ASTM C374-70(1998)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Fusion Flow of Porcelain Enamel Frits (Flow-Button Methods)
Standard Test Methods for Fusion Flow of Porcelain Enamel Frits (Flow-Button Methods)
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover evaluation of the relative fusion flow characteristics of samples of a given porcelain enamel frit by comparison with an established standard for that frit.
1.2 Two methods are included, differing only in certain details of the samples and in the apparatus and procedure for preparation of test specimens. Both methods give equally reproducible results and provide a satisfactory basis for comparison of fusion flow of the sample with that of the established standard.
1.2.1 Method A employs granular particles of frit to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are formed under high pressure in a hydraulic press.
1.2.2 Method B employs crushed, sized particles of frit to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are formed in a steel mold by hand.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C 374 – 70 (Reapproved 1998)
Standard Test Methods for
Fusion Flow of Porcelain Enamel Frits (Flow-Button
Methods)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 374; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover evaluation of the relative
fusion flow characteristics of samples of a given porcelain
enamel frit by comparison with an established standard for that
frit.
1.2 Two test methods are included, differing only in certain
details of the samples and in the apparatus and procedure for
preparation of test specimens. Both test methods give equally
reproducible results and provide a satisfactory basis for com-
parison of fusion flow of the sample with that of the established
standard.
1.2.1 Test Method A employs granular particles of frit to
which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens are
formed under high pressure in a hydraulic press.
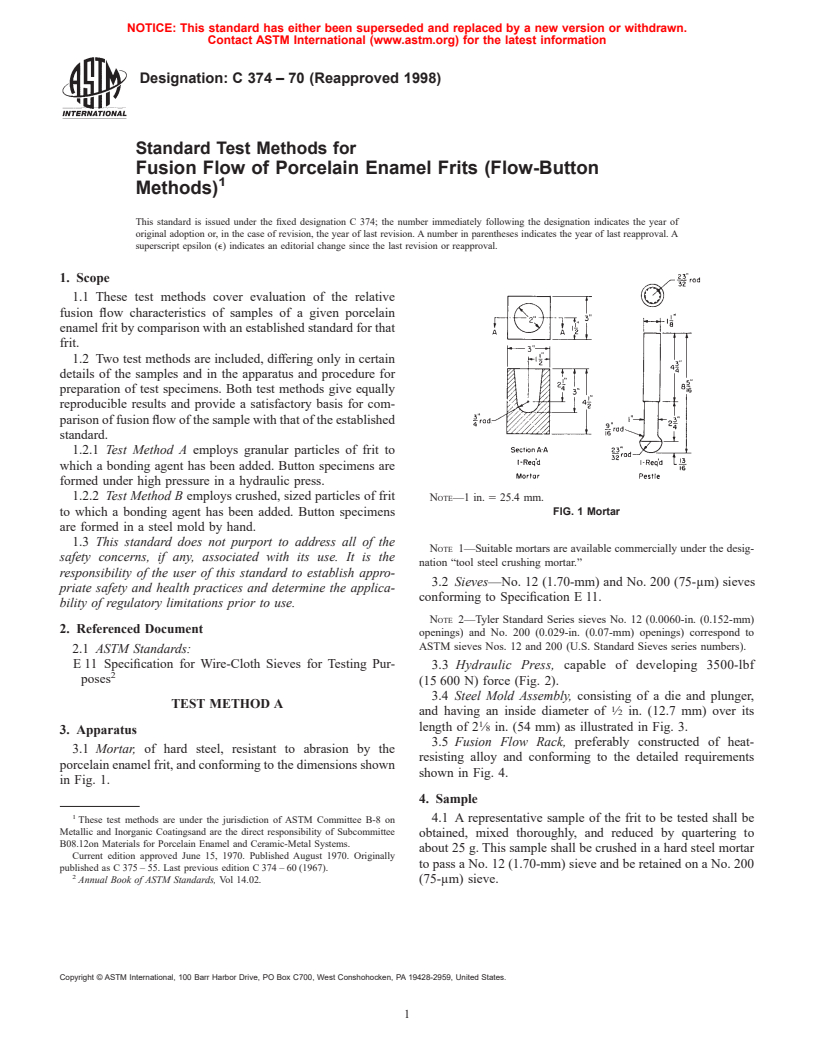
1.2.2 Test Method B employs crushed, sized particles of frit NOTE—1 in. 5 25.4 mm.
to which a bonding agent has been added. Button specimens FIG. 1 Mortar
are formed in a steel mold by hand.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
NOTE 1—Suitable mortars are available commercially under the desig-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
nation “tool steel crushing mortar.”
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Sieves—No. 12 (1.70-mm) and No. 200 (75-μm) sieves
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
conforming to Specification E 11.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 2—Tyler Standard Series sieves No. 12 (0.0060-in. (0.152-mm)
2. Referenced Document
openings) and No. 200 (0.029-in. (0.07-mm) openings) correspond to
ASTM sieves Nos. 12 and 200 (U.S. Standard Sieves series numbers).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E 11 Specification for Wire-Cloth Sieves for Testing Pur-
3.3 Hydraulic Press, capable of developing 3500-lbf
poses
(15 600 N) force (Fig. 2).
