ASTM E878-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Titanium in Iron Ores and Related Materials by Diantipyrylmethane Ultraviolet Spectrometry
Standard Test Method for Determination of Titanium in Iron Ores and Related Materials by Diantipyrylmethane Ultraviolet Spectrometry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is intended to be used for compliance with compositional specifications for titanium content. It is assumed that all who use these procedures will be trained analysts capable of performing common laboratory procedures skillfully and safely. It is expected that work will be performed in a properly equipped laboratory and that proper waste disposal procedures will be followed. Appropriate quality control practices must be followed such as those described in Guide E882.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of titanium in iron ores, concentrates, and agglomerates in the compositional range from 0.01 % to 6.0 % titanium.
Note 1—As used in this test method (except as related to the term relative standard deviation), percent or “%” refers to mass fraction (wt/wt) of the form g/100g.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This test method has been evaluated in accordance with Practice E1601 and Guide E1763. Unless otherwise noted in 13, the lower limit in the scope of each method specifies the lowest analyte content that may be analyzed with acceptable error (defined as a nominal 5 % risk of obtaining a 50 % or larger relative difference in results on the same test sample in two laboratories).
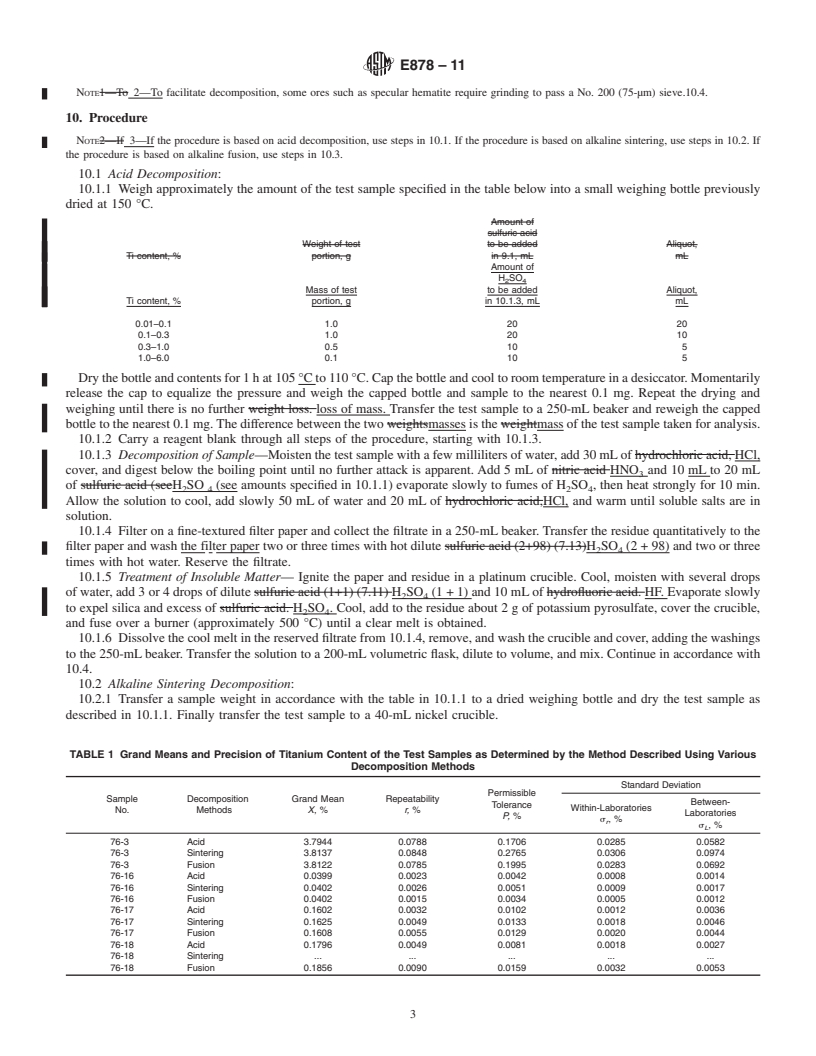
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
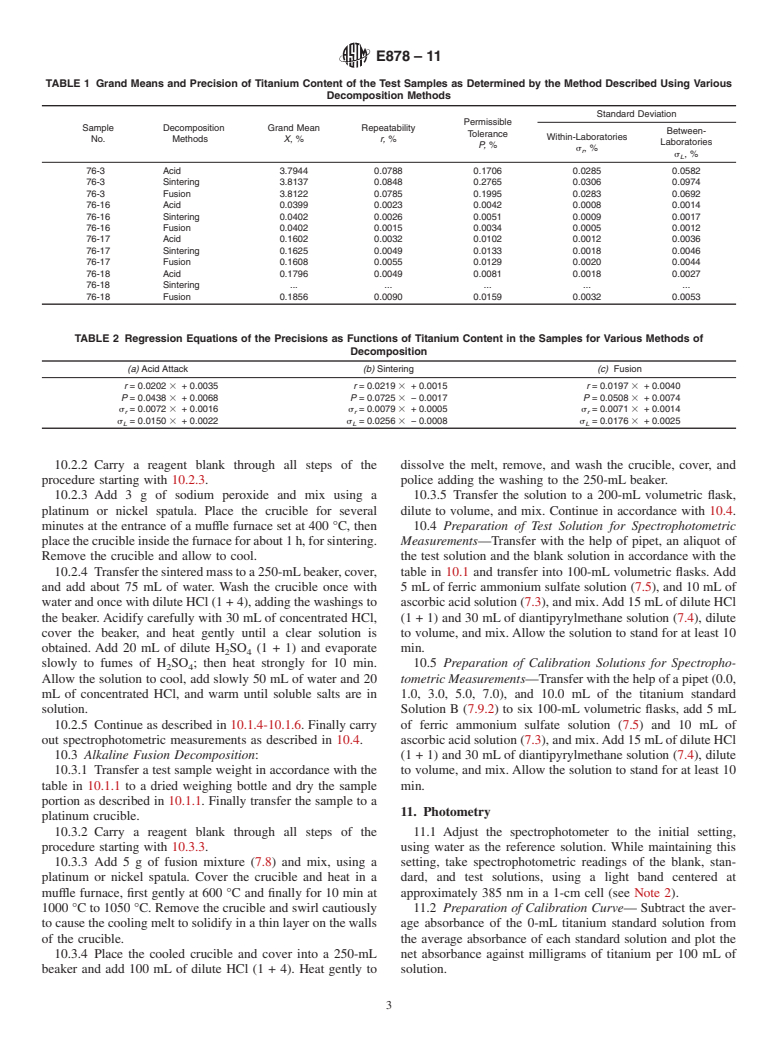
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E878–11
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Titanium in Iron Ores and Related
1
Materials by Diantipyrylmethane Ultraviolet Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E878; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E877 Practice for Sampling and Sample Preparation of Iron
Ores and Related Materials for Determination of Chemical
1.1 This test method covers the determination of titanium in
Composition
iron ores, concentrates, and agglomerates in the compositional
E882 Guide for Accountability and Quality Control in the
range from 0.01 % to 6.0 % titanium.
Chemical Analysis Laboratory
NOTE 1—As used in this test method (except as related to the term
E1601 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
relative standard deviation), percent or “%” refers to mass fraction
Evaluate the Performance of an Analytical Method
(wt/wt) of the form g/100g.
E1763 Guide for Interpretation and Use of Results from
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Interlaboratory Testing of Chemical Analysis Methods
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3. Terminology
standard.
1.3 This test method has been evaluated in accordance with
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to
Practice E1601 and Guide E1763. Unless otherwise noted in
Terminology E135.
