ASTM B888/B888M-17
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper Alloy Strip for Use in Manufacture of Electrical Connectors or Spring Contacts
Standard Specification for Copper Alloy Strip for Use in Manufacture of Electrical Connectors or Spring Contacts
ABSTRACT
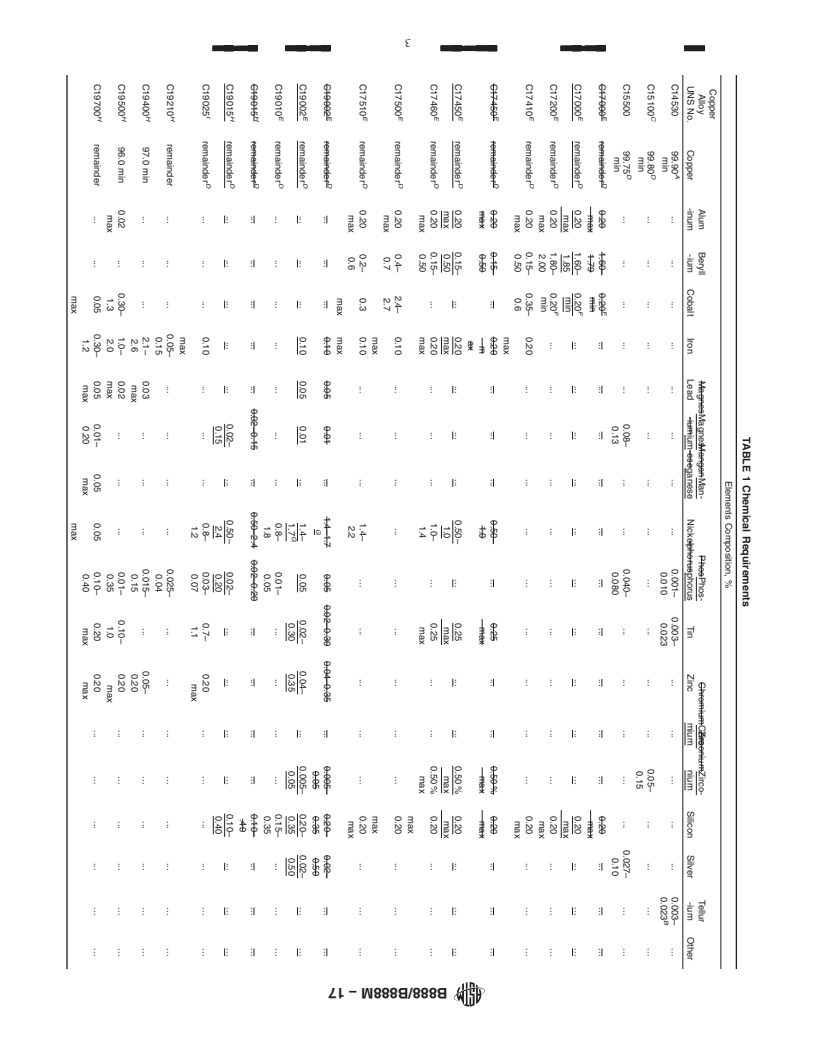
This specification establishes the requirements for copper alloy strips for use in the manufacture of electrical connectors or spring contacts produced from one of the following Copper Alloy UNS Nos.: C14530, C15100, C15500, C17000, C17200, C17410, C17450, C17460, C17500, C17510, C19010, C19025, C19210, C19400, C19500, C19700, C23000, C26000, C40810, C40850, C40860, C42200, C42500, C42520, C42600, C50580, C50780, C51000, C51080, C51100, C51180, C51980, C52100, C52180, C52480, C63800, C65400, C68800, C70250, C70260, C70265, C75200, and C76200. The material for manufacture shall be a cast bar, slab, cake, billet, or other form of such composition as to be suitable for processing by either hot- or cold-working to produce the products prescribed in this specification. Products shall be finished by hot working, cold working, annealing, or heat treatment as may be necessary to meet mechanical property requirements, which include tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation. Tempers shall be available in the annealed, rolled, or mill hardened conditions. Products shall also adhere to tolerances as to dimension such as thickness, width, length, straightness, and mass.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for copper alloy strip for use in the manufacture of electrical connectors or spring contacts produced from one of the following Copper Alloy UNS Nos.2: C14530, C15100, C15500, C17000, C17200, C17410, C17450, C17460, C17500, C17510, C19002, C19010, C19015, C19025, C19210, C19400, C19500, C19700, C23000, C26000, C40810, C40850, C40860, C42200, C42500, C42520, C42600, C50580, C50780, C51000, C51080, C51100, C51180, C51980, C52100, C52180, C52480, C63800, C64725, C65400, C68800, C70250, C70260, C70265, C70310, C70350, C75200, and C76200.