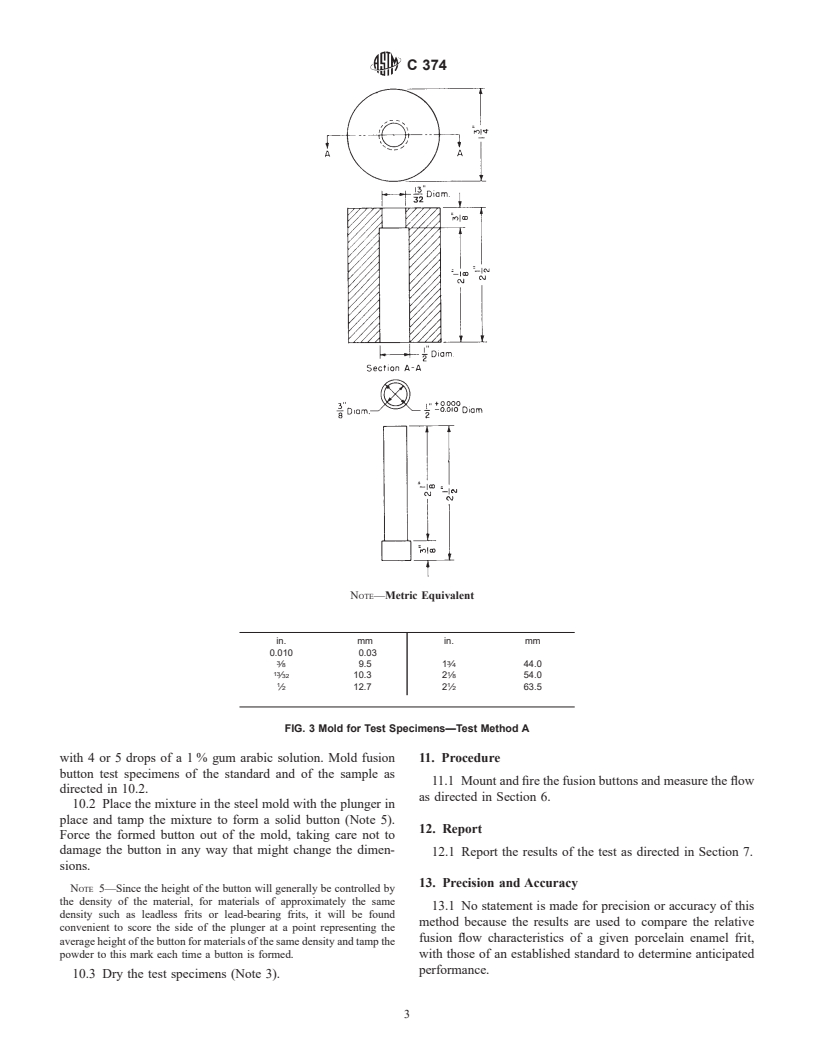
3.4 Steel Mold Assembly, consisting of a die and plunger,
TEST METHOD A
and having an inside diameter of ⁄2 in. (12.7 mm) over its
length of 2 ⁄8 in. (54 mm) as illustrated in Fig. 3.
3. Apparatus
3.5 Fusion Flow Rack, preferably constructed of heat-
3.1 Mortar, of hard steel, resistant to abrasion by the
resisting alloy and conforming to the detailed requirements
porcelain enamel frit, and conforming to the dimensions shown
shown in Fig. 4.
in Fig. 1.
4. Sample
4.1 A representative sample of the frit to be tested shall be
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B-8 on
Metallic and Inorganic Coatingsand are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
obtained, mixed thoroughly, and reduced by quartering to
B08.12on Materials for Porcelain Enamel and Ceramic-Metal Systems.
about 25 g. This sample shall be crushed in a hard steel mortar
Current edition approved June 15, 1970. Published August 1970. Originally
to pass a No. 12 (1.70-mm) sieve and be retained on a No. 200
published as C 375 – 55. Last previous edition C 374 – 60 (1967).
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02. (75-μm) sieve.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C 374
other button or portion thereof. The temperature shall approxi-
mate the median firing temperature for the standard that is used
as a basis for comparison. Allow the buttons to remain in the
horizontal position (Fig. 5(a)) until such time as fusion of the
buttons is evident from the rounded appearance of the tops of
the buttons. Then release the groundcoat plate to the vertical
position (Fig. 5(b)) and allow the fusion buttons to flow a
minimum of 50 mm, following which remove the test assembly
from the furnace and allow the buttons to cool. When the flow
is completed, the sides of the fusion buttons should be
approximately parallel; that is, there should be no excessive
spreading of the fusion buttons in the horizontal position,
indicating that the buttons were allowed to remain in the
horizontal position for too long a time.
6.3 Measuring Flow—Measure the greatest length of the
fusion flow to the nearest 1 mm for each fusion button,
including the standard.
FIG. 2 Hydraulic Press
7. Report
7.1 Report the length of the fusion flow for each test
5. Test Specimen
specimen in comparison with the standard run at the same time.
5.1 Weigh 3.5 6 0.05-g samples of the standard frit and of
For example, if a given specimen flows 50 mm against a flow
the material to be tested and thoroughly mix each of these
for the standard of 55 mm, the results shall be reported as
samples with 4 or 5 drops of a 1 % gum arabic solution. Mold
“50/55 mm.” If the width of the test specimen is observed to
fusion button test specimens of the standard and of the sample
vary more than 10 % from the width of the standard, length-
as directed in 5.2.
times-width values shall be calculated for the comparison.
5.2 Place the sample in the steel mold. Place the mold
assembly containing the sample in a hydraulic press and bring
TEST METHOD B
the press up to 3000 to 3500 lbf (13.3 to 15.6 kN) total load,
and immediately release (Fig. 2). Force the formed button out
of the mold with the plunger, taking care not to damage the
8. Apparatus
button in any way that might change the dimensions.
8.1 Mortar—See 3.1.
5.3 Dry the test specimens in a su
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.