ASTM D5824-98(2011)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Resistance to Delamination of Adhesive Bonds in Overlay-Wood Core Laminates Exposed to Heat and Water
Standard Test Method for Determining Resistance to Delamination of Adhesive Bonds in Overlay-Wood Core Laminates Exposed to Heat and Water
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method measures quantitatively the effects of water soaking and drying, and their associated swelling and shrinking stresses on adhesive bonds in overlay-laminated assemblies.
Adhesive bond performance is based on the ability of the adhesive and adhesive bonds to resist delamination during accelerated exposure to water and heat.
Resistance to delamination when subjected to environmental factors is critical to the performance of the laminated assembly in service.
This test method is to be used to determine the quality of adhesive bonds in overlay-wood core laminates after the adhesive has been certified by a specification appropriate for the product, class, and end use.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides a procedure to determine the quality of bond between an overlay and a wood core in an adhesively bonded laminate. The quality of bond is determined by measuring the resistance to delamination of the adhesively bonded laminate when tested under specific conditions of preparation, conditioning, and testing. Such products include, but are not limited to, window and door components, such as stiles and rails, and other overlaid panels. Typical wood-based cores are finger-jointed lumber, particleboard, oriented strand board, and hardboard. Typical overlays would be veneer, high-pressure laminate, high-density polyethylene, and fiberglass-reinforced plastic.
1.2 Adhesive bond performance as measured by resistance to delamination in this test method is suitable for use in adhesive product development, manufacturing quality control, and monitoring bonding processes.
1.3 This test method does not provide guidance for determining bond line performance for plywood products.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5824 − 98 (Reapproved 2011)
Standard Test Method for
Determining Resistance to Delamination of Adhesive Bonds
in Overlay-Wood Core Laminates Exposed to Heat and
Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5824; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This test method provides a procedure to determine the 2.1 ASTM Standards:
quality of bond between an overlay and a wood core in an D907 Terminology of Adhesives
adhesively bonded laminate.The quality of bond is determined D4442 Test Methods for Direct Moisture Content Measure-
by measuring the resistance to delamination of the adhesively ment of Wood and Wood-Based Materials
bonded laminate when tested under specific conditions of D5266 Practice for Estimating the Percentage of Wood
preparation, conditioning, and testing. Such products include, Failure in Adhesive Bonded Joints
but are not limited to, window and door components, such as E6 Terminology Relating to Methods of Mechanical Testing
stiles and rails, and other overlaid panels. Typical wood-based E41 Terminology Relating To Conditioning
cores are finger-jointed lumber, particleboard, oriented strand E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
board, and hardboard. Typical overlays would be veneer, ASTM Test Methods
high-pressure laminate, high-density polyethylene, and E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
fiberglass-reinforced plastic. Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.2 Adhesive bond performance as measured by resistance
3. Terminology
to delamination in this test method is suitable for use in
3.1 Definitions:
adhesive product development, manufacturing quality control,
3.1.1 Certain terms in this test method are defined in
and monitoring bonding processes.
Terminologies D907, E6, and E41.
1.3 This test method does not provide guidance for deter-
3.1.2 delamination, n—the separation of layers in a laminate
mining bond line performance for plywood products.
because of failure of the adhesive, either in the adhesive itself
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded or at the interface between the adhesive and the adherend. (See
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Terminology D907.)
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.1.3 overlay, n—a uniform layer of material, usually in the
and are not considered standard.
form of a sheet, adhesively bonded to an adherend with the
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the purpose of improving the appearance or physical properties of
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
the laminate.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.2.1 edge, n—in an adhesively bonded laminate, the di-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
mension along its length [and parallel to the grain] where the
overlay is bonded to the core.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D14 on
Adhesives and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D14.30 on Wood
Adhesives. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved April 1, 2011. Published April 2011. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D5824 – 98 (2003). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D5824-98R11. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5824 − 98 (2011)
3.2.2 end, n—in an adhesively bonded laminate, the dimen- 6. Test Specimens
sion which is perpendicular to the length of the laminate where
6.1 Cut laboratory specimens from prepared test panels (see
the overlay is bonded to the core.
Fig. 1) as described in Sections 7 and 8 to the form and
dimensions shown in Fig. 2 and Table 1.
4. Significance and Use
6.2 Cut field specimens from test panels (see Fig. 3)tothe
4.1 This test method measures quantitatively the effects of
form and dimensions shown in Fig. 2 and Table 1. When the
water soaking and drying, and their associated swelling and
nominalwidthofthepanelisused,theedgesaretobeprepared
shrinking stresses on adhesive bonds in overlay-laminated
as the product would exist in service.
assemblies.
6.3 Test ten specimens, representing at least four different
4.2 Adhesive bond performance is based on the ability of
panels.
the adhesive and adhesive bonds to resist delamination during
accelerated exposure to water and heat.
7. Preparation and Conditioning of Laboratory Test
4.3 Resistance to delamination when subjected to environ-
Panels
mental factors is critical to the performance of the laminated
7.1 Select veneer, either rotary cut or sliced, 0.063 in. (1.6
assembly in service.
mm) in thickness, and wood-based core, a minimum of 0.5 in.
