ASTM D4582-91(1996)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Calculation and Adjustment of the Stiff and Davis Stability Index for Reverse Osmosis
Standard Practice for Calculation and Adjustment of the Stiff and Davis Stability Index for Reverse Osmosis
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the calculation and adjustment of the Stiff and Davis Stability Index (S & DSI) for the concentrate stream of a reverse osmosis device. This index is used to determine the need for calcium carbonate scale control in the operation and design of reverse osmosis installations. This practice is applicable for concentrate streams containing more than 10 000 mg/L of total dissolved solids. For concentrate streams containing less than 10 000 mg/L of total dissolved solids, refer to Practice D3739.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
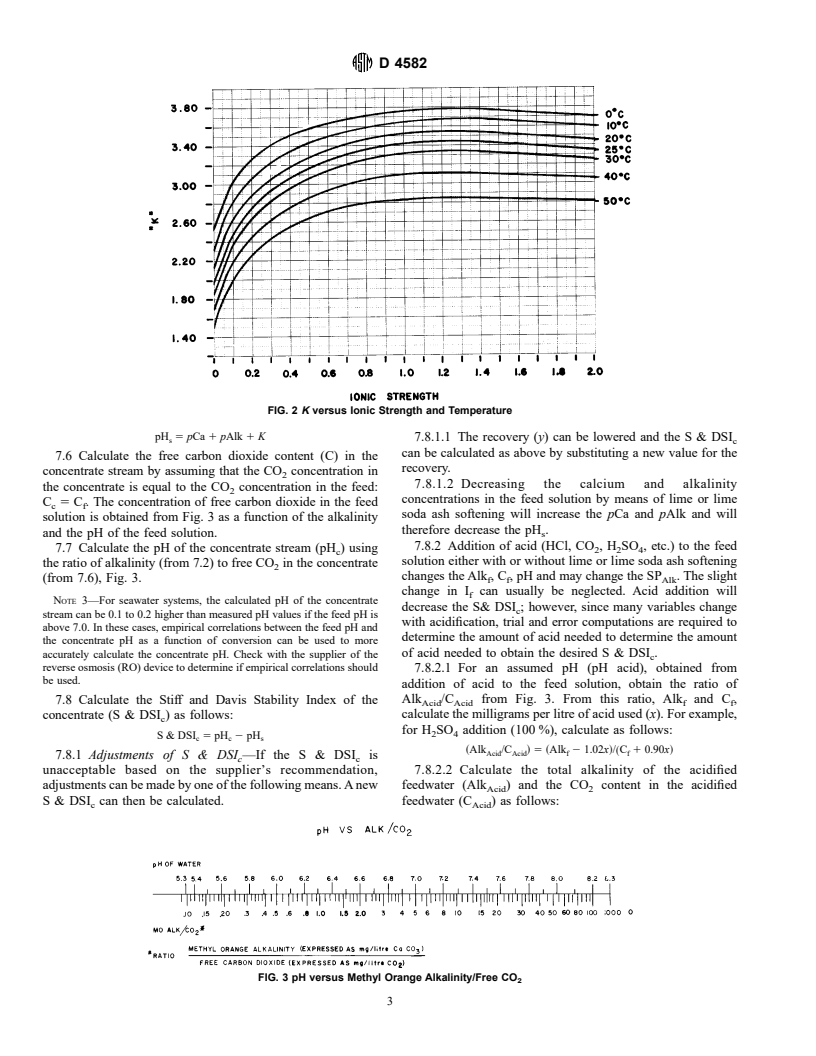
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4582 – 91 (Reapproved 1996)
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Practice for
Calculation and Adjustment of the Stiff and Davis Stability
Index for Reverse Osmosis
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4582; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope refer to Test Methods D 4194.
3.2.2 Stiff and Davis Stability Index (S & DSI) —an index
1.1 This practice covers the calculation and adjustment of
calculated from total dissolved solids, calcium concentration,
the Stiff and Davis Stability Index (S & DSI) for the concen-
total alkalinity, pH, and solution temperature that shows the
trate stream of a reverse osmosis device. This index is used to
tendency of a water solution to precipitate or dissolve calcium
determine the need for calcium carbonate scale control in the
carbonate.
operation and design of reverse osmosis installations. This
practice is applicable for concentrate streams containing more
4. Summary of Practices
than 10 000 mg/L of total dissolved solids. For concentrate
4.1 This practice consists of calculating the S & DSI index
streams containing less than 10 000 mg/L of total dissolved
for a reverse osmosis concentrate stream from the total
solids, refer