ASTM D5338-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Aerobic Biodegradation of Plastic Materials Under Controlled Composting Conditions, Incorporating Thermophilic Temperatures
Standard Test Method for Determining Aerobic Biodegradation of Plastic Materials Under Controlled Composting Conditions, Incorporating Thermophilic Temperatures
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Biodegradation of a plastic within a composting unit is an important phenomenon because it may affect the decomposition of other materials enclosed by the plastic and the resulting quality and appearance of the composted material. Biodegradation of plastics will also allow the safe disposal of these plastics through large, professionally-managed composting plants and well-run residential units, where thermophilic temperatures are achieved. This procedure has been developed to permit the determination of the rate and degree of aerobic biodegradability of plastic products when placed in a controlled composting process.
Limitations—Because there is a wide variation in the construction and operation of composting facilities and because regulatory requirements for composting systems vary, this procedure is not intended to simulate the environment of any particular composting system. However, it is expected to resemble the environment of a composting process operated under optimum conditions where thermophilic temperatures are achieved. More specifically, the procedure is intended to create a standard laboratory environment that will permit a rapid and reproducible determination of the aerobic biodegradability under controlled composting conditions.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method determines the degree and rate of aerobic biodegradation of plastic materials on exposure to a controlled-composting environment under laboratory conditions, at thermophilic temperatures. This test method is designed to yield reproducible and repeatable test results under controlled conditions that resemble composting conditions, where thermophilic temperatures are achieved. The test substances are exposed to an inoculum that is derived from compost from municipal solid waste. The aerobic composting takes place in an environment where temperature, aeration and humidity are closely monitored and controlled.
Note 1—During composting, thermophilic temperatures are most readily achieved in large-scale, professionally-managed facilities. However, these temperatures may also be reached in smaller residential composting units, frequently referred to as “backyard” or “home” composting.
1.2 This test method is designed to yield a percentage of conversion of carbon in the sample to carbon dioxide. The rate of biodegradation is monitored as well.
1.3 This test method is designed to be applicable to all plastic materials, which are intended to be composted in facilities that achieve thermophilic temperatures.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 8.
1.6 This test method is equivalent to ISO 14855.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5338 − 11
StandardTest Method for
Determining Aerobic Biodegradation of Plastic Materials
Under Controlled Composting Conditions, Incorporating
1
Thermophilic Temperatures
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5338; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method determines the degree and rate of
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
aerobic biodegradation of plastic materials on exposure to a
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
controlled-composting environment under laboratory
D1293Test Methods for pH of Water
conditions, at thermophilic temperatures. This test method is
D2908Practice for Measuring Volatile Organic Matter in
designedtoyieldreproducibleandrepeatabletestresultsunder
Water by Aqueous-Injection Gas Chromatography
controlled conditions that resemble composting conditions,
D3590Test Methods for Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen in Water
where thermophilic temperatures are achieved. The test sub-
D4129Test Method for Total and Organic Carbon in Water
stances are exposed to an inoculum that is derived from
by High Temperature Oxidation and by Coulometric
compost from municipal solid waste. The aerobic composting
Detection
takes place in an environment where temperature, aeration and
E260Practice for Packed Column Gas Chromatography
humidity are closely monitored and controlled.
E355PracticeforGasChromatographyTermsandRelation-
NOTE 1—During composting, thermophilic temperatures are most
ships
readily achieved in large-scale, professionally-managed facilities.
2.2 APHA—AWWA—WPCF Standards:
However, these temperatures may also be reached in smaller residential
3
2540DTotal Suspended Solids Dried at 103 to 105°C
composting units, frequently referred to as “backyard” or “home” com-
3
posting.
2540EFixed and Volatile Solids Ignited at 550°C
2.3 ISO Standard:
1.2 This test method is designed to yield a percentage of
ISO14855 Plastics—Evaluation of the Ultimate Aerobic
conversion of carbon in the sample to carbon dioxide.The rate
Biodegradability and Disintegration Under Controlled
of biodegradation is monitored as well.
Composting Conditions—Method by Analysis of Re-
1.3 This test method is designed to be applicable to all 4
leased Carbon Dioxide
plastic materials, which are intended to be composted in
facilities that achieve thermophilic temperatures.
3. Terminology
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of terms applying to this test
standard.
method appear in Terminology D883.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Summary of Test Method
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 4.1 This test method consists of the following:
4.1.1 Selection of plastic material for the determination of
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard the aerobic biodegradability in a controlled-composting
system,
statements are given in Section 8.
