ASTM D6245-98(2002)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Using Indoor Carbon Dioxide Concentrations to Evaluate Indoor Air Quality and Ventilation
Standard Guide for Using Indoor Carbon Dioxide Concentrations to Evaluate Indoor Air Quality and Ventilation
SCOPE
1.1 This guide describes how measured values of indoor carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations can be used in evaluations of indoor air quality and building ventilation.
1.2 This guide describes the determination of CO 2 generation rates from people as a function of body size and level of physical activity.
1.3 This guide describes the experimentally-determined relationship between CO2 concentrations and the acceptability of a space in terms of human body odor.
1.4 This guide describes the following uses of indoor CO2 concentrations to evaluate building ventilation-mass balance analysis to determine the percent outdoor air intake at an air handler, the tracer gas decay technique to estimate whole building air change rates, and the constant injection tracer gas technique at equilibrium to estimate whole building air change rates.
1.5 This guide discusses the use of continuous monitoring of indoor and outdoor CO2 concentrations as a means of evaluating building ventilation and indoor air quality.
1.6 This guide discusses some concentration measurement issues, but it does not include or recommend a method for measuring CO 2 concentrations.
1.7 This guide does not address the use of indoor CO 2 to control outdoor air intake rates.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 6245 – 98 (Reapproved 2002)
Standard Guide for
Using Indoor Carbon Dioxide Concentrations to Evaluate
1
Indoor Air Quality and Ventilation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6245; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 3249 Practice for General Ambient Air Analyzer Proce-
dures
1.1 This guide describes how measured values of indoor
E 741 Test Method for DeterminingAir Change in a Single
