ASTM D7027-05e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Evaluation of Scratch Resistance of Polymeric Coatings and Plastics Using an Instrumented Scratch Machine
Standard Test Method for Evaluation of Scratch Resistance of Polymeric Coatings and Plastics Using an Instrumented Scratch Machine
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Scratch tests are performed on specimens:
(1) to evaluate the scratch or mar resistance of a particular material,
(2) to rank the relative scratch resistance of different materials, or
(3) to determine the scratching coefficient of friction of materials.
Since polymers exhibit mechanical properties that are strongly dependent on temperature, the test method prescribed herein is designed to yield reproducible results when users perform tests under the similar testing environment and on specimens of the same material and surface texture that are subjected to the same conditioning procedures.
Certain polymers are self-healing (recoverable) when subjected to scratches and other physical deformations because of their viscoelastic and relaxation properties. It is important to note the difference between the instantaneous (if readily measurable) and the post-scratch damages and appropriately compare results to ensure reproducibility.
“Whitening” of the scratched surface is a key damage mechanism that has prompted much concern in automotive and other applications where surface aestheticism is important. This type of damage is undesirable because it is evident to human eyes. The critical normal load at which this phenomenon appears serves as a benchmark in ranking material performance.
For polymers that do not exhibit whitening, a scratch groove from severe ploughing is still highly noticeable. In such cases, the normal load required to achieve a certain scratch width shall be reported to characterize scratch visibility and scratch resistance. The critical scratch width shall be decided by users in accordance with the specific material and remains the same throughout a set of tests for a consistent comparison. The variation of the scratch width as a function of the applied load shall also be plotted for comparison purposes.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a laboratory procedure using an instrumented scratch machine to produce and quantify surface damage under controlled conditions. This test method is able to characterize the mar and scratch resistance of polymers by measuring many significant material parameters. The scratch-inducing and data acquisition process is automated to avoid user-influenced effects that may affect the results.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—FLTM BN 108-13, ISO 1518 and ISO 12137-2 are related to this test method; the contents are significantly different from this method.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: D7027 − 05
StandardTest Method for
Evaluation of Scratch Resistance of Polymeric Coatings and
1
Plastics Using an Instrumented Scratch Machine
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7027; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Footnote 5 was editorially revised in April 2009.
1. Scope G171 Test Method for Scratch Hardness of Materials Using
a Diamond Stylus
1.1 This test method describes a laboratory procedure using
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
an instrumented scratch machine to produce and quantify
ISO 1518 Methods of Test for Paints—Part E2: Scratch Test
surface damage under controlled conditions. This test method
ISO 12137-2 Methods of Test for Paints—Part E18: Deter-
is able to characterize the mar and scratch resistance of
mination of Mar Resistance using a Pointed Stylus
polymers by measuring many significant material parameters.
ISO 3290 Rolling Bearings: Balls—Dimensions and Toler-
Thescratch-inducinganddataacquisitionprocessisautomated
ances
to avoid user-influenced effects that may affect the results.
2.3 Other Standards:
4
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
FLTM BN 108-13 Resistance to Scratching
standard.
