ASTM F2247-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Metal Doors Used in Blast Resistant Applications (Equivalent Static Load Method)
Standard Test Method for Metal Doors Used in Blast Resistant Applications (Equivalent Static Load Method)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Blast resistant doors are designed to protect against the problems and dangers created by a planned or accidental explosion or pressure leak. This test method will provide reasonable assurance to the specifier of the reliability of a door's structure, the restraining hardware, the frame, and the frame anchors when used in a blast resistant application.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the structural performance of metal doors and frames and their restraining hardware (such as latches and hinges) used as a blast resistant barrier. This method involves applying an equivalent static pressure based on the characteristics of the specified blast pressure and structural properties of the door panel design.
1.2 The static tests are valid for the unit size tested or for smaller units of analogous construction. Extrapolation of test results for units larger than the test specimen are not permitted.
1.3 This standard test method is not applicable to tests where the forces are created by explosive charges, forced air from a shock tube apparatus, or any other method used to generate a dynamic load.
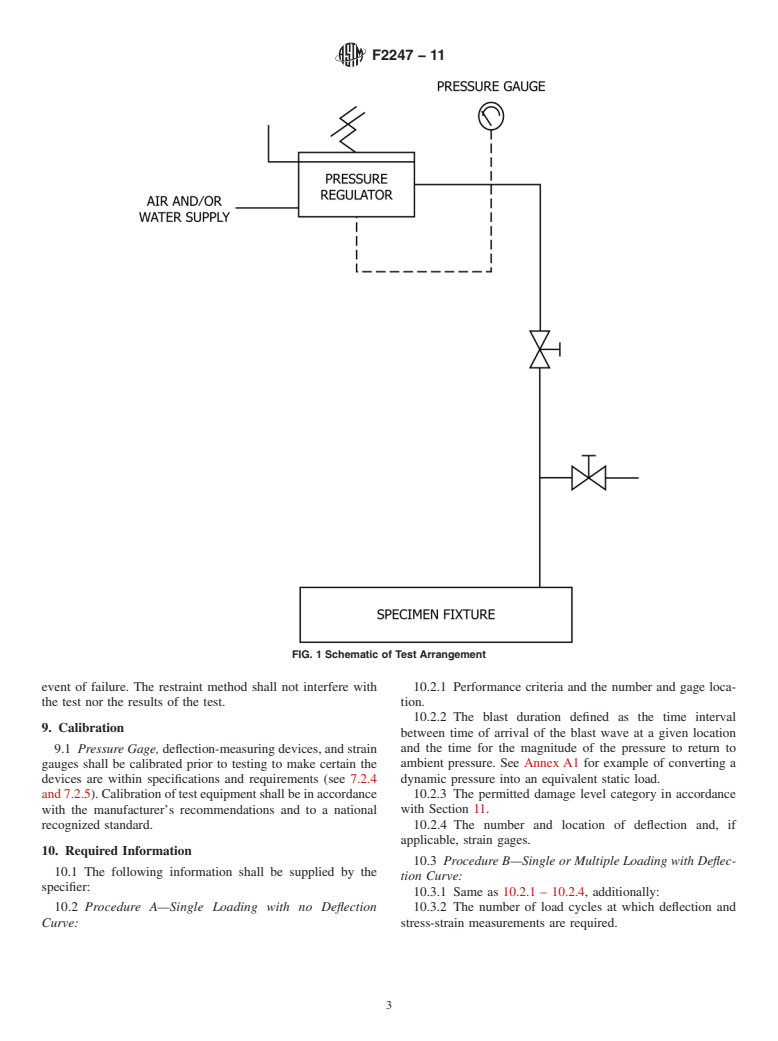
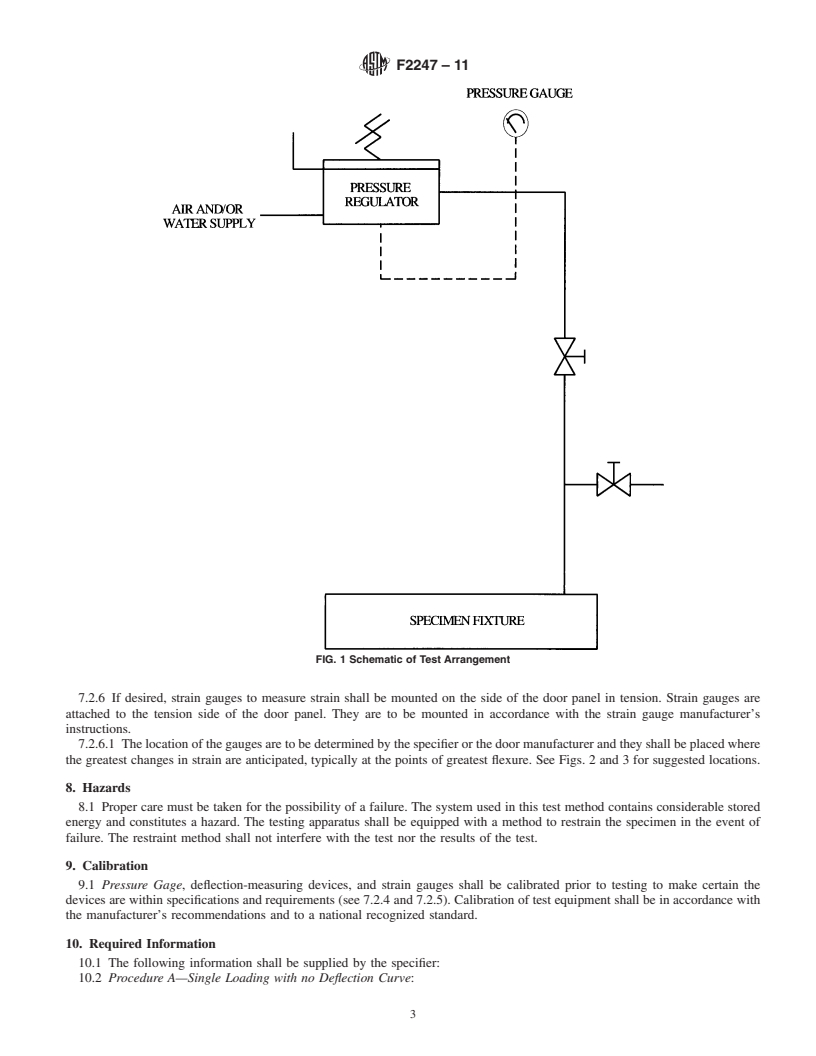
1.4 The proper use of this method requires knowledge of the principles of pressure, deflection, and when applicable, strain gauge measurement.
1.5 Using this method, specimens may be tested to determine ultimate static capacity or tested to specific static test loads.
1.5.1 Procedure A shall be used when a load-deflection curve is not required and a single load is applied.
1.5.2 Procedure B shall be used when a load-deflection curve is required and a single or multiple loads are applied.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values provided in parenthesis are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F2247 − 11
