ASTM D7351-07
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Sediment Retention Device Effectiveness in Sheet Flow Applications
Standard Test Method for Determination of Sediment Retention Device Effectiveness in Sheet Flow Applications
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method quantifies the ability of a sediment retention device (SRD) to retain eroded sediments caused by sheet flowing water under full-scale conditions. This test method may also assist in identifying physical attributes of SRDs that contribute to their erosion control performance.
The effectiveness of SRDs is installation dependent. Thus, replicating field installation techniques is an important aspect of this test method. This test method is full-scale and therefore, appropriate as an indication of product performance, for general comparison of product capabilities, and for assessment of product installation techniques.
Note 1—Test Method D 5141 is an alternate test method for evaluating sediment retention device effectiveness, if it is not necessary to simulate field installation conditions.
Note 2—The quality of the result produced by this standard is dependent on the competence of the personnel performing it, and the suitability of the equipment and facilities used. Agencies that meet the criteria of Practice D 3740 are generally considered capable of competent and objective testing/sampling/inspection/etc. Users of this standard are cautioned that compliance with Practice D 3740 does not in itself assure reliable results. Reliable results depend on many factors: Practice D 3740 provides a means of evaluating some of those factors.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method establishes the guidelines, requirements and procedures for evaluating the ability of Sediment Retention Devices (SRDs) to retain sediment when exposed to sediment-laden water "sheet" flows.
1.2 This test method is applicable to the use of an SRD as a vertical permeable interceptor designed to remove suspended soil from overland, nonconcentrated water flow. The function of an SRD is to trap and allow settlement of soil particles from sediment laden water. The purpose is to reduce the transport of eroded soil from a disturbed site by water runoff.
1.3 The test method presented herein is intended to indicate representative performance and is not necessarily adequate for all purposes in view of the wide variety of possible sediments and performance objectives.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The inch-pound values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
1.5 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in Practice D 6026.
1.5.1 The procedures used to specify how data are collected/recorded and calculated in this standard are regarded as the industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the significant digits that should generally be retained. The procedures used do not consider material variation, purpose for obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any consideration for the users objectives; and it is common practice to increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to commensurate with these considerations. It is beyond the scope of this standard to consider significant digits used in analysis methods for engineering design.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D7351 −07
StandardTest Method for
Determination of Sediment Retention Device Effectiveness
in Sheet Flow Applications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7351; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This test method establishes the guidelines, require-
ments and procedures for evaluating the ability of Sediment
2. Referenced Documents
Retention Devices (SRDs) to retain sediment when exposed to
2.1 ASTM Standards:
sediment-laden water “sheet” flows.
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
1.2 This test method is applicable to the use of an SRD as a
Fluids
vertical permeable interceptor designed to remove suspended
D698 Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Character-
soil from overland, nonconcentrated water flow. The function
istics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12 400 ft-lbf/ft (600
of an SRD is to trap and allow settlement of soil particles from
kN-m/m ))
sediment laden water. The purpose is to reduce the transport of
D3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
eroded soil from a disturbed site by water runoff.
Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as
1.3 The test method presented herein is intended to indicate
Used in Engineering Design and Construction
representative performance and is not necessarily adequate for
D5141 TestMethodforDeterminingFilteringEfficiencyand
all purposes in view of the wide variety of possible sediments
Flow Rate of the Filtration Component of a Sediment
and performance objectives.
Retention Device
D6026 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Geotechnical
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Data
standard. The inch-pound values given in parentheses are
provided for information purposes only.
3. Terminology
1.5 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, see
guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in
Terminology D653.
Practice D6026.
1.5.1 Theproceduresusedtospecifyhowdataarecollected/
4. Summary of Test Method
recorded and calculated in this standard are regarded as the
4.1 Sediment-laden water is allowed to “sheet flow” up to
industry standard. In addition, they are representative of the
and seep through, over, and/or under an installed sediment
significant digits that should generally be retained. The proce-
retention device (SRD). At a minimum, the amount (via water
dures used do not consider material variation, purpose for
and soil weight) of sediment-laden flow is measured both
obtaining the data, special purpose studies, or any consider-
upstream and downstream of the SRD.
ation for the user’s objectives; and it is common practice to
increase or reduce significant digits of reported data to com-
4.2 The measurement of sediment that passes through, over,
mensurate with these considerations. It is beyond the scope of
and/or under the SRD compared to the amount in the upstream
this standard to consider significant digits used in analysis
flow is used to quantify the effectiveness of the SRD in
3,4
methods for engineering design.
retaining sediments .
