ASTM D351-97(2003)
(Classification)Standard Classification for Natural Muscovite Block Mica and Thins Based on Visual Quality
Standard Classification for Natural Muscovite Block Mica and Thins Based on Visual Quality
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The properties included in this standard are those required to control the visual quality, usable area, thickness, hardness, and stiffness.
SCOPE
1.1 This classification covers the determination of commercially available natural muscovite block mica and is intended to be independent of the basic color of the mica or its source.
1.2 Muscovite mica is characterized by having an optical axial angle between 50 and 75° (see Appendix X1); and has a weight loss when heated for 5 min at 600°C not exceeding 0.2% (based on the weight after drying at 120°C).
1.3 The visual system of classifying the quality of natural muscovite mica covered by this specification is based upon relative amounts of visible foreign inclusions such as air bubbles, stains, and spots in combination with relative amounts and types of waviness, as well as other physical properties. In this system, a perfectly clear, transparent, flat specimen of mica is the visual standard of perfection. Increasing amounts of visual defects lower the visual quality, and a total of 13 levels of visual quality are covered by this standard. This method of classification, generally known as the Bengal India System, is purely qualitative and is entirely dependent on personal opinion and judgment.
1.4 The standards for visual quality classification that are covered in this classification are the best commercially available concept of the various qualities and their relative positions. Variations in the methods of using and applying these standards from those herein defined may be specified by the purchaser, or defined by agreement between the supplier and the purchaser.
1.5 Standard size classifications are defined, based upon available usable rectangular areas and the minimum dimensions of the rectangles that the pieces will yield. Precautions to be taken in making thickness measurements are also described.
1.6 This standard covers the following two definite forms of commercial preparation:
1.6.1 Form 1—Full-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007 in. (0.178 mm) minimum thickness.
1.6.2 Form 2 -Partially-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007 in. minimum thickness.
1.7 The basic color of mica, such as white, ruby, light green, dark green, brownish green, and rum, as well as other colors, and the method of controlling the color and other problems associated with the basic color, are not a part of this classification.
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D 351 – 97 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Classification for
Natural Muscovite Block Mica and Thins Based on Visual
Quality
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 351; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 1.6.2 Form 2—Partially-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007
in. minimum thickness.
1.1 This classification covers the determination of commer-
1.7 Thebasiccolorofmica,suchaswhite,ruby,lightgreen,
ciallyavailablenaturalmuscoviteblockmicaandisintendedto
dark green, brownish green, and rum, as well as other colors,
be independent of the basic color of the mica or its source.
and the method of controlling the color and other problems
1.2 Muscovite mica is characterized by having an optical
associated with the basic color, are not a part of this classifi-
axial angle between 50 and 75° (see Appendix X1); and has a
cation.
weight loss when heated for 5 min at 600°C not exceeding
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
0.2 % (based on the weight after drying at 120°C).
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
1.3 The visual system of classifying the quality of natural
information only.
muscovite mica covered by this specification is based upon
1.9 Section 5 is technically identical to procedures specified
relative amounts of visible foreign inclusions such as air
in ISO 67.
bubbles,stains,andspotsincombinationwithrelativeamounts
1.10 Section 6 differs somewhat in procedure from ISO
and types of waviness, as well as other physical properties. In
5972, but data obtained by either should be identical.
thissystem,aperfectlyclear,transparent,flatspecimenofmica
1.11 Section 7 is technically identical to procedures speci-
is the visual standard of perfection. Increasing amounts of
fied in ISO 2185.
visual defects lower the visual quality, and a total of 13 levels
of visual quality are covered by this standard. This method of
2. Referenced Documents
classification, generally known as the Bengal India System, is
2.1 ASTM Standards:
purely qualitative and is entirely dependent on personal opin-
D 374 Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insu-
ion and judgment.
lation
1.4 The standards for visual quality classification that are
D 1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
covered in this classification are the best commercially avail-
2.2 ISO Publications:
able concept of the various qualities and their relative posi-
ISO 67-1981 Muscovite Mica Blocks, Thins, and Films—
tions. Variations in the methods of using and applying these
Grading by Size
standards from those herein defined may be specified by the
ISO 2185-1972 Muscovite Mica Blocks, Thins, and
purchaser, or defined by agreement between the supplier and
Films—Visual Classification
the purchaser.
ISO5972-1978 MicaBlocks,Thins,Films,andSplittings—
1.5 Standard size classifications are defined, based upon
Measurement of Thickness
available usable rectangular areas and the minimum dimen-
sions of the rectangles that the pieces will yield. Precautions to
3. Terminology
be taken in making thickness measurements are also described.
3.1 For definitions of terms relating to mica refer to Termi-
1.6 This standard covers the following two definite forms of
nology D 1711, Part III.
commercial preparation:
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.6.1 Form 1—Full-trimmed natural block mica, 0.007 in.