1.2 The requirements for the other copper alloys such as copper-nickel-tin spinodal, UNS C72650, C72700, and C72900, shall be as prescribed in the current edition of Specification B740.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B888/B888M −17
Standard Specification for
Copper Alloy Strip for Use in Manufacture of Electrical
1
Connectors or Spring Contacts
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B888/B888M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
3
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for cop- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
per alloy strip for use in the manufacture of electrical connec- B193Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor
tors or spring contacts produced from one of the following Materials
2
CopperAlloy UNS Nos. : C14530, C15100, C15500, C17000, B248Specification for General Requirements for Wrought
C17200, C17410, C17450, C17460, C17500, C17510, Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled
C19002, C19010, C19015, C19025, C19210, C19400, Bar
C19500, C19700, C23000, C26000, C40810, C40850, B248MSpecificationforGeneralRequirementsforWrought
C40860, C42200, C42500, C42520, C42600, C50580, Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled
C50780,C51000,C51080,C51100,C51180,C51980,C52100, Bar (Metric)
C52180, C52480, C63800, C64725, C65400, C68800, B601ClassificationforTemperDesignationsforCopperand
C70250, C70260, C70265, C70310, C70350, C75200, and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
C76200. B740Specification for Copper-Nickel-Tin Spinodal Alloy
Strip
1.2 The requirements for the other copper alloys such as
B820Test Method for BendTest for Determining the Form-
copper-nickel-tin spinodal, UNS C72650, C72700, and
ability of Copper and Copper Alloy Strip
C72900, shall be as prescribed in the current edition of
B846Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
Specification B740.
E8/E8MTest Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Ma-
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
terials
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
E54Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Special Brasses
4
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
and Bronzes (Withdrawn 2002)
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
E62Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and
4
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
CopperAlloys(PhotometricMethods)(Withdrawn2010)
with the standard.
E75Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel
4
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor- and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys (Withdrawn 2010)
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
E478Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of CopperAlloys
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the E527Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
5
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical 2.2 ISO Standards:
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ISO 4744Copper and Copper Alloys—Determination of
Chromium Content—Flame Atomic Absorption Spectro-
metric Method
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of Committee B05 on Copper and
Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.01 on Plate,
3
Sheet, and Strip. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2017. Published April 2017. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approvedin1998.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2013asB888/B888M-13.DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/B0888_B0888M-17. the ASTM website.
2 4
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E527) is a simple The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition www.astm.org.
5
of a prefix “c” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
composition variations of the base alloy. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B888/B888M−17
ISO 7602Copper and Copper Alloys—Determination of 6.2.2 Width and straightness tolerances, slit-metal
Tellurium Content tolerances, square-sheared metal tolerances, sawed metal
tolerances, straightened or edge-rolled metal tolerances (Sec-
3. Terminology tion 11),
6.2.3 Identification marking (Section 22),
3.
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B888/B888M − 13 B888/B888M − 17
Standard Specification for
Copper Alloy Strip for Use in Manufacture of Electrical
1
Connectors or Spring Contacts
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B888/B888M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishes the requirements for copper alloy strip for use in the manufacture of electrical connectors or
2
spring contacts produced from one of the following Copper Alloy UNS Nos. : C14530, C15100, C15500, C17000, C17200,
C17410, C17450, C17460, C17500, C17510, C19002, C19010, C19015, C19025, C19210, C19400, C19500, C19700, C23000,
C26000, C40810, C40850, C40860, C42200, C42500, C42520, C42600, C50580, C50780, C51000, C51080, C51100, C51180,
C51980, C52100, C52180, C52480, C63800, C64725, C65400, C68800, C70250, C70260, C70265, C70310, C70350, C75200,
and C76200.
1.2 The requirements for the other copper alloys such as copper-nickel-tin spinodal, UNS C72650, C72700, and C72900, shall
be as prescribed in the current edition of Specification B740.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B193 Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials
B248 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
B248M Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
(Metric)
B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
B740 Specification for Copper-Nickel-Tin Spinodal Alloy Strip
B820 Test Method for Bend Test for Determining the Formability of Copper and Copper Alloy Strip
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
E8/E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
4
E54 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Special Brasses and Bronzes (Withdrawn 2002)
4
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods) (Withdrawn 2010)
4
E75 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys (Withdrawn 2010)
E478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.01 on Plate, Sheet, and
Strip.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2013April 1, 2017. Published November 2013April 2017. Originally approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 20122013 as
B888 – 12.B888/B888M-13. DOI: 10.1520/B0888_B0888M-13.10.1520/B0888_B0888M-17.
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E527) is a simple expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of a
prefix “c” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of the base alloy.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B888/B888M − 17
5
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 4744 Copper and Copper Alloys—Determination of Chromium Content—Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Method
ISO 7602 Copper and Copper Al
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.