1.6 This test method is equivalent to ISO14855.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20onPlastics Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.19 on Film, Sheeting, and the ASTM website.
3
Molded Products. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th Edition,
Current edition approved . Published April 2011. Originally approved in 1992. 1989,American Public HealthAssociation, 1740 Broadway, NewYork, NY19919.
4
Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2003asD5338-98(2003).DOI:10.1520/D5338- Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
11. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5338 − 11
4.1.2 Obtaining an inoculum from composted municipal
solid waste,
4.1.3 Exposing the test substances to a controlled aerobic
composting process in conjunction with the inoculum,
4.1.4 Measuring carbon dioxide evolved as a function of
time, and
4.1.5 Assessing the degree of biodegradability.
4.2 The percentage of biodegradability is obtained by de-
termining the percentage of carbon in
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D5338–98 (Reapproved 2003) Designation:D5338–11
Standard Test Method for
Determining Aerobic Biodegradation of Plastic Materials
Under Controlled Composting Conditions. Incorporating
1
Thermophilic Temperatures
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5338; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1This test method determines the degree and rate of aerobic biodegradation of plastic materials on exposure to a
controlled-compostingenvironmentunderlaboratoryconditions.Thistestmethodisdesignedtoyieldreproducibleandrepeatable
test results under controlled conditions that resemble composting conditions. The test substances are exposed to an inoculum that
is derived from compost from municipal solid waste. The aerobic composting takes place in an environment where temperature,
aeration and humidity are closely monitored and controlled.
1.1 This test method determines the degree and rate of aerobic biodegradation of plastic materials on exposure to a
controlled-composting environment under laboratory conditions, at thermophilic temperatures. This test method is designed to
yieldreproducibleandrepeatabletestresultsundercontrolledconditionsthatresemblecompostingconditions,wherethermophilic
temperatures are achieved. The test substances are exposed to an inoculum that is derived from compost from municipal solid
waste.Theaerobiccompostingtakesplaceinanenvironmentwheretemperature,aerationandhumidityarecloselymonitoredand
controlled.
NOTE 1—During composting, thermophilic temperatures are most readily achieved in large-scale, professionally-managed facilities. However, these
temperatures may also be reached in smaller residential composting units, frequently referred to as “backyard” or “home” composting.
1.2 This test method is designed to yield a percentage of conversion of carbon in the sample to carbon dioxide. The rate of
biodegradation is monitored as well.
1.3This test method is designed to be applicable to all plastic materials that are not inhibitory to the microorganisms present in
aerobic composting piles.
1.3 This test method is designed to be applicable to all plastic materials, which are intended to be composted in facilities that
achieve thermophilic temperatures.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 8.
1.6 This test method is equivalent to ISO14855.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1293 Test Methods for pH of Water
D1888Test Methods for Particulate and Dissolved Matter, Solids, or Residue in Water
D2908 Practice for Measuring Volatile Organic Matter in Water by Aqueous-Injection Gas Chromatography
D3590 Test Methods for Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen in Water
D4129 Test Method for Total and Organic Carbon in Water by High Temperature Oxidation and by Coulometric Detection
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.96 on Environmentally Degradable
Plastics and Biobased Products.
´1
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2003. Published January 2004. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as D5338-98 . DOI:
10.1520/D5338-98R03.
Current edition approved April 1, 2011. Published April 2011. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D5338-98(2003). DOI:
10.1520/D5338-11.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5338–11
E260 Practice for Packed Column Gas Chromatography
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relationships
2.2 APHA—AW
...