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
1 3
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD18onSoiland Sprague, C.J. (2004), “Testing the Effectiveness of Sediment Retention
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.25 on Erosion and Devices”, StormCon ‘04, Palm Desert, CA, (digital proceedings).
Sediment Control Technology. Sprague, C.J. and Carpenter, T. (2004), “A New Procedure for Testing the
Current edition approved May 1, 2007. Published June 2007. DOI: 10.1520/ Effectiveness of Sediment Retention Devices”, Conf. XXXV, International Erosion
D7351-07. Control Assoc., Philadelphia, pp. 265-275.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7351−07
5. Significance and Use soil type to be used for testing shall be loam with target grain
sizesandplasticityindexasshowninTable1,unlessotherwise
5.1 This test method quantifies the ability of a sediment
specified.
retention device (SRD) to retain eroded sediments caused by
6.1.4 A loader for moving the soil to the mixer—Afront-end
sheet flowing water under full-scale conditions. This test
loader of sufficient reach and capacity to dump a prescribed
method may also assist in identifying physical attributes of
amount of soil into the mixing tank.
SRDs that contribute to their erosion control performance.
6.1.5 A variable discharge apparatus from the mixer—A
5.2 The effectiveness of SRDs is installation dependent.
variable discharge apparatus from the mixer – A valve-
Thus, replicating field installation techniques is an important
controlled discharge hose that allows for controlled, uniform
aspect of this test method. This test method is full-scale and
discharge from the mixing tank.
therefore, appropriate as an indication of product performance,
6.1.6 Soil and water sampling equipment —Sampling jars
for general comparison of product capabilities, and for assess-
(at least 12 per test) for taking “grab” samples periodically
ment of product installation techniques.
during the test.
NOTE 1—Test Method D5141 is an alternate test method for evaluating
6.1.7 Excavating/compacting machinery for cleaning and
sediment retention device effectiveness, if it is not necessary to simulate
preparing the test area — Earthmoving and compacting
field installation conditions.
NOTE 2—The quality of the result produced by this standard is equipment is needed to prepare/replace the soil in the installa-
dependent on the competence of the personnel performing it, and the
tion zone.
suitability of the equipment and facilities used. Agencies that meet the
6.1.8 A scaled collection system adequate to handle the
criteria of Practice D3740 are generally considered capable of competent
released runoff— A tank mounted on scales of sufficient
and objective testing/sampling/inspection/etc. Users of this standard are
volume to collect all runoff passing the SRD.
cautioned that compliance with Practice D3740 does not in itself assure
reliable results. Reliable results depend on many factors: Practice D3740
6.2 Retention Area:
provides a means of evaluating some of those factors.
6.2.1 Anon-permeable, smooth, 3:1 slope surface (at least 5
6. Apparatus
m long) immediately below the mixer discharge shall be
provided to spread the discharge to the width of the retention
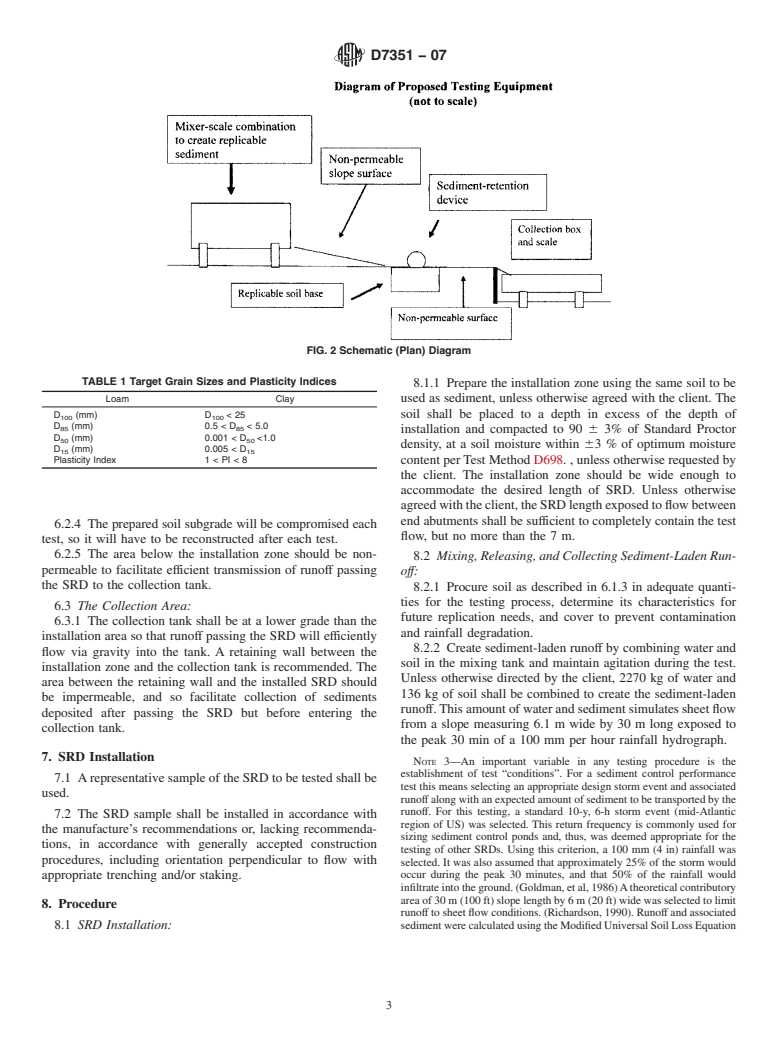
6.1 Equipment required. (See Fig. 1 and Fig. 2)
zone (length of the SRD installation) and to provide a retention
6.1.1 Combination mixing tank and scale—A tank with an
zone above the installation zone.