Standard Test Method for
Metal Doors Used in Blast Resistant Applications
1
(Equivalent Static Load Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2247; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method covers the structural performance of 2.1 ASTM Standards:
E330 Test Method for Structural Performance of Exterior
metal doors and frames and their restraining hardware (such as
latches and hinges) used as a blast resistant barrier. This Windows, Doors, Skylights and CurtainWalls by Uniform
method involves applying an equivalent static pressure based Static Air Pressure Difference
on the characteristics of the specified blast pressure and
2.2 Other Standard:
structural properties of the door panel design.
UFC 3-340-02 Unified Facilities Criteria (UFC), Structures
3
to Resist the Effects of Accidental Explosions
1.2 The static tests are valid for the unit size tested or for
smaller units of analogous construction. Extrapolation of test
3. Terminology
results for units larger than the test specimen are not permitted.
3.1 Definitions:
1.3 This standard test method is not applicable to tests
3.1.1 metal door—a term used in reference to doors which
where the forces are created by explosive charges, forced air
are built from steel sheets, internally stiffened with cold-
from a shock tube apparatus, or any other method used to
formed shapes or structural steel shapes. Materials can be
generate a dynamic load.
carbon or stainless steel. The materials may be joined together
1.4 Theproperuseofthismethodrequiresknowledgeofthe
by any fabrication technique (that is, welding, bolting, struc-
principles of pressure, deflection, and when applicable, strain
tural adhesive, etc.). The material voids may be filled with
gauge measurement.
insulation.
1.5 Using this method, specimens may be tested to deter-
3.1.2 permanent deformation—the permanent displacement
mine ultimate static capacity or tested to specific static test
from an original position that remains after an applied load has
loads.
been removed. Measured in millimetres (mm) (inches (in.)).
