ASTM B961-13(2019)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Silver Coated Copper and Copper Alloy Stranded Conductors for Electronic Space Application
Standard Specification for Silver Coated Copper and Copper Alloy Stranded Conductors for Electronic Space Application
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers uninsulated silver-coated soft or annealed copper and copper alloy stranded conductors for use in electronic space application.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. This precautionary caveat pertains only to Section 9.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: B961 −13 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Specification for
Silver Coated Copper and Copper Alloy Stranded
Conductors for Electronic Space Application
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B961; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Wires Used as Electrical Conductors
B298Specification for Silver-Coated Soft orAnnealed Cop-
1.1 This specification covers uninsulated silver-coated soft
per Wire
or annealed copper and copper alloy stranded conductors for
B286 Specification for Copper Conductors for Use in
use in electronic space application.
Hookup Wire for Electronic Equipment
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
B624Specification for High-Strength, High-Conductivity
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
Copper-Alloy Wire for Electronic Application
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
E3Guide for Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
2.2 European Space Agency (ESA):
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
ESA/SCC3901Generic Specification No. 3901
with the standard.
2.3 European Cooperation for Space Standardization
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
(ECSS):
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ECSS-Q-70-20ADetermination of the Susceptibility of Sil-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ver Plated Copper wire and Cable to “Red Plague”
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
Corrosion
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
This precautionary caveat pertains only to Section 9.
3. Ordering Information
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- 3.1 Ordersformaterialunderthisspecificationshallinclude
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the the following information:
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- 3.1.1 Quantity of each size.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.1.2 Customer specification requirements including con-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. ductor size, designation, and construction.
3.1.3 Whether silver-coated copper or silver-coated copper-
2. Referenced Documents
alloy.
3.1.4 Package size (Section 12).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.5 Special package marking if required (Section 11), and
NOTE 1—The following documents of the issue in effect on date of
3.1.6 Place of inspection (Section 10).
material purchase form a part of this specification to the extent referenced
herein.
4. Coating of Wires
B193Test Method for Resistivity of Electrical Conductor
Materials
4.1 Coating Thickness—The silver coating of wires com-
B258Specification for Standard Nominal Diameters and
posing stranded conductors shall be uniform such that no area
Cross-Sectional Areas of AWG Sizes of Solid Round
around the strand circumference is covered by less than 80
micro-inches of silver. Uniform silver coating shall be verified
by micro-sectioning as outlined in 9.1.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B01 on
4.1.1 Single points caused by eccentric strands or minute
Electrical Conductors and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B01.02 on
scratches shall not be less than 60 micro-inches minimum or
Methods of Test and Sampling Procedure.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2019. Published October 2019. Originally exceed 3 points in number around the micro-sectioned strand
approved in 2008. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as B961–13. DOI:
circumference.
10.1520/B0961-13R19.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on ESA Publications Division, ESTEC, P.O. Box 299, 2200 AG Noordwijk, The
the ASTM website. Netherlands (ESA/SCC3901 download available from www.escies.org).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
B961 − 13 (2019)
4.2 Thesilvercoatingofwirescomposingstrandedconduc- 8.3 Tests to determine conformance to electrical resistance
tors (before and after stranding) shall conform to the polysul- requirements prescribed in 3.1.2 shall be made on the uninsu-
fide test in accordance with Specification B298. lated conductor in accordance with Test Method B193.
4.3 Theaveragesilvercoatingthicknessofwirescomposing
9. Test Methods
stranded conductors shall be verified by electronic determina-
tion (Method A) in accordance with Specification B298. 9.1 Micro-Sectioning of Strands:
9.1.1 The silver coating shall be evaluated for uniform
4.4 Red Plague Corrosion Test—Representative samples of
coating requirements using the following procedure for micro-
thesilvercoatedconductorsshallconformtocodes0–3ofthe
sectioningofstrands.Section9.1shallbeperformedaccording
accelerated corrosion test for un-insulated silver-plated con-
to best commercial metallographic practice. Guide E3 would
ductors as outlined in 9.2 (Explanatory Note 1).
provide a good background reference for metallographic ex-
5. General Requirements
amination and preparation of samples.
9.1.2 The test specimen shall consist of untwisted strands
5.1 Temper—Unless otherwise specified, all coated conduc-
from the completed conductor. The test specimen shall be
tors shall be furnished in the annealed temper.
electroplated with a copper or nickel coating, which is not less
5.2 Elongation—The elongation of stranded conductors
than 25µm. The copper or nickel coating will provide protec-
shall be permitted to vary from the requirements of the
tion of the specimen edges for follow-up grinding and polish-
applicable Specifications B298 and B624 by the following
ing preparation.
amounts:
9.1.2.1 Unlessotherwiseagreeduponbetweenthemanufac-
5.2.1 Forstrandedsilvercoatedcopperconductors22AWG
turer and purchaser, the manufacturer may have the option to
andsmaller,thetestshallbeperformedonthewholeconductor
perform the micro-sectioning without the copper or nickel
and the elongation measured when the first strand of the
over-coating. The over-coating could be used at the discretion
conductor breaks. The minimum average elongation shall not
of the metallographer to referee suspect results.
be less than 10 % with no individual specimen less than 5%.