internal paddle mixer device mounted on scales capable of
6.2.2 An installation zone approximately 2 m wide by the
holding/weighing 4500 kg of sediment-laden water.
intended length of the SRD installation (typically 20 ft)
6.1.2 A clean water source and pumping equipment—A
comprised of prepared soil subgrade to allow full-scale instal-
sourceofwaterandassociatedpumpingequipmentsufficientto
lation of the SRD to be tested.
repeatedly fill the mixing tank in a timely manner.
6.1.3 A consistent soil stockpile —A stockpile of soil in 6.2.3 The center of the installed SRD should be placed in
sufficient quantity to both create sediment-laden water and to the center of the installation zone each time to replicate height
create/replace subgrade in the installation zone. The general of water as it relates to volume retained.
FIG. 1Profile Schematic
D7351−07
FIG. 2Schematic (Plan) Diagram
TABLE 1 Target Grain Sizes and Plasticity Indices
8.1.1 Prepare the installation zone using the same soil to be
Loam Clay used as sediment, unless otherwise agreed with the client. The
D (mm) D <25 soil shall be placed to a depth in excess of the depth of
100 100
D (mm) 0.5 < D <5.0
85 85
installation and compacted to 90 6 3% of Standard Proctor
D (mm) 0.001 < D <1.0
50 50
density, at a soil moisture within 63 % of optimum moisture
D (mm) 0.005 < D
15 15
Plasticity Index 1 < PI < 8 content perTest Method D698. , unless otherwise requested by
the client. The installation zone should be wide enough to
accommodate the desired length of SRD. Unless otherwise
agreedwiththeclient,theSRDlengthexposedtoflowbetween
end abutments shall be sufficient to completely contain the test
6.2.4 The prepared soil subgrade will be compromised each
flow, but no more than the 7 m.
test, so it will have to be reconstructed after each test.
6.2.5 The area below the installation zone should be non-
8.2 Mixing, Releasing, and Collecting Sediment-Laden Run-
permeable to facilitate efficient transmission of runoff passing
off:
the SRD to the collection tank.
8.2.1 Procure soil as described in 6.1.3 in adequate quanti-
ties for the testing process, determine its characteristics for
6.3 The Collection Area:
future replication needs, and cover to prevent contamination
6.3.1 The collection tank shall be at a lower grade than the
and rainfall degradation.
installation area so that runoff passing the SRD will efficiently
8.2.2 Create sediment-laden runoff by combining water and
flow via gravity into the tank. A retaining wall between the
soil in the mixing tank and maintain agitation during the test.
installation zone and the collection tank is recommended. The
Unless otherwise directed by the client, 2270 kg of water and
area between the retaining wall and the installed SRD should
136 kg of soil shall be combined to create the sediment-laden
be impermeable, and so facilitate collection of sediments
runoff.Thisamountofwaterandsedimentsimulatessheetflow
deposited after passing the SRD but before entering the
from a slope measuring 6.1 m wide by 30 m long exposed to
collection tank.
the peak 30 min of a 100 mm per hour rainfall hydrograph.
7. SRD Installation
NOTE 3—An important variable in any testing procedure is the
establishment of test “conditions”.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.