13, the lower limit in the scope of each method specifies the
4. Summary of Test Method
lowest analyte content that may be analyzed with acceptable
error (defined as a nominal 5 % risk of obtaining a 50 % or
4.1 The sample is decomposed by treatment with hydro-
larger relative difference in results on the same test sample in
chloric, nitric, and sulfuric acids, or by sintering with sodium
two laboratories).
peroxide, or by fusion with sodium tetraborate and sodium
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
carbonate. Iron is reduced in an acid medium with ascorbic
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
acid, the color is developed with diantipyrylmethane, and the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
absorbance is measured at approximately 385 nm.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5. Significance and Use
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.1 This test method is intended to be used for compliance
2. Referenced Documents
with compositional specifications for titanium content. It is
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
assumed that all who use these procedures will be trained
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
analysts capable of performing common laboratory procedures
E50 Practices for Apparatus, Reagents, and Safety Consid-
skillfully and safely. It is expected that work will be performed
erations for Chemical Analysis of Metals, Ores, and
in a properly equipped laboratory and that proper waste
Related Materials
disposal procedures will be followed. Appropriate quality
E135 Terminology Relating to Analytical Chemistry for
control practices must be followed such as those described in
Metals, Ores, and Related Materials
Guide E882.
6. Interferences
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E01 on
6.1 None of the elements normally found in iron ores
Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials and is the direct
responsibility of Subcommittee E01.02 on Ores, Concentrates, and Related Metal-
interfere.
lurgical Materials.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2011. Published January 2012. Originally
7. Reagents and Materials
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as E878 – 01 (2005).
7.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
DOI: 10.1520/E0878-11.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
all reagents conform to the specifications of the Committee on
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E878–11
hematite require grinding to pass a No. 200 (75-µm) sieve.10.4.
Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society where
3
such specifications are available. Other grades may be used,
10. Procedure
provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficient
high purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of
NO
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E878–01(Reapproved2005) Designation:E878–11
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Titanium in Iron Ores and Related
1
Materials by Diantipyrylmethane Ultraviolet Spectrometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E878; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1This test method covers the determination of titanium in iron ores, concentrates, and agglomerates in the concentration range
from 0.01 to 6.0% titanium.
1.2
1.1 This test method covers the determination of titanium in iron ores, concentrates, and agglomerates in the compositional
range from 0.01 % to 6.0 % titanium.
NOTE 1—As used in this test method (except as related to the term relative standard deviation), percent or “%” refers to mass fraction (wt/wt) of the
form g/100g.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This test method has been evaluated in accordance with Practice E1601 and Guide E1763. Unless otherwise noted in 13,
thelowerlimitinthescopeofeachmethodspecifiesthelowestanalytecontentthatmaybeanalyzedwithacceptableerror(defined
as a nominal 5 % risk of obtaining a 50 % or larger relative difference in results on the same test sample in two laboratories).
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
E50 PracticesforApparatus,Reagents,andSafetyConsiderationsforChemicalAnalysisofMetals,Ores,andRelatedMaterials
E135 Terminology Relating to Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials
E877 Practice for Sampling and Sample Preparation of Iron Ores and Related Materials for Determination of Chemical
Composition
E882 Guide forAccountability and Quality Control in the ChemicalAnalysis Laboratory Guide forAccountability and Quality
Control in the Chemical Analysis Laboratory
E1601 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Evaluate the Performance of an Analytical Method
E1763 Guide for Interpretation and Use of Results from Interlaboratory Testing of Chemical Analysis Methods
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology E135.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The sample is decomposed by treatment with hydrochloric, nitric, and sulfuric acids, or by sintering with sodium peroxide,
or by fusion with sodium tetraborate and sodium carbonate. Iron is reduced in an acid medium with ascorbic acid, the color is
developed with diantipyrylmethane, and the absorbance is measured at approximately 385 nm.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E01 on Analytical Chemistry for Metals, Ores, and Related Materials and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee E01.02 on Ores, Concentrates, and Related Metallurgical Materials.
Current edition approved May 1, 2005. Published June 2005. Originally approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as E878–01. DOI:
10.1520/E0878-01R05.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2011. Published January 2012. Originally approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as E878 – 01 (2005). DOI:
10.1520/E0878-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E878–11
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is intended to be used for compliance with compositional specifications for titanium content. It is assumed
that all who use these procedures will be trained analysts capable of performing common laboratory procedures skillfully and
safely. It is expected that work will be performed in a properly equipped laboratory and that proper waste disposal procedures will
be followed. Appropriate quality control practices must be fol
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.