1.5.1 Procedure A shall be used when a load-deflection
3.1.3 rebound—stress reversal in the material of the door.
curve is not required and a single load is applied.
3.1.4 seating pressure—an applied pressure that causes the
1.5.2 Procedure B shall be used when a load-deflection
door panel to seat against the frame that is expressed in pascals
curve is required and a single or multiple loads are applied.
(Pa) (pounds-force per square foot (psf) or pounds-force per
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
square inch (psi)).
standard. The values provided in parenthesis are for informa-
3.1.5 specifier—individual or party requesting that a metal
tion only.
door assembly meet specific blast resistance criteria.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.6 specimen—the entire assembly unit submitted for test
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
as described in Section 6.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 3.1.7 steady state pressure—a test pressure held for a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. minimum of 3 min.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F12 on Security For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Systems and Equipment and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F12.10 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Systems Products and Services. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved March 1, 2011. Published April 2011. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as F2247 – 03 (2010). Available from National Institute of Building Sciences, 1090 VermontAvenue,
DOI: 10.1520/F2247-11. NW, Suite 700, Washington, DC 20005, http://www.wbdg.org/index.php.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2247 − 11
3.1.8 test director—the individual identified as being re- installation. The door frame will be attached to the test fixture
sponsible to complete the specified tests as required and to using the same quantity, size, and spacing of fasteners or
document the results. anchors that the specifier or door manufact
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:F2247–03 (Reapproved 2010) Designation:F2247–11
Standard Test Method for
Metal Doors Used in Blast Resistant Applications
1
(Equivalent Static Load Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2247; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthestructuralperformanceofmetaldoorsandframesandtheirrestraininghardware(suchaslatches
andhinges)usedasablastresistantbarrier.Thismethodinvolvesapplyinganequivalentstaticpressurebasedonthecharacteristics
of the specified blast pressure and structural properties of the door panel design.
1.2 The static tests are valid for the unit size tested or for smaller units of analogous construction. Extrapolation of test results
for units larger than the test specimen are not permitted.
1.3 Thisstandardtestmethodisnotapplicabletotestswheretheforcesarecreatedbyexplosivecharges,forcedairfromashock
tube apparatus, or any other method used to generate a dynamic load.
1.4 The proper use of this method requires knowledge of the principles of pressure, deflection, and when applicable, strain
gauge measurement.
1.5 Using this method, specimens may be tested to determine ultimate static capacity or tested to specific static test loads.
1.5.1 Procedure A shall be used when a load-deflection curve is not required and a single load is applied.
1.5.2 Procedure B shall be used when a load-deflection curve is required and a single or multiple loads are applied.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values provided in parenthesis are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E330 Test Method for Structural Performance of Exterior Windows, Doors, Skylights and Curtain Walls by Uniform StaticAir
Pressure Difference
2.2 Other Standard:
TM5-1300 Structures to Resist Effects of Accidental Explosions, Volume V, Structural Steel Design, Special Publication No.
ARLCD-SP-840001UFC 3-340-02 Unified Facilities Criteria (UFC), Structures to Resist the Effects of Accidental
3
Explosions
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 metal door—a term used in reference to doors which are built from steel sheets, internally stiffened with cold-formed
shapesorstructuralsteelshapes.Materialscanbecarbonorstainlesssteel.Thematerialsmaybejoinedtogetherbyanyfabrication
technique (that is, welding, bolting, structural adhesive, etc.). The material voids may be filled with insulation.
3.1.2 permanentdeformation—thepermanentdisplacementfromanoriginalpositionthatremainsafteranappliedloadhasbeen
removed. Measured in millimetres (mm) (inches (in.)).
3.1.3 rebound—stress reversal in the material of the door.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F12 on Security Systems and Equipment and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F12.10 on
Systems Products and Services.
Current edition approved May 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F2247 – 03. DOI:
10.1520/F2247-03R10.
Current edition approved March 1, 2011. Published April 2011. Originally approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as F2247 – 03 (2010). DOI:
10.1520/F2247-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from U.S. Army Armament Research Development and Engineering Center, Dover, NJ.
3
Available from National Institute of Building Sciences, 1090 Vermont Avenue, NW, Suite 700, Washington, DC 20005, http://www.wbdg.org/index.php.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2247–11
3.1.4 seating pressure—an applied pressure that causes the door panel to seat against the frame that is expressed in pascals (Pa)
(pounds-force per square foot (psf) or
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.