ASTM D7747/D7747M-11e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Integrity of Seams Produced Using Thermo-Fusion Methods for Reinforced Geomembranes by the Strip Tensile Method
Standard Test Method for Determining Integrity of Seams Produced Using Thermo-Fusion Methods for Reinforced Geomembranes by the Strip Tensile Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The use of reinforced geomembranes as barrier materials has created a need for a standard test method to evaluate the quality of seams produced by thermo-fusion methods. This test method is used for quality control purposes and is intended to provide quality control and quality assurance personnel with data to evaluate seam quality.
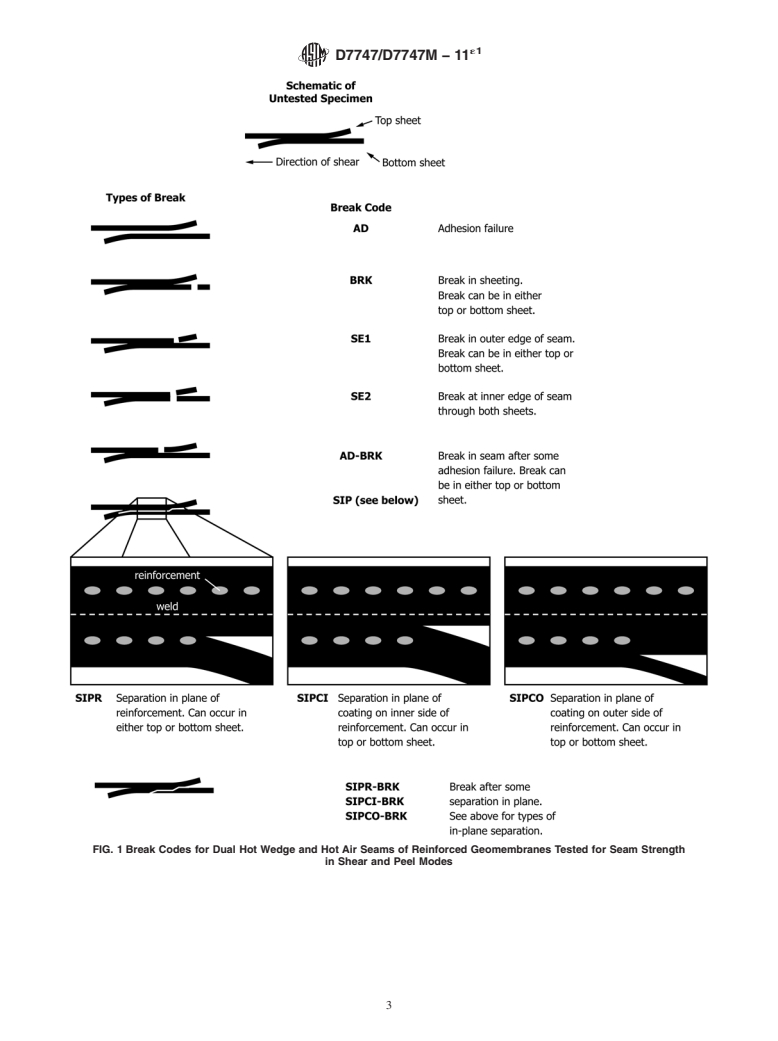
4.2 This standard arose from the need for a destructive test method for evaluating seams of reinforced geomembranes. Standards written for destructive testing of nonreinforced geomembranes do not include all Break Codes (Fig. 1) applicable to reinforced geomembranes.
4.3 When reinforcement occurs in directions other than machine and cross machine, scrim are cut at specimen edges, generally lowering results. To partially compensate for this, testing can be performed according to Test Method D7749, or the 2 in. wide strip specimen specified in this method can be utilized. Testing of 1 in. and 2 in. specimens is Method A and Method B respectively.
4.4 The shear test outlined in this method correlates to strength of parent material measured according to Test Method D7003/D7003M only if reinforcement is parallel to TD. For other materials, seam strength and parent material strength can be compared through Test Methods D7749 and D7004/D7004M. Values obtained with the strip methods shall not be compared to values obtained with grab methods.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes destructive quality control tests used to determine the integrity of thermo-fusion seams made with reinforced geomembranes. Test procedures are described for seam tests for peel and shear properties using strip specimens.
1.2 The types of thermal field and factory seaming techniques used to construct geomembrane seams include the following:
1.2.1 Hot Air—This technique introduces high-temperature air between two geomembrane surfaces to facilitate melting. Pressure is applied to the top or bottom geomembrane, forcing together the two surfaces to form a continuous bond.