carbon dioxide (CO ) concentrations can be used in evalua-
2
Zone by Means of Tracer Gas Dilution
tions of indoor air quality and building ventilation.
2.2 Other Documents
1.2 This guide describes the determination of CO genera-
2
ASHRAE Standard 62 Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor
tion rates from people as a function of body size and level of
3
Air Quality
physical activity.
1.3 This guide describes the experimentally-determined re-
3. Terminology
lationship between CO concentrations and the acceptability of
2
3.1 Definitions—For definitions and terms used in this
a space in terms of human body odor.
guide, refer to Terminology D 1356.
1.4 This guide describes the following uses of indoor CO
2
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
concentrations to evaluate building ventilation–mass balance
3.2.1 air change rate, n—the total volume of air passing
analysis to determine the percent outdoor air intake at an air
through a zone to and from the outdoors per unit time, divided
handler, the tracer gas decay technique to estimate whole
–1 –1 4
by the volume of the zone (s ,h ).
building air change rates, and the constant injection tracer gas
3.2.2 bioeffluents, n—gases emitted by people as a product
technique at equilibrium to estimate whole building air change
of their metabolism that can result in unpleasant odors.
rates.
3.2.3 single-zone, n—an indoor space, or group of spaces,
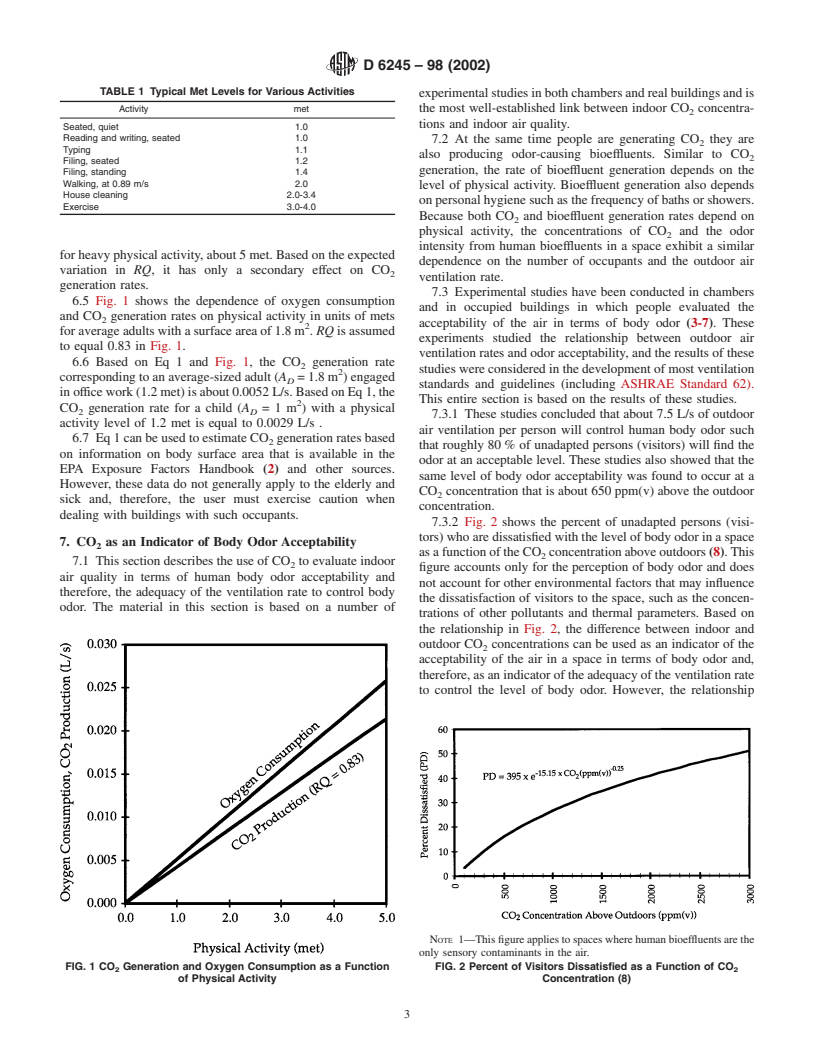
1.5 This guide discusses the use of continuous monitoring
wherein the CO concentration is uniform and that only
2
of indoor and outdoor CO concentrations as a means of
2
exchanges air with the outdoors.
evaluating building ventilation and indoor air quality.
1.6 This guide discusses some concentration measurement
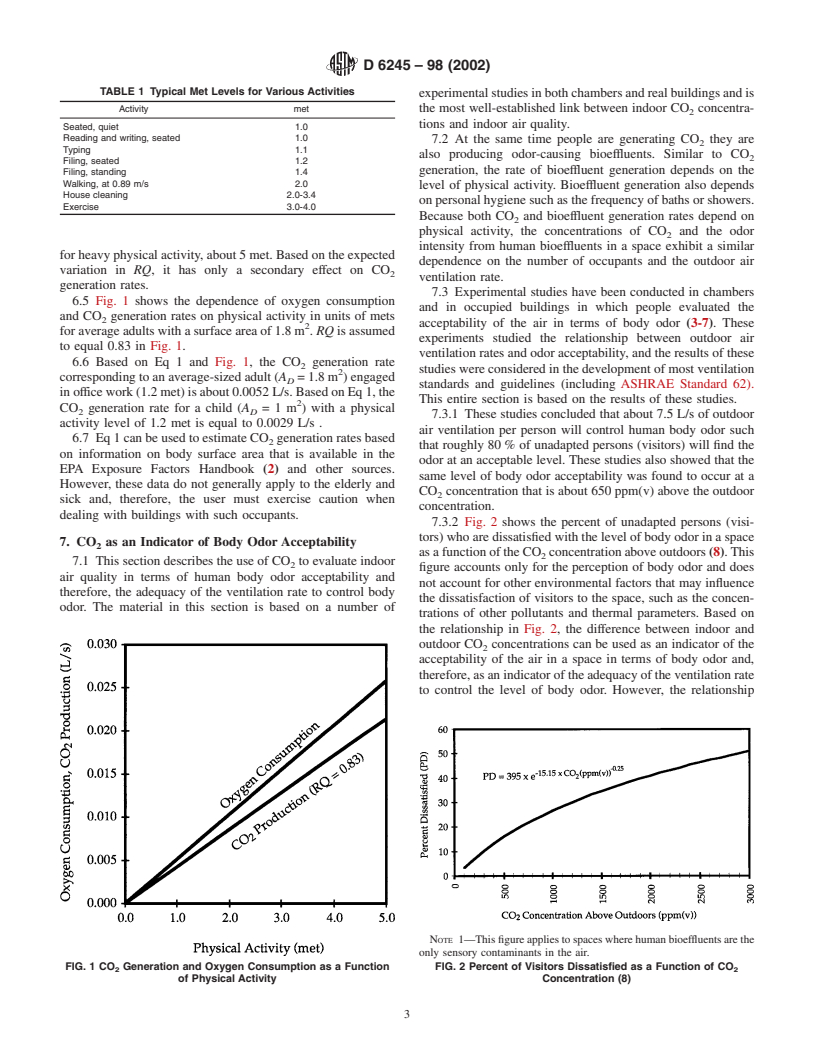
4. Summary of Guide
issues, but it does not include or recommend a method for
4.1 When investigating indoor air quality and building
measuring CO concentrations.