4.4 Thistestmethodistobeusedtodeterminethequalityof
(13 mm) in thickness, so that they are free from defects such as
adhesive bonds in overlay-wood core laminates after the
knots, cracks, rough surfaces, or any unusual amount of
adhesive has been certified by a specification appropriate for
discoloration. The species and type of veneer and composition
the product, class, and end use.
of the wood core are to be agreed upon between the purchaser
and the manufacturer of the adhesive. As an alternative to
5. Apparatus
veneer, specific overlays can be used as agreed upon between
5.1 Oven(s)—Forced-airovencapableofmaintaining170 6 the purchaser and the adhesive manufacturer. Surface the core
5°F (77 6 3°C), with sufficient air circulation to ensure that the to a thickness tolerance of 60.005 in. (0.13 mm) (see Table 1).
prescribed drying temperature is uniformly maintained when Iffinger-jointed/edge-bondedcorestockisused,itmustremain
intact without delamination during the test cycle. Both the
the oven is fully loaded and the air flow is parallel to the faces
of the specimens. A mechanism is to be provided for moisture veneer and the wood-based core are to be 61 % of the
moisture content recommended by the manufacture of the
to be removed from the chamber during drying of the speci-
mens. adhesive. In the absence of such a recommendation, the
5.1.1 Use an oven to accommodate a sufficient number of moisture content is to be from 10 to 12 %, based on oven-dry
test specimens and to provide for at least 3-in. (76-mm) weight as determined on representative samples in accordance
separation between the test specimens so that the drying with Method A of Test Methods D4442. Cut the veneer and
temperature is uniformly maintained. wood core to a suitable size and grain orientation in order to
build a panel with the grain of the veneer parallel to the grain
5.2 Vacuum-Pressure Vessel—Autoclave or similar vessel
of the wood core. A size that has been found to be convenient
capable of withstanding 80-psi (562-kPa) pressure, equipped
is shown in Fig. 1.
with a pump or similar device capable of drawing a vacuum of
25 in. Hg (84.4 kPa). Provide a system so that pressure is 7.2 Follow the adhesive manufacturer’s instructions for
maintained at 75 psi (517 kPa). conditions and procedures for preparing the adhesive and
5.2.1 Use a vessel so that all the specimens are at least 2 in. applying it to the wood core, as well as for assembling,
(51 mm) below the water level during the complete cycle. pressing, and curing the panel.
FIG. 1 Laboratory Test Panel
D5824 − 98 (2011)
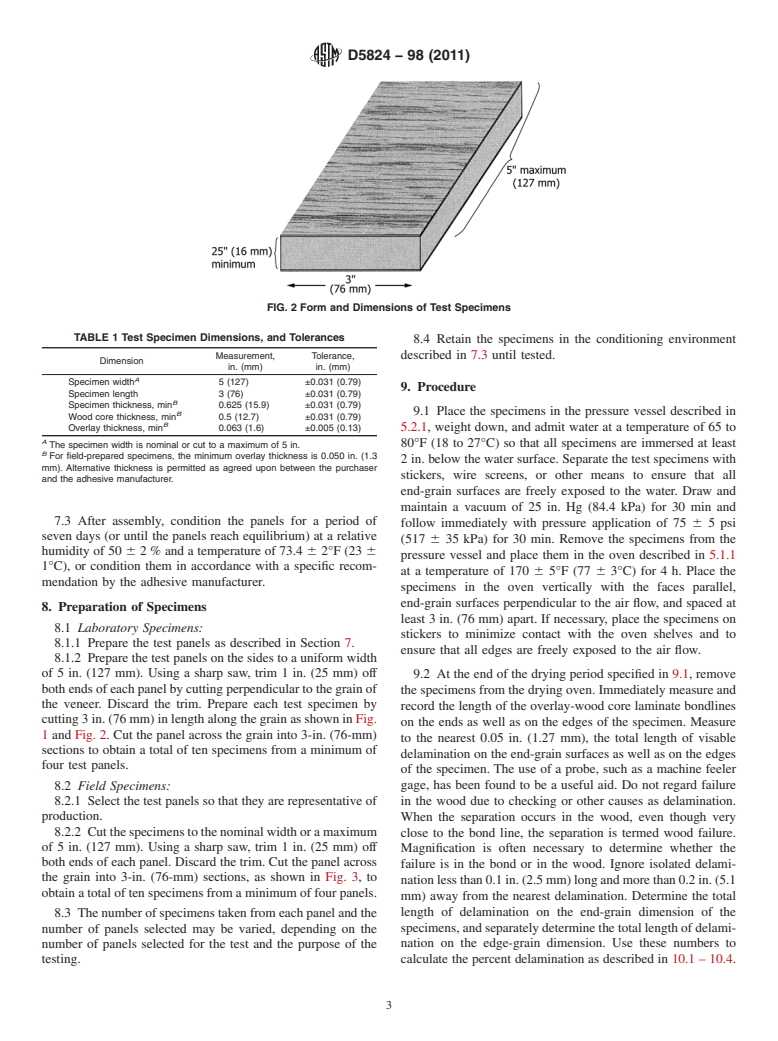
FIG. 2 Form and Dimensions of Test Specimens
TABLE 1 Test Specimen Dimensions, and Tolerances
8.4 Retain the specimens in the conditioning environment
Measurement, Tolerance, described in 7.3 until tested.
Dimension
in. (mm) in. (mm)
A
Specimen width 5 (127) ±0.031 (0.79)
9. Procedure
Specimen length 3 (76) ±0.031 (0.79)
B
Specimen thickness, min 0.625 (15.9) ±0.031 (0.79)
9.1 Place the specimens in the pressure vessel described in
B
Wood core
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.