1.2.2 Hot Wedge—This technique melts the two geomembrane surfaces to be seamed by running a hot metal wedge between them. Pressure is applied to the top and bottom geomembrane to form a continuous bond. Some seams of this kind are made with dual tracks separated by a non-bonded gap. These seams are sometimes referred to as dual hot wedge seams or double-track seams.
1.2.3 Extrusion—This technique encompasses extruding molten resin between two geomembranes or at the edge of two overlapped geomembranes to effect a continuous bond.
1.2.4 Radio Frequency (RF) or Dielectric—High frequency dielectric equipment is used to generate heat and pressure to form an overlap seam in factory fabrication.
1.2.5 Impulse—Clamping bars heated by wires or a ribbon melts the sheets clamped between them. A cooling period while still clamped allows the polymer to solidify before being released.
1.3 The types of materials covered by this test method include, but are not limited to, reinforced geomembranes made from the following polymers:
1.3.1 Very Low Density Polyethylene (VLDPE).
1.3.2 Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE).
1.3.3 Flexible Polypropylene (fPP).
1.3.4 Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC).
1.3.5 Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE).
1.3.6 Ethylene Interpolymer Alloy (EIA).
1.4 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: D7747/D7747M − 11
Standard Test Method for
Determining Integrity of Seams Produced Using Thermo-
Fusion Methods for Reinforced Geomembranes by the Strip
1
Tensile Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7747/D7747M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Designation was corrected and editorial changes were made throughout in October 2013.
1. Scope 1.3.1 Very Low Density Polyethylene (VLDPE).
1.3.2 Linear Low Density Polyethylene (LLDPE).
1.1 This test method describes destructive quality control
1.3.3 Flexible Polypropylene (fPP).
tests used to determine the integrity of thermo-fusion seams
1.3.4 Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC).
made with reinforced geomembranes. Test procedures are
1.3.5 Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSPE).
described for seam tests for peel and shear properties using
1.3.6 Ethylene Interpolymer Alloy (EIA).
strip specimens.
1.4 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-
1.2 The types of thermal field and factory seaming tech-
pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The
niques used to construct geomembrane seams include the
values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents;
following:
therefore,eachsystemshallbeusedindependentlyoftheother.
1.2.1 Hot Air—This technique introduces high-temperature
Combining values from the two systems may result in non-
air between two geomembrane surfaces to facilitate melting.
conformance with the standard.
Pressure is applied to the top or bottom geomembrane, forcing
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
together the two surfaces to form a continuous bond.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.2.2 Hot Wedge—This technique melts the two geomem-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
brane surfaces to be seamed by running a hot metal wedge
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
between them. Pressure is applied to the top and bottom
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
geomembrane to form a continuous bond. Some seams of this
kind are made with dual tracks separated by a non-bonded gap.
2. Referenced Documents
These seams are sometimes referred to as dual hot wedge
2
seams or double-track seams. 2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.2.3 Extrusion—This technique encompasses extruding
D76/D76M Specification for Tensile Testing Machines for
molten resin between two geomembranes or at the edge of two Textiles
overlapped geomembranes to effect a continuous bond.
D7003/D7003M Test Method for Strip Tensile Properties of
1.2.4 Radio Frequency (RF) or Dielectric—High frequency Reinforced Geomembranes
dielectric equipment is used to generate heat and pressure to
D7004/D7004M Test Method for Grab Tensile Properties of
form an overlap seam in factory fabrication. Reinforced Geomembranes
1.2.5 Impulse—Clamping bars heated by wires or a ribbon
D4439 Terminology for Geosynthetics
meltsthesheetsclampedbetweenthem.Acoolingperiodwhile D7749 Test Method for Determining Integrity of Seams
still clamped allows the polymer to solidify before being
Produced Using Thermo-Fusion Methods for Reinforced
released. Geomembranes by the Grab Method
1.3 The types of materials covered by this test method
3. Terminology
include, but are not limited to, reinforced geomembranes made
3.1 Definitions—Refer to Terminology for Geosynthetics,
from the following polymers:
D4439, for definitions of terms applying to this test method.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D35 on
2
GeosyntheticsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD35.10onGeomem- For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
branes. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2011. Published October 2011. DOI: 10.1520/ Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
D7747_D7747M–11E01. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
D7747/D7747M − 11
4. Significance and Use specimens shall be 25.4 mm [1.00 in.] in the direction parallel
to the seam. For Method B, specimens shall be 50.8 mm [2.00
4.1 The use of reinforced geomembranes as barrier materi-
in.] in the direction parallel to the seam. The seam should be
alshascreatedaneedforastandardtestmethodtoevaluatethe
centered in the specimen.
quality of seams produced by thermo-fusion methods.This test
method is used for qual
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.