3.2.1 “A”—aseriesofrulingsorstriationsintersectingatan
(0.178 mm) minimum thickness.
angle of about 60°.
This classification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D09.19 on Dielectric Sheet and Roll Products. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 10.01.
Current edition approved March 10, 2003. Published April 2003. Originally Available from American National Standards Institute, 25 W. 43rd St., 4th
approved in 1932. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as D 351 – 97. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 351 – 97 (2003)
3.2.2 blocks—mica thickness of 0.007 in. (0.178 mm) untrimmed sides, no defects of the designated quality are
minimum thickness, full-trimmed, unless otherwise desig- acceptable within the minimum rectangle of the designated
nated. grade.
3.2.3 buckle—one or more large depression(s) and eleva- 5.3 Natural Block and Thins—Natural block and thins,
muscovite mica shall be graded for size according to the area
tion(s).
of the rectangle (maximum rectangle for full-trimmed, maxi-
3.2.4 cracks—irregular fractures within the crystal that may
mum rectangle of designated quality for half-trimmed) having
be natural or may arise from blasting, rough handling, etc.
at least the minimum dimension of one side for the specified
3.2.5 full-trimmed mica—mica trimmed on all sides with all
grade. The area within such a rectangle shall meet the
cracks, reeves, and cross-grains removed.
requirements of the quality specified by the purchaser as listed
3.2.6 haircracks or hairline cracks—minute, irregular
in Table 1.
cracks that are barely noticeable until mica is split into films,
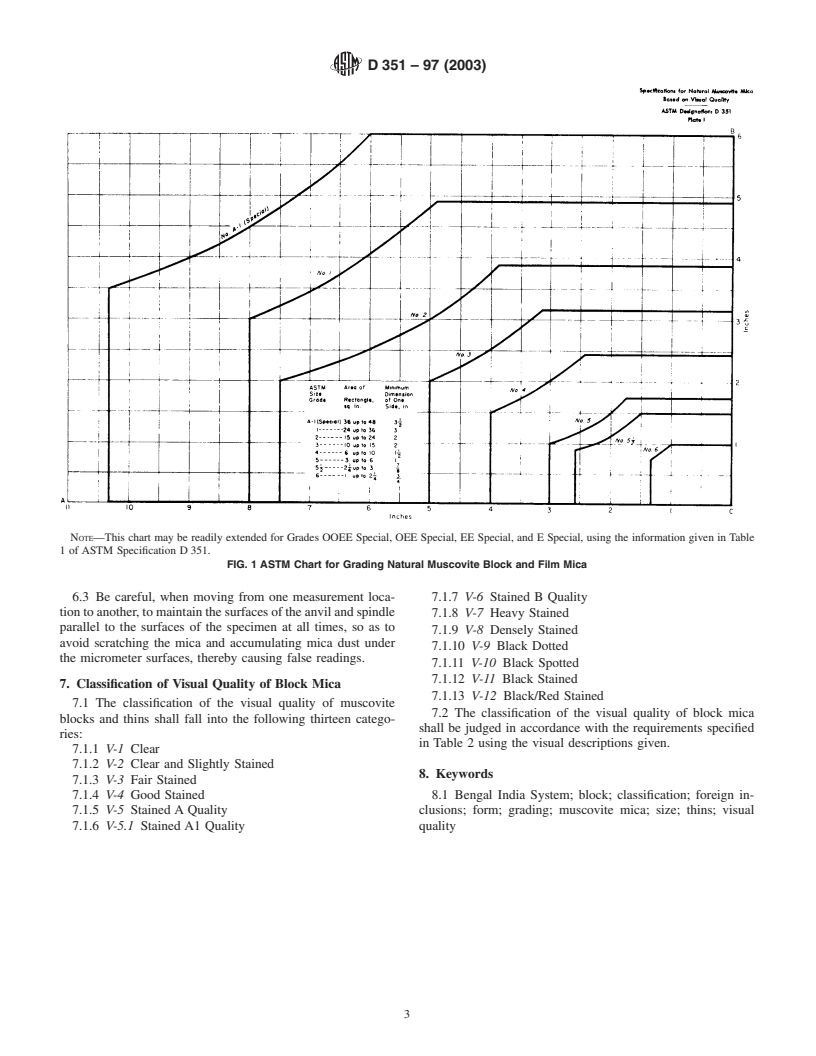
5.4 Method of Grading for Size—The Standard ASTM
resulting in production of torn films.