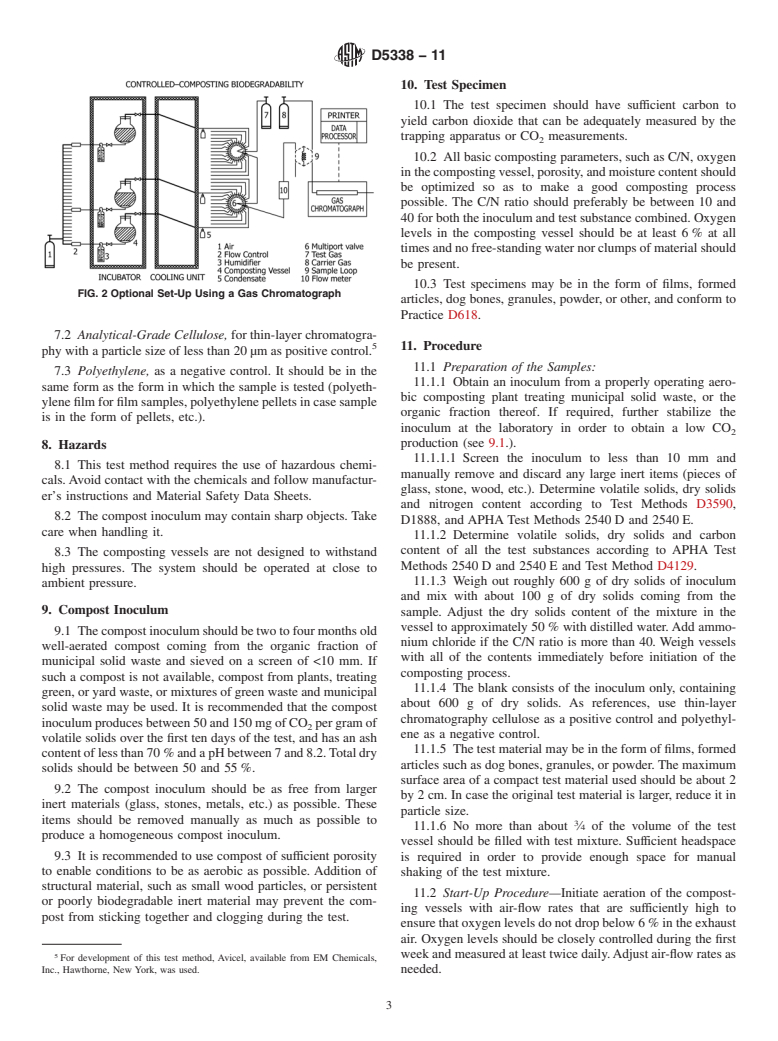

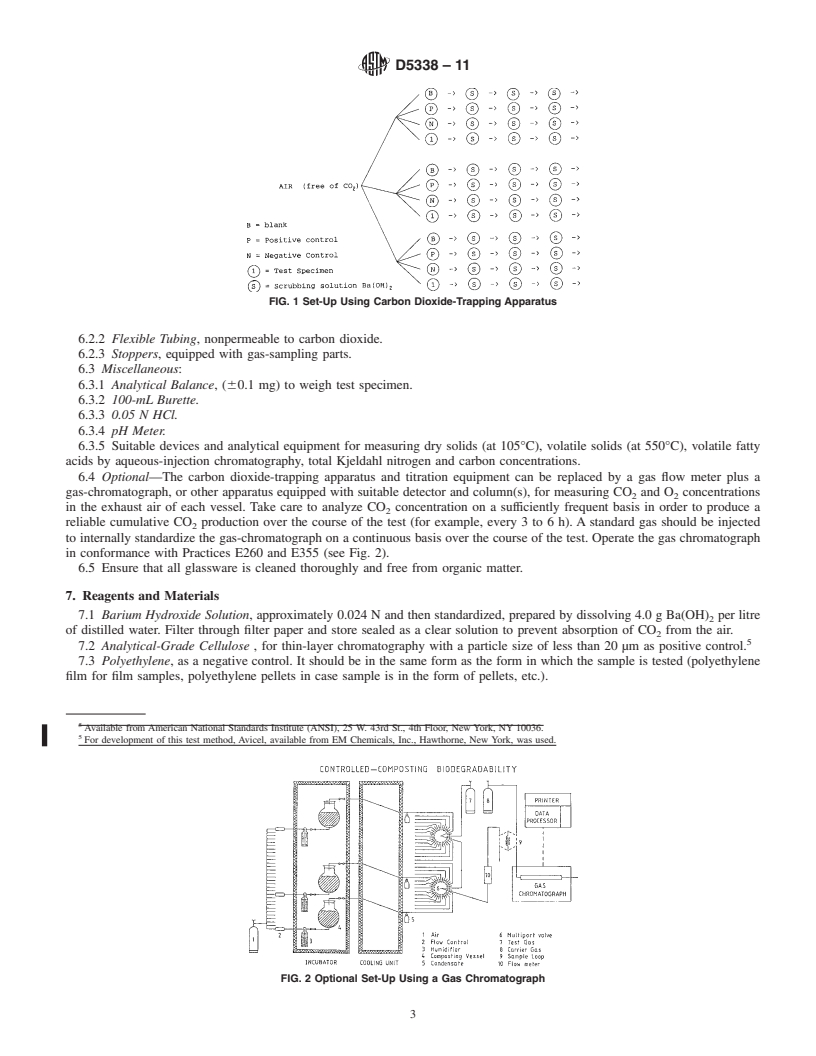
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.