ASTM E430-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Measurement of Gloss of High-Gloss Surfaces by Abridged Goniophotometry
Standard Test Methods for Measurement of Gloss of High-Gloss Surfaces by Abridged Goniophotometry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The gloss of metallic finishes is important commercially on metals for automotive, architectural, and other uses where these metals undergo special finishing processes to produce the appearances desired. It is important for the end-products, which use such finished metals that parts placed together have the same glossy appearance.
It is also important that automotive finishes and other high-gloss nonmetallic surfaces possess the desired finished appearance. The present method identifies by measurements important aspects of finishes. Those having identical sets of numbers normally have the same gloss characteristics. It usually requires more than one measurement to identify properly the glossy appearance of any finish (see Refs 3 and 4).
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the measurement of the reflection characteristics responsible for the glossy appearance of high-gloss surfaces. Three test methods, A, B and C, are provided for evaluating such surface characteristics at specular angles of 30°, 20° and 30°, respectively. These test methods are not suitable for diffuse finish surfaces nor do they measure color, another appearance attribute.
1.2 As originally developed by Tingle and others (see Refs 1 and 2), the test methods were applied only to bright metals. Recently they have been applied to high-gloss automotive finishes and other nonmetallic surfaces.
1.3 The DOI of a glossy surface is generally independent of its curvature. The DOI measurement by this test method is limited to flat or flattenable surfaces.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E430 − 11
Standard Test Methods for
Measurement of Gloss of High-Gloss Surfaces by Abridged
1
Goniophotometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E430; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.1 These test methods cover the measurement of the
E1347Test Method for Color and Color-Difference Mea-
reflection characteristics responsible for the glossy appearance
surement by Tristimulus Colorimetry
of high-gloss surfaces. Three test methods, A, B and C, are
provided for evaluating such surface characteristics at specular
3. Terminology
anglesof30°,20°and30°,respectively.Thesetestmethodsare
3.1 Definitions:
not suitable for diffuse finish surfaces nor do they measure
3.1.1 Appearance terms in this test method are in accor-
color, another appearance attribute.
dance with Terminology E284.
1.2 As originally developed by Tingle and others (see Refs
3.1.2 Terms that are defined inTerminology E284, but have
2
1 and 2), the test methods were applied only to bright metals.
a specific definition in this method are
Recently they have been applied to high-gloss automotive
3.1.3 reflectance, p, n—ratio of the reflected radiant or
finishes and other nonmetallic surfaces.
luminous flux to the incident flux in the given conditions.
(E284)
1.3 The DOI of a glossy surface is generally independent of
3.1.3.1 Discussion—The term reflectance is often used in a
its curvature. The DOI measurement by this test method is
general sense or as an abbreviation for reflectance factor. Such
limited to flat or flattenable surfaces.
usage is not assumed in this method. The definition may
2. Referenced Documents
require that the term be modified by adjectives denoting the
3
spectral and geometric conditions of measurement.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D523Test Method for Specular Gloss
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
D2457Test Method for Specular Gloss of Plastic Films and
3.2.1 reflection haze, H, n—for a specified specular angle,
Solid Plastics
ratio of flux reflected at a specified angle (or angles) from the
E171Practice for Conditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier
specular direction to the flux similarly reflected at the specular
Packaging
angle by a specified gloss standard.
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
3.2.1.1 Discussion—Modifiers may be used to specify the
ASTM Test Methods
angles at which the haze is measured (for example, 2°, –5° or
E179Guide for Selection of Geometric Conditions for
15°); whether –H or a logarithmic form is to be stated; or
Measurement of Reflection and Transmission Properties
whether H is to be compensated for the luminance of the
of Materials
specimenbymultiplicationbyY /Y ,wherendenotesthe
specimen n
E284Terminology of Appearance
reference white; or any combination of these.
E308PracticeforComputingtheColorsofObjectsbyUsing
3.2.2 metallic brightness, n—freedom of a metal surface
the CIE System
from diffuse haze or texture.
3.2.3 ‘with-machine’ direction, n—the axis of a specimen
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E12 on
that is parallel to the direction of mill rolling or extrusion, or
Color andAppearance and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E12.03 on
other surface-finish texture.
Geometry.
Current edition approved June 1, 2011. Published June 2011. Originally
3.2.4 ‘across-machine’ direction, n—the perpendicular to
approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as E430–05. DOI:
‘with-machine’ direction.
10.1520/E0430-11.