Chart shown in Fig. 1 shall be used for grading natural block
3.2.7 reeves or cross grains—tangled laminations giving
and thins, muscovite mica according to size. In grading natural
imperfect cleavage, that results in tears or breaks during
block mica and thins for size, all dimensions apply to the
splitting.
smaller surface measured from the foot of the bevel-trimmed
3.2.8 ribboned or rules mica—mica that breaks into narrow
edge.The specimen to be graded shall be laid upon the chart so
strips because of parallel fractures.
that it covers point O and has its maximum and minimum
3.2.9 ribs or ridges—crenulations in the form of steps.
dimensions extending along and covering lines OA and OB,
3.2.10 ripple—multiple short waves.
respectively.Thespecimenshallbeshifteduntiltheusablearea
3.2.11 stains—stains arise from foreign materials, resulting
completely covers the largest rectangle, determined by a
in a partial or total loss of transparency. They may be in the
diagonal extending from point O to or beyond a point on any
form of specks or patches of appreciable area for example,
of the curves. The number of the curve at the greatest distance
slight stain, “vegetable” stain, clay stain, black stain, red stain,
from O cut by the diagonal of the rectangle designates the
blackspeckled,lightdotorspot,black,redorgreendotorspot,
grade of the specimen.
etc. (see “inclusions” in Terminology D 1711).
6. Thickness of Block Mica
3.2.12 stones and stone holes—small embedded crystals or
holes resulting from them.
6.1 Measure the thickness with a micrometer as specified in
3.2.13 thins—knife-dressed mica, 0.002 in. (0.05 mm) to
Test Methods D 374. In determining thickness of mica that
less than 0.007 in. (0.18 mm) in thickness. They may be
must be kept within small permissible variations, or where two
classified as follows:
or more specimens are to be measured at once, use Method A
3.2.13.1 Thins, 0.002 to 0.004 in. (0.05 to 0.10 mm), and
of Test Methods D 374. Where the maximum accuracy is not
3.2.13.2 Thick-thins, 0.004 to 0.007 in. (0.10 to 0.18 mm). required, Method B may be used.
6.2 Because of the abrasive nature of mica, test the mi-
3.2.14 unmanufactured mica—commercial form of mica
crometer frequently for conformity to the requirements speci-
known as blocks, thins, films, and splittings, as described.
fied in Test Methods D 374. Clean the anvil and spindle as
3.2.15 waves—alternate elevations and depressions that
frequently as necessary to prevent the accumulation of mica
may be classified as slight, medium, or heavy.
dust on the surfaces and to preserve the accuracy of the
measurements. To clean, close the micrometer lightly on a
4. Significance and Use
clean sheet of bond paper and move the paper between the
4.1 The properties included in this standard are those
surfaces.
required to control the visual quality, usable area, thickness,
hardness, and stiffness.
TABLE 1 ASTM Grade Sizes of Muscovite Uncut Mica Block and
Thins
5. Grading for Size
Minimum
Area of
Dimen-
5.1 Full-Trimmed—All full-trimmed mica blocks and thins Minimum
ASTM
sion of
Rectangle
Grade
shall be fully trimmed to remove all cracks, holes, reeves, and
One Side
Sizes
cross-grainsaccordingtothequalitydesired.Asfaraspossible,
Equiva- Equiva-
in. in.
lent, cm lent, mm
all marginal cracks should be removed by recutting. The
average area of the pieces for Grade 4 and larger shall be not
OOEE Special 100 650 4 100
OEE Special 80 520 4 100
more than 1.54 times the average area of the largest usable
EE Special 60 390 4 100
rectangles. This would constitute a minimum yield of 65 %.
E Special 48 310 4 100
For Grades 5 and smaller, the average area of the pieces shall 1
A-1 (Special) 36 235 3 ⁄2 89
No. 1 24 155 3 76
be not more than two times the average area of the largest
No. 2 15 97 2 51
usable rectangles. This would constitute a yield of 50 %.
No. 3 10 65 2 51
5.2 Half-Trimmed—For half-trimmed mica, follow the No. 4 6 40 1 ⁄2 38
No. 5 3 20 1 25
grading described in 5.1 for trimmed sides with no cracks
1 1 7
No. 5 ⁄2 2 ⁄4 15 ⁄8 22
extendingfromthetrimmedsides,exceptforsizes6and5 ⁄2on
No. 6 1 6.5 ⁄4 19
which only side must be trimmed free of cracks. On the
D 351 – 97 (2003)
NOTE—This chart may be readily extended for Grades OOEE Special, OEE Special, EE Special, and E Special, using the information given in Table
1 of ASTM Specification D 351.
FIG. 1 ASTM Chart for Grading Natural Muscovite Block and Film Mica
6.3 Be careful, when moving from one measurement loca- 7.1.7 V-6 Stained B Quality
tiontoanother,tomaintainthesurfacesoftheanvilandspindle
7.1.8 V-7 Heavy Stained
parallel to the surfaces of the specimen at all times, so as to
7.1.9 V-8 Densely Stained
avoid scratching the mica and accumulating mica dust under
7.1.10 V-9 Black Dotted
the micrometer surfaces, thereby causing false readings.
7.1.11 V-10 Black Sp
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.