ASTM D1518-85(2003)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Thermal Transmittance of Textile Materials
Standard Test Method for Thermal Transmittance of Textile Materials
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the overall thermal transmission coefficients due to the combined action of conduction, convection, and radiation for dry specimens of textile fabrics, battings, and other materials within the limits specified in 1.2. It measures the time rate of heat transfer from a warm, dry, constant-temperature, horizontal flat-plate up through a layer of the test material to a relatively calm, cool atmosphere.
1.2 For practical purposes, this test method is limited to determinations on specimens of fabrics, layered fabric assemblies, and battings having thermal transmittances (U2, as defined in 3.1.2) within a range of 0.7 to 14 W/m2K and thicknesses not in excess of 50 mm.
1.3 The coefficients obtained apply strictly only to the particular specimens tested and for the specified thermal and environmental conditions of each test. This test method gives values that are valid for comparison under the same conditions of test, that is, with the specified air velocity, temperature difference between the warm plate and the cool air, and air gap for measuring cool air temperature.
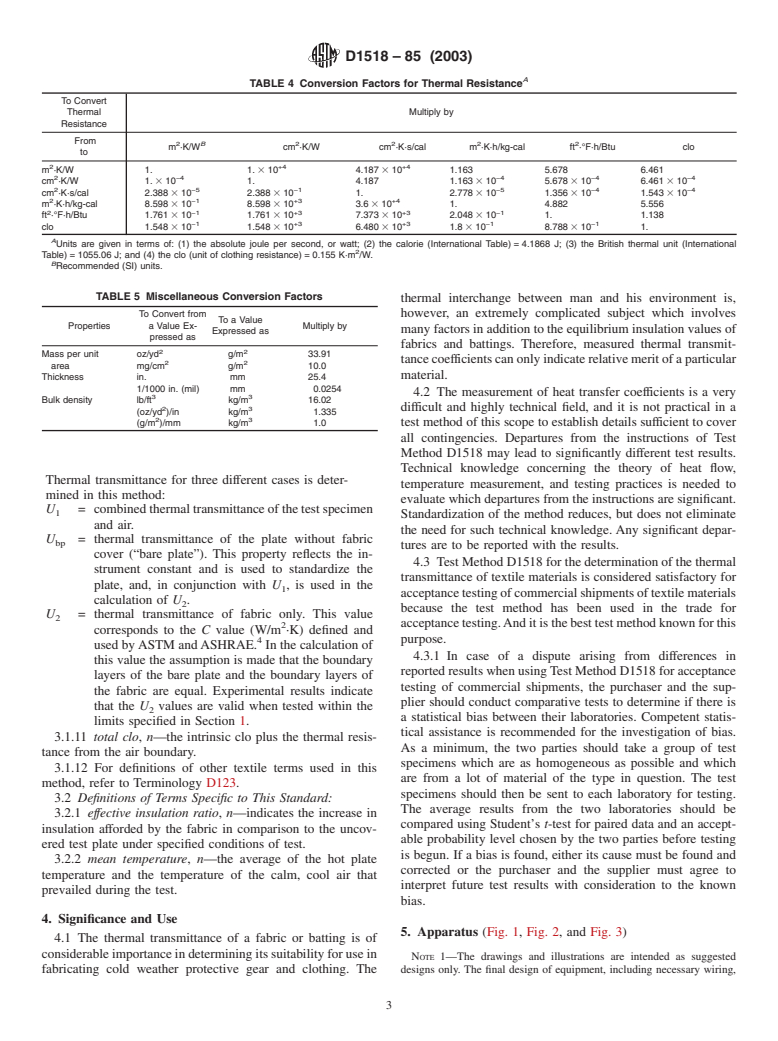
1.4 The values stated in metric units are to be regarded as the standard. Conversion factors, for thermal conductance and conductivity and thermal resistance and resistivity, to other units in common use are given in 1-5
1.5 This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of whoever uses this standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1518 – 85 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Test Method for
1
Thermal Transmittance of Textile Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1518; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the overall 3.1 Definitions:
thermaltransmissioncoefficientsduetothecombinedactionof 3.1.1 bulk density, n—apparent mass per unit volume.
conduction, convection, and radiation for dry specimens of 3.1.1.1 Discussion—In testing the thermal transmittance of
textile fabrics, battings, and other materials within the limits fabrics, bulk density is calculated from the fabric weight per
specified in 1.2. It measures the time rate of heat transfer from unit area and the thickness value used to calculate thermal
a warm, dry, constant-temperature, horizontal flat-plate up conductivity.
through a layer of the test material to a relatively calm, cool 3.1.2 clo, n—unit of thermal resistance defined as the
atmosphere. insulationrequiredtokeeparestingman(producingheatatthe
2
1.2 For practical purposes, this test method is limited to rate of 58 W/m ) comfortable in an environment at 21°C, air
determinations on specimens of fabrics, layered fabric assem- movement 0.1 m/s, or roughly the insulation value of typical
,
3 4
blies, and battings having thermal transmittances (U,as indoor clothing. (Syn. intrinsic clo).
2
2
defined in 3.1.2) within a range of 0.7 to 14 W/m ·K and 3.1.2.1 Discussion—Numerically the clo is equal to 0.155
2
thicknesses not in excess of 50 mm. K·m /W.
1.3 The coefficients obtained apply strictly only to the 3.1.3 heat transfer coeffıcient, n—see thermal transmit-
particular specimens tested and for the specified thermal and tance.
environmental conditions of each test. This test method gives 3.1.4 intrinsic clo, n—see clo.
values that are valid for comparison under the same conditions 3.1.5 specific clo, n—the specific thermal resistance in clo
of test, that is, with the specified air velocity, temperature units per unit thickness.
difference between the warm plate and the cool air, and air gap 3.1.6 thermal conductance, n—see thermal transmittance.
for measuring cool air temperature. 3.1.7 thermal conductivity, n—time rate of unidirectional
1.4 The values stated in metric units are to be regarded as heat transfer per unit area, in the steady-state, between parallel
the standard. Conversion factors, for thermal conductance and planes separated by unit distance, per unit difference of
conductivity and thermal resistance and resistivity, to other temperature of the planes.
units in common use are given in Tables 1-5 3.1.7.1 Discussion—Numerically, thermal conductivity
1.5 This standard does not purport to address the safety equals the product of the heat transfer coefficient and the
concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of distance separating the planes. Thus, k, the thermal conductiv-
whoever uses this standard to consult and establish appropri- ity of the fabric only, is the product of U and the fabric
2
ate safety and health practices and determine the applicability thickness. Units of thermal conductivity are W/m·K.
of regulatory limitations prior to use. 3.1.8 thermal resistance, n—reciprocal of thermal transmit-
tance.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.9 thermal resistivity, n—reciprocal of thermal conduc-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: tivity.
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
3.1.10 thermal transmittance, n—time rate of unidirectional
D1777 Test Method for Thickness of Textile Materials heat transfer per unit area, in the steady-state, between parallel
planes, per unit difference of temperature of the planes (Syn.
thermal conductance, heat transfer coefficient).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 onTextiles
3.1.10.1 Discussion—Thermaltransmittanceisexpressedas
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.51 on Chemical Conditioning
watts per square metre of test specimen per kelvin difference
and Performance.
2
Current edition approved July 26, 1985. Published September 1985. Originally
between the hot plate and the cool atmosphere (W/m ·K).
published as D1518 – 57 T. Last previous edition D1518 – 77. DOI: 10.1520/
D1518-85R03.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Gagge, A. P., Burton, A. C., B
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.