9.1.3 Mount the test specimen in a low exotherm (heat)
5.2.2 For stranded silver coated copper conductors larger
casting resin encapsulating the specimen for metallographic
than 22 AWG, strands shall be carefully removed from the
preparation and cross-sectioning.
conductor and tested for elongation. The minimum average
9.1.4 The specimen should be ground and polished using
elongationshallnotbelessthan10%withnoindividualstrand
appropriate grinding disk pads and diamond paste. The dia-
less than 5%.
mond paste should go down to at least 0.25 µm.
5.2.3 Forstrandedsilvercoatedcopperalloyconductors,the
9.1.5 Etch the polished specimen in a new solution of
test shall be performed on the whole conductor only and the
ammonia (commercially pure), which contains two drops of
elongation measured when the first strand of the conductor
37% hydrogen peroxide.
breaks. The minimum elongation shall not be less than 6%.
9.1.6 Use a metallographic microscope to examine the
etched cross-section with at least 400× magnification. The
6. Lay of Stranded Conductors
specimen shall meet the requirements of 4.1.
6.1 The direction of lay of the outside layer of stranded
9.2 Red Plague Corrosion Test:
conductors shall be left-hand.
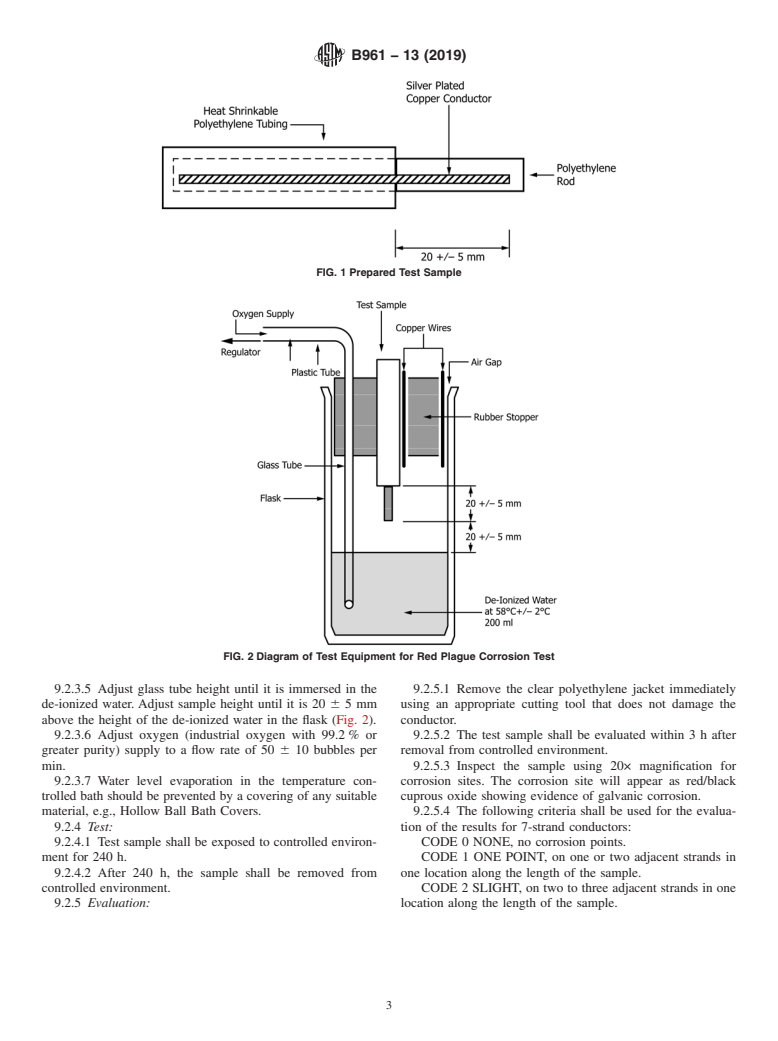
9.2.1 Apparatus: (See Appendix X1 and Fig. 2).
6.2 The direction of lay of the other layers shall be reversed
9.2.2 Preparation of Sample:
insuccessivelayers,unlessotherwiseagreeduponbetweenthe
9.2.2.1 The conductor to be used in test shall be taken from
manufacturer and the purchaser.
the test spool with a minimum of handling. Handling of the
6.3 The length of lay of the individual wires composing the
conductor must be done using powder free gloves.
outside layer of the stranded conductor shall not be less than 8
9.2.2.2 The test samples shall be 8 to 16 in. in length and
nor more than 16 times the outside diameter of that layer.
attached to the polyethylene rod.
9.2.2.3 The rod sample shall then be encapsulated in the
7. Joints
heat shrinkable polyethylene tubing with one end having 20 6
7.1 No joints shall be made at the final draw prior to
5 mm of conductor exposed. (Fig. 1).
stranding. No joints shall be made in the individual strands or
9.2.3 Preparation of Test Equipment:
in the completed conductor during the stranding process.
9.2.3.1 Temperature controlled bath shall be filled with
Necessary joints made in the wire and rods prior to final
de-ionized water and allowed sufficient time for bath to reach
drawing shall be in accordance with the best workmanship
testing temperature. (58°C 6 2°C).
practice.
9.2.3.2 Fill glass flask with 200 ml of de-ionized water and
place in temperature controlled bath to allow it to reach an
8. Physical and Electrical Test
equilibrium temperature.
8.1 Tests to determine conformance of the coating to the
9.2.3.3 The test sample shall be inserted in a hole in the
requirementsprescribedinSection4shallbeperformedbefore
rubber stopper. Insert copper wire between glass flask and
insulating.
rubber stopper to allow for air gap.
8.2 Tests to determine conformance to the elongation re- 9.2.3.4 The glass
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.