ASTM D7754-11e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Trace Oxygenates in Automotive Spark-Ignition Engine Fuel by Multidimensional Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of Trace Oxygenates in Automotive Spark-Ignition Engine Fuel by Multidimensional Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The analysis of trace oxygenates in automotive spark-ignition engine fuel has become routine in certain areas to ensure compliance whenever oxygenated fuels are used. In addition, test methods to measure trace levels of oxygenates in automotive spark-ignition fuel are necessary to assess product quality.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of trace oxygenates in automotive spark-ignition engine fuel. The method used is a multidimensional gas chromatographic method using 1,2-dimethoxy ethane as the internal standard. The oxygenates that are analyzed are: methyl-tertiary butyl ether (MTBE), ethyl-tertiary butyl ether (ETBE), diisopropyl ether (DIPE), methanol, tertiary-amyl methyl ether (TAME), n-propanol, i-propanol, n-butanol, i-butanol, tert-butyl alcohol, sec-butyl alcohol, and tert-pentanol. Ethanol is usually not measured as a trace oxygenate since ethanol can be used as the main oxygenate compound in finished automotive spark-ignition fuels such as reformulated automotive spark-ignition fuels. The concentration range of the oxygenates covered in the ILS study was from 10 µg/Kg to 2000 µg/Kg. In addition this method is also suitable for the measurement of the C5 isomeric alcohols (2-methyl-1-butanol, 2-methyl-2-butanol) present from the fermentation of ethanol.
1.2 The ethanol blending concentration for which this test method applies ranges from 1 to 15% by volume. Higher concentrations of ethanol coelute with methanol in the analytical column. Lower levels of ethanol, similar to the other oxygenate, can be calibrated and analyzed also. If higher ethanol concentrations are expected, the window cutting technique can be used to avoid ethanol from entering the analytical column and interfere with the determination of the other oxygenates of interest. Refer to Appendix X1 for details.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3.1 Alternate units, in common usage, are also provided to increase clarity and aid the users of this test method.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: D7754 − 11
StandardTest Method for
Determination of Trace Oxygenates in Automotive Spark-
Ignition Engine Fuel by Multidimensional Gas
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7754; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Research report information was added editorially to Section 14 in November 2015.
1. Scope 1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 This test method covers the determination of trace
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
oxygenates in automotive spark-ignition engine fuel. The
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
method used is a multidimensional gas chromatographic
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
method using 1,2-dimethoxy ethane as the internal standard.
The oxygenates that are analyzed are: methyl-tertiary butyl
2. Referenced Documents
ether (MTBE), ethyl-tertiary butyl ether (ETBE), diisopropyl
2
ether (DIPE), methanol, tertiary-amyl methyl ether (TAME),
2.1 ASTM Standards:
n-propanol, i-propanol, n-butanol, i-butanol, tert-butyl alcohol,
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
sec-butyl alcohol, and tert-pentanol. Ethanol is usually not
Petroleum Products
measured as a trace oxygenate since ethanol can be used as the
D4307 Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as
main oxygenate compound in finished automotive spark-
Analytical Standards
ignition fuels such as reformulated automotive spark-ignition
D4815 Test Method for Determination of MTBE, ETBE,
fuels.Theconcentrationrangeoftheoxygenatescoveredinthe
TAME, DIPE, tertiary-Amyl Alcohol and C to C Alco-
1 4
ILS study was from 10 µg/Kg to 2000 µg/Kg. In addition this
hols in Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
method is also suitable for the measurement of the C5 isomeric
D6304 Test Method for Determination of Water in Petro-
alcohols (2-methyl-1-butanol, 2-methyl-2-butanol) present
leum Products, Lubricating Oils, and Additives by Cou-
from the fermentation of ethanol.
lometric Karl Fischer Titration
1.2 The ethanol blending concentration for which this test
3. Terminology
method applies ranges from 1 to 15% by volume. Higher
concentrations of ethanol coelute with methanol in the analyti- 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
cal column. Lower levels of ethanol, similar to the other
3.1.1 electronic pressure control, n—electronic pneumatic
oxygenate, can be calibrated and analyzed also. If higher
control of carrier gas flows. Can be flow or pressure pro-
ethanol concentrations are expected, the window cutting tech-
grammed to speed up elution of components.
nique can be used to avoid ethanol from entering the analytical
3.1.2 flame ionization detector (FID), n—detector used to
column and interfere with the determination of the other
analyze the components eluting from the column.
oxygenates of interest. Refer to Appendix X1 for details.