2
ventilation, a number of tools are available to understand the
1.7 This guide does not address the use of indoor CO to
2
building being studied. One such tool is the measurement and
control outdoor air intake rates.
interpretationofindoorandoutdoorCO concentrations.Using
2
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
CO concentrations to evaluate building indoor air quality and
2
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ventilation requires the proper use of the procedures involved,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
as well as consideration of several factors related to building
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
and ventilation system configuration, occupancy patterns, non-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
occupant CO sources, time and location of air sampling, and
2
2. Referenced Documents instrumentation for concentration measurement. This guide
2 discusses ways in which CO concentrations can be used to
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
evaluate building indoor air quality and ventilation.
D 1356 Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of
4.2 Section 6 discusses the rate at which people generate
Atmospheres
CO and the factors that affect this rate.
2
4.3 Section 7 discusses the use of indoor concentrations of
1
CO as an indicator of the acceptability of a space in terms of
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D22 on Sampling and 2
Analysis of Atmospheres and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.05 perceptions of human body odor.
on Indoor Air.
Current edition approved March 10, 1998. Published May 1998.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Conditioning Engineers, Inc., 1791 Tullie Circle, NE, Atlanta, GA 30329.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on A common way of expressing air change rate units is ach = air changes per
the ASTM website. hour.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
----
...
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 6245 – 98 (Reapproved 2002)
Standard Guide for
Using Indoor Carbon Dioxide Concentrations to Evaluate
1
Indoor Air Quality and Ventilation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6245; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 3249 Practice for General Ambient Air Analyzer Proce-
dures
1.1 This guide describes how measured values of indoor
E 741 Test Method for DeterminingAir Change in a Single
carbon dioxide (CO ) concentrations can be used in evalua-
2
Zone by Means of Tracer Gas Dilution
tions of indoor air quality and building ventilation.
2.2 Other Documents
1.2 This guide describes the determination of CO genera-
2
ASHRAE Standard 62 Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor
tion rates from people as a function of body size and level of
3
Air Quality
physical activity.
1.3 This guide describes the experimentally-determined re-
3. Terminology
lationship between CO concentrations and the acceptability of
2
3.1 Definitions—For definitions and terms used in this
a space in terms of human body odor.
guide, refer to Terminology D 1356.
1.4 This guide describes the following uses of indoor CO
2
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
concentrations to evaluate building ventilation–mass balance
3.2.1 air change rate, n—the total volume of air passing
analysis to determine the percent outdoor air intake at an air
through a zone to and from the outdoors per unit time, divided
handler, the tracer gas decay technique to estimate whole
–1 –1 4
by the volume of the zone (s ,h ).
building air change rates, and the constant injection tracer gas
3.2.2 bioeffluents, n—gases emitted by people as a product
technique at equilibrium to estimate whole building air change
of their metabolism that can result in unpleasant odors.
rates.
3.2.3 single-zone, n—an indoor space, or group of spaces,
1.5 This guide discusses the use of continuous monitoring
wherein the CO concentration is uniform and that only
2
of indoor and outdoor CO concentrations as a means of
2
exchanges air with the outdoors.
evaluating building ventilation and indoor air quality.
1.6 This guide discusses some concentration measurement
4. Summary of Guide
issues, but it does not include or recommend a method for
4.1 When investigating indoor air quality and building
measuring CO concentrations.
2
ventilation, a number of tools are available to understand the
1.7 This guide does not address the use of indoor CO to
2
building being studied. One such tool is the measurement and
control outdoor air intake rates.
interpretationofindoorandoutdoorCO concentrations.Using
2
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
CO concentrations to evaluate building indoor air quality and
2
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ventilation requires the proper use of the procedures involved,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
as well as consideration of several factors related to building
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
and ventilation system configuration, occupancy patterns, non-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
occupant CO sources, time and location of air sampling, and
2
2. Referenced Documents instrumentation for concentration measurement. This guide
2 discusses ways in which CO concentrations can be used to
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
evaluate building indoor air quality and ventilation.
D 1356 Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of
4.2 Section 6 discusses the rate at which people generate
Atmospheres
CO and the factors that affect this rate.
2
4.3 Section 7 discusses the use of indoor concentrations of
1
CO as an indicator of the acceptability of a space in terms of
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D22 on Sampling and 2
Analysis of Atmospheres and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.05 perceptions of human body odor.
on Indoor Air.
Current edition approved March 10, 1998. Published May 1998.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Conditioning Engineers, Inc., 1791 Tullie Circle, NE, Atlanta, GA 30329.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on A common way of expressing air change rate units is ach = air changes per
the ASTM website. hour.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
----
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.