3. Terminology
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 Definitions:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1 critical normal load, n—the normal load at which
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
whitening(see3.1.10)ofthematerialwithinthescratchgroove
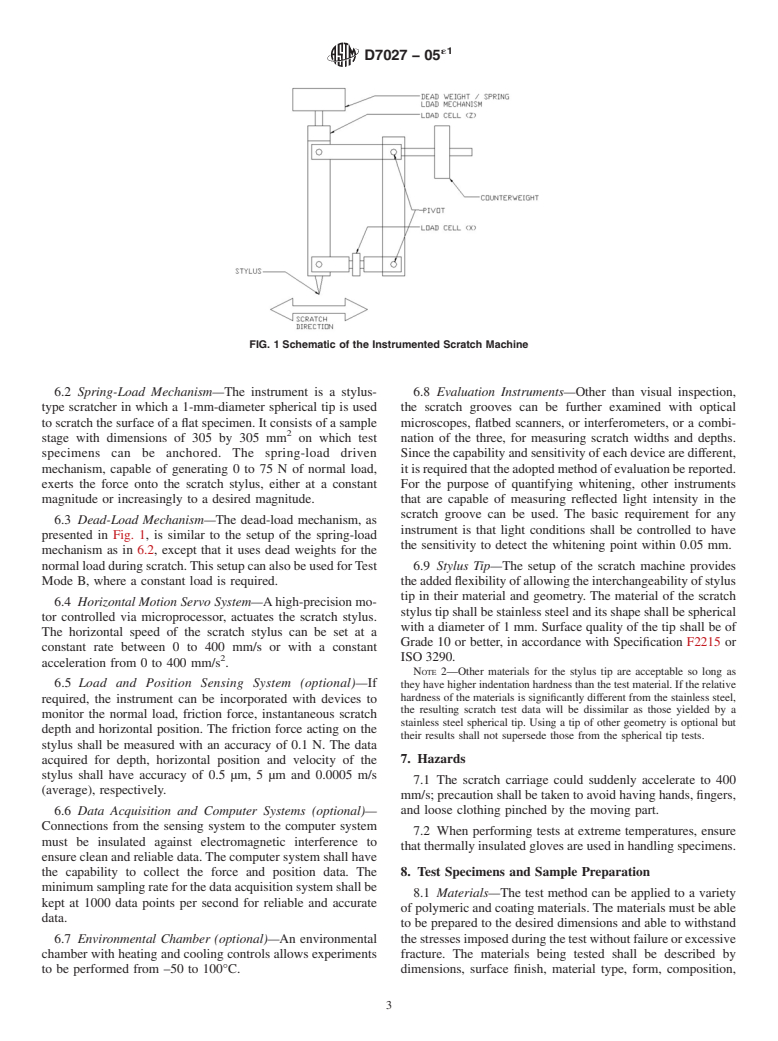
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
first occurs.
NOTE 1—FLTM BN 108-13, ISO 1518 and ISO 12137-2 are related to 3.1.2 friction force, n—the tangential force present at the
this test method; the contents are significantly different from this method.
interfacebetweentwobodieswhenonebodymovesortendsto
moverelativetotheother,undertheactionofanexternalforce.
2. Referenced Documents
Depending on the penetration of the indenter into the test
2
surface,frictionforcecanbecausedbysliding(relativelysmall
2.1 ASTM Standards:
displacement of material) or ploughing (gross removal/
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
displacement of materials).
D638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
D1894 Test Method for Static and Kinetic Coefficients of
3.1.3 mar resistance, n—ability to resist surface damage
Friction of Plastic Film and Sheeting
from the light abrasion by small objects. Quantitatively, it can
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
be characterized by the loss in gloss, increase in haze, or slight
ASTM Test Methods
shift in gray level.
F2215 Specification for Balls, Bearings, Ferrous and Non-
3.1.4 normal load, n—a load acted onto the scratch stylus
ferrous for Use in Bearings, Valves, and Bearing Appli-
that is imposed in a vertically downward direction while
cations
maintaining its perpendicularity with the direction of scratch.
G99 Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-Disk
3.1.5 scratch depth, n—the vertical distance to be measured
Apparatus
from the trough of the scratch groove to (a) its peak or (b) to
the undisturbed specimen surface.
3.1.6 scratchresistance,n—abilitytowithstanddamagethat
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
is accompanied by the gross deformation typically associated
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.10 on Mechanical Properties.
Current edition approved June 1, 2005. Published June 2005. DOI: 10.1520/
D7027-05E01.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Ford Motor Company, Central Laboratories, 15000 Century
the ASTM website. Drive, Dearborn, MI 48120.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
D7027 − 05
with sharp objects that may involve compressing, ploughing, 5. Significance and Use
and shearing off of material. Quantification can be accom-
5.1 Scratch tests are performed on specimens:
plished through the measurement of scratch depth (3.1.5),
(1) to evaluate the scratch or mar resistance of a particular
scratch width (3.1.7) and other geometric characteri
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.