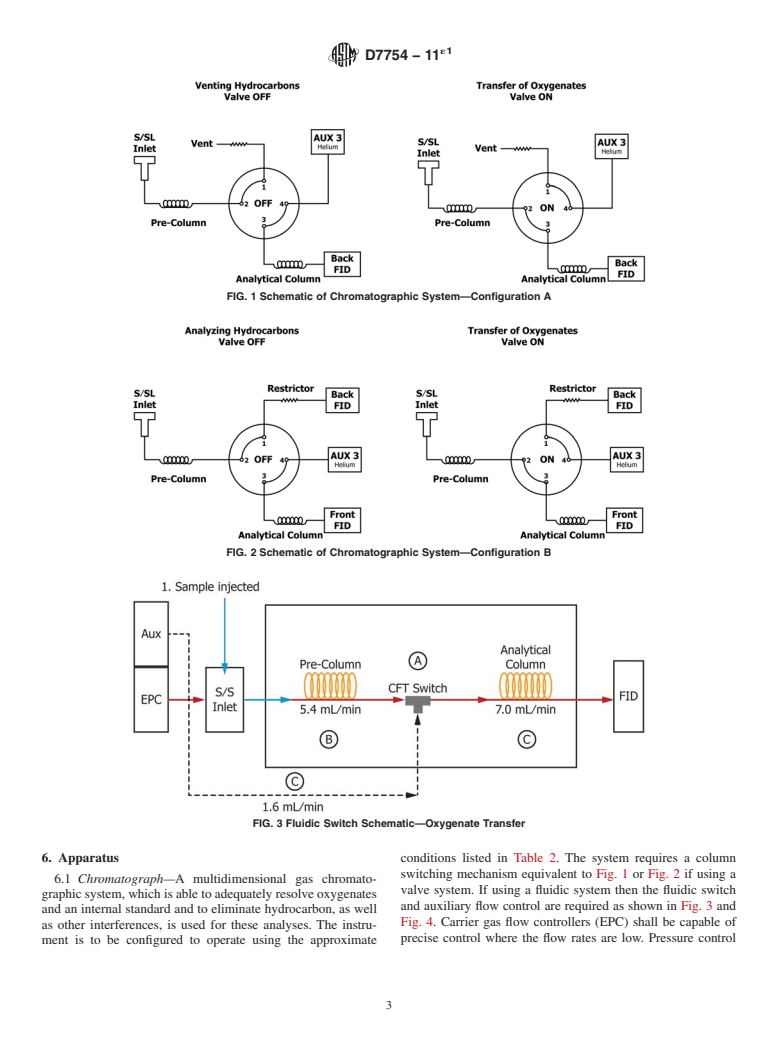
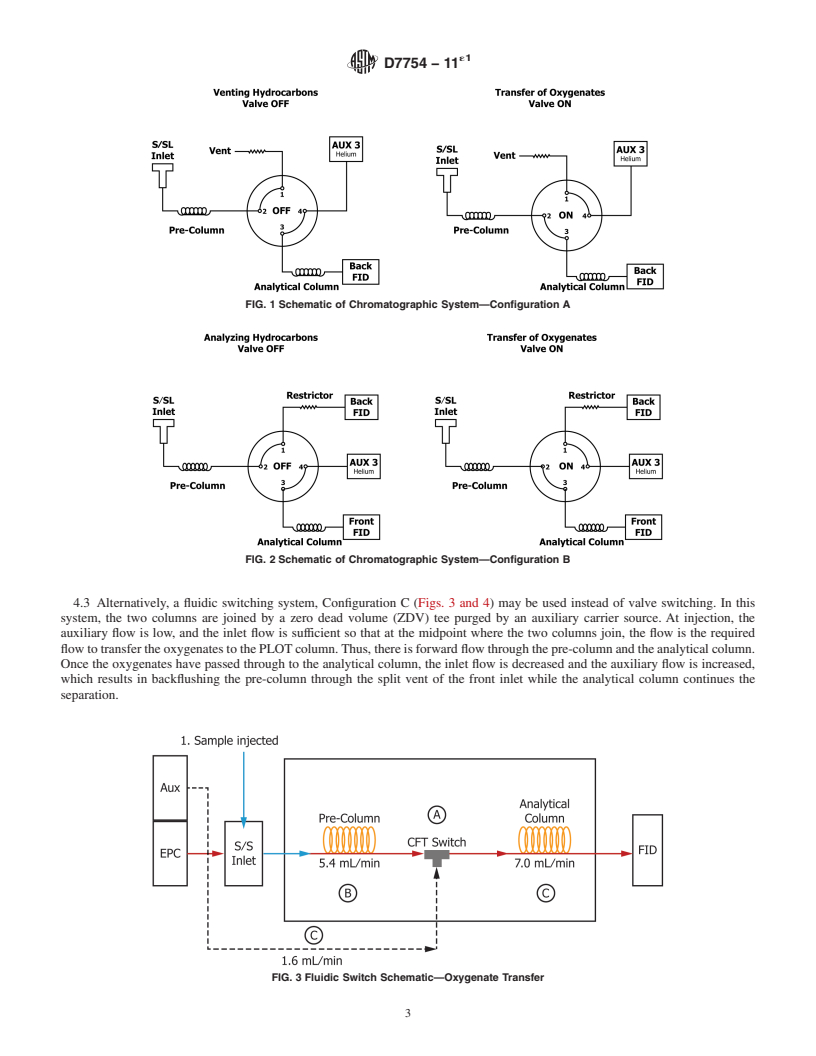
3.1.3 fluidic switch, n—device that reverses the directional
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
flow in a union T altering the pressure at the midpoint. In its
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
simplest design it is also known as a Dean Switch.
standard.
3.1.4 inlet, n—capillary split/splitless inlet system operated
1.3.1 Alternateunits,incommonusage,arealsoprovidedto
in the split mode is recommended. Operate the inlet within its
increase clarity and aid the users of this test method.
linear range.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
2
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Subcommittee D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
CurrenteditionapprovedOct.1,2011.PublishedNovember2011.DOI:10.1520/ Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
D7754-11E01. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
D7754 − 11
3.1.4.1 split ratio, n— in capillary gas chromatography, the and the DME are transferred to the analytical oxygen selective
ratio of the total flow of carrier gas to the sample inlet versus column by the switching valve. While the oxygenates and the
the flow of the carrier gas to the capillary column is expressed DM
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D7754 − 11 D7754 − 11
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Trace Oxygenates in Automotive Spark-
Ignition Engine Fuel by Multidimensional Gas
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7754; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Research report information was added editorially to Section 14 in November 2015.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of trace oxygenates in automotive spark-ignition engine fuel. The method used
is a multidimensional gas chromatographic method using 1,2-dimethoxy ethane as the internal standard. The oxygenates that are
analyzed are: methyl-tertiary butyl ether (MTBE), ethyl-tertiary butyl ether (ETBE), diisopropyl ether (DIPE), methanol,
tertiary-amyl methyl ether (TAME), n-propanol, i-propanol, n-butanol, i-butanol, tert-butyl alcohol, sec-butyl alcohol, and
tert-pentanol. Ethanol is usually not measured as a trace oxygenate since ethanol can be used as the main oxygenate compound
in finished automotive spark-ignition fuels such as reformulated automotive spark-ignition fuels. The concentration range of the
oxygenates covered in the ILS study was from 10 μg/Kg to 2000 μg/Kg. In addition this method is also suitable for the
measurement of the C5 isomeric alcohols (2-methyl-1-butanol, 2-methyl-2-butanol) present from the fermentation of ethanol.
1.2 The ethanol blending concentration for which this test method applies ranges from 1 to 15% by volume. Higher
concentrations of ethanol coelute with methanol in the analytical column. Lower levels of ethanol, similar to the other oxygenate,
can be calibrated and analyzed also. If higher ethanol concentrations are expected, the window cutting technique can be used to
avoid ethanol from entering the analytical column and interfere with the determination of the other oxygenates of interest. Refer
to Appendix X1 for details.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3.1 Alternate units, in common usage, are also provided to increase clarity and aid the users of this test method.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4307 Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as Analytical Standards
D4815 Test Method for Determination of MTBE, ETBE, TAME, DIPE, tertiary-Amyl Alcohol and C to C Alcohols in
1 4
Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
D6304 Test Method for Determination of Water in Petroleum Products, Lubricating Oils, and Additives by Coulometric Karl
Fischer Titration
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 electronic pressure control, n—electronic pneumatic control of carrier gas flows. Can be flow or pressure programmed to
speed up elution of components.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2011. Published November 2011. DOI:10.1520/D7754–11DOI:10.1520/D7754-11E01.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
D7754 − 11
3.1.2 flame ionization detector (FID), n—detector used to analyze the components eluting from the column.
3.1.3 fluidic switch, n—device that reverses the directional flow in a union T altering the pressure at the midpoint. In its simplest
design it is also known as a Dean Switch.
3.1.4 inlet, n—capillary split/splitless inlet system operated in the split mode is recommended. Operate the inlet within its linear
ran
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.