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of
4. Summary of Test Method
this method.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4.1 Several geometrically different measures of light re-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
flected by a surface are proposed for use in describing its gloss
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. appearance.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E430 − 11
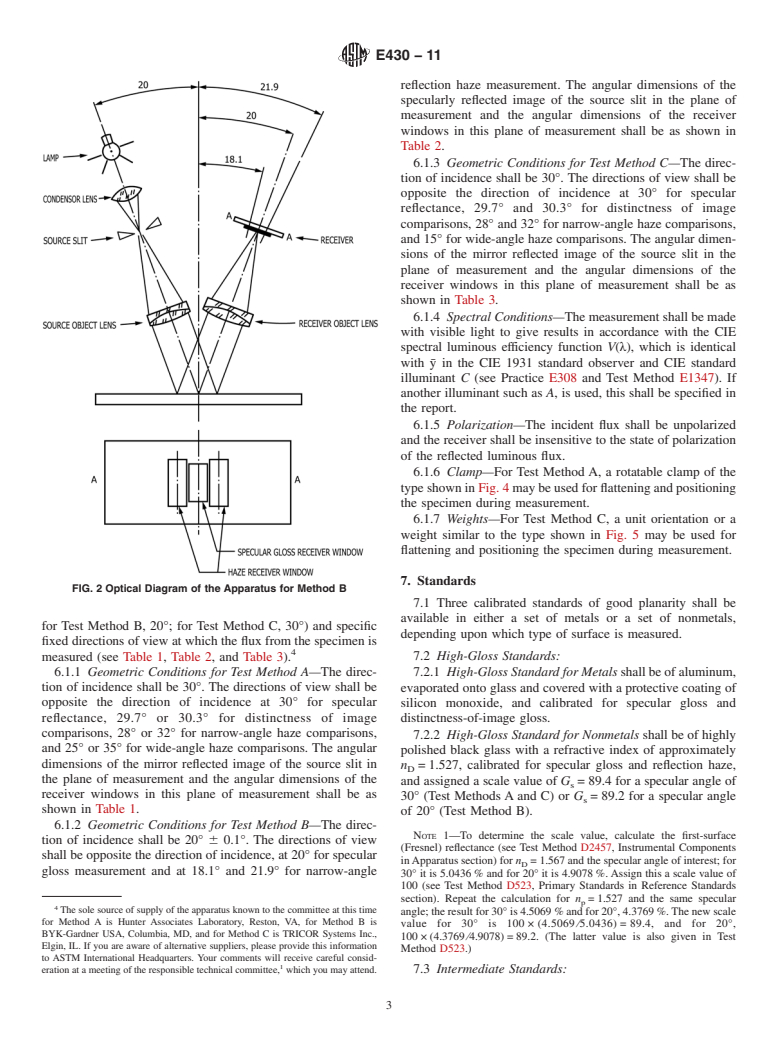
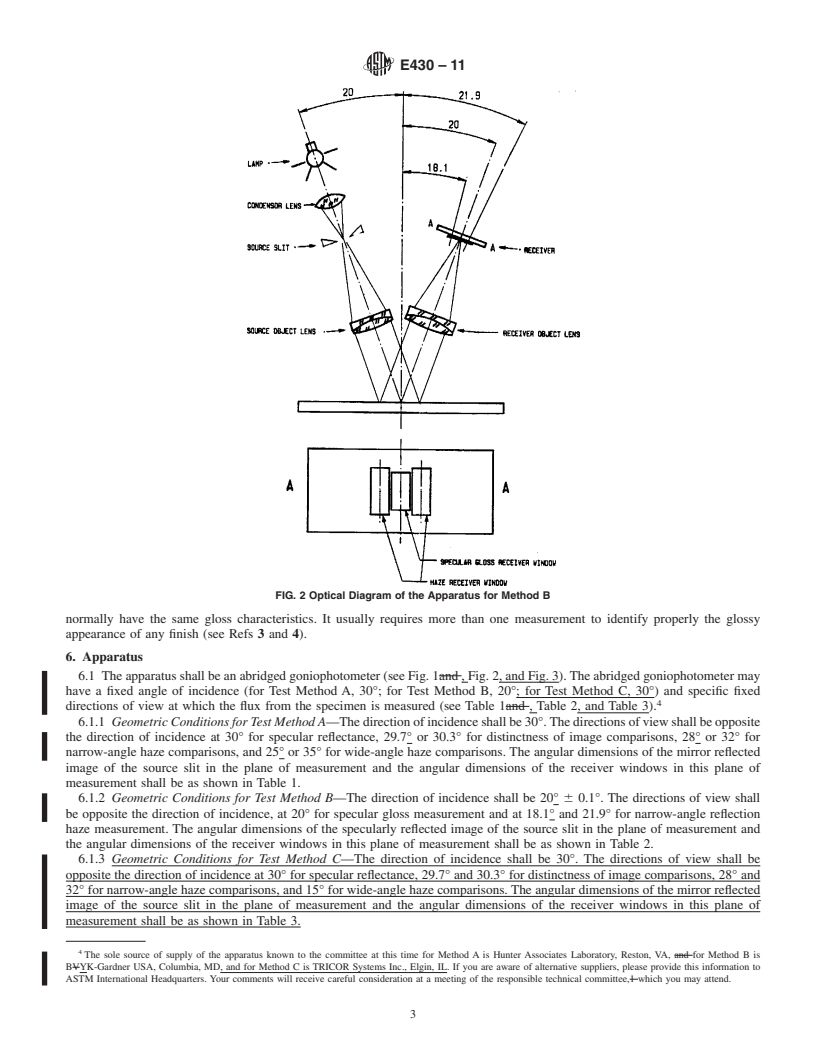
FIG. 1 Optical Diagram of the Apparatus for Method A
4.1.1 Test Method A—Aglossreflectancefactorismeasured 5. Significance and Use
at 30° to the specimen normal using narrow illuminator and
5.1 Theglossofmetallicfinishesisimportantcommercially
receiver aperture angles (0.5° wide maximum). Distinctness-
on metals fo
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E430–05 Designation:E430–11
Standard Test Methods for
Measurement of Gloss of High-Gloss Surfaces by Abridged
1
Goniophotometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E430; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover the measurement of the reflection characteristics responsible for the glossy appearance of
high-gloss surfaces. TwoThree test methods, A, B and B,C, are provided for evaluating such surface characteristics at specular
angles of 30°, 20° and 20°,30°, respectively. These test methods are not suitable for diffuse finish surfaces nor do they measure
color, another appearance attribute.
2
1.2 As originally developed by Tingle and others (see Refs 1 and 2), the test methods were applied only to bright metals.
Recently they have been applied to high-gloss automotive finishes and other nonmetallic surfaces.
1.3 The DOI of a glossy surface is generally independent of its curvature.The DOI measurement by this test method is limited
to flat or flattenable surfaces.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D523 Test Method for Specular Gloss
D2457 Test Method for Specular Gloss of Plastic Films and Solid Plastics
E171 Specification for Atmospheres for Conditioning and Testing Flexible Barrier Materials
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E179 Guide for Selection of Geometric Conditions for Measurement of Reflection and Transmission Properties of Materials
E284 Terminology of Appearance
E308 Practice for Computing the Colors of Objects by Using the CIE System
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E1347 Test Method for Color and Color-Difference Measurement by Tristimulus Colorimetry
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Appearance terms in this test method are in accordance with Terminology E284.
3.2 Terms that are defined in Terminology E284.,, but have a specific definition in this method are:
3.2.1 reflectance, p, n—ratio of the reflected radiant or luminous flux to the incident flux in the given conditions. (E284)
3.2.1.1 Discussion—The term reflectance is often used in a general sense or as an abbreviation for reflectance factor. Such
usage is not assumed in this method. The definition may require that the term be modified by adjectives denoting the spectral and
geometric conditions of measurement.
3.3 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.3.1 reflection haze, H, n—for a specified specular angle, ratio of flux reflected at a specified angle (or angles) formfrom the
specular direction to the flux similarly reflected at the specular angle by a specified gloss standard.
3.3.1.1 Discussion—Modifiers may be used to specify the angles at which the haze is measured (for example, 2°, –5° or
–5°);15°); whether –H or a logarithmic form is to be stated; or whether H is to be compensated for the luminance of the specimen
by multiplication by Y /Y , where ndenotes the reference white; or any combination of these.
specimen n
3.3.2 metallic brightness, n—freedom of a metal surface from diffuse haze or texture.
3.3.3 ‘with-machine’direction, n—the axis of a specimen that is parallel to the direction of mill rolling or extrusion, or other
surface-finish texture.
1
ThesetestmethodsareunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeE12onColorandAppearanceandarethedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeE12.03onGeometry.
Current edition approved June 1, 2005.2011. Published July 2005.June 2011. Originally approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 20032005 as
E430–97(2003).E430–05. DOI: 10.1520/E0430-05.10.1520/E0430-11.
2
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of this method.
3
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E430–11
3.3.4 ‘across-machine’direction, n—the perpendicular to ‘with-machine’ direction.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Several geometrically different measures of light reflected by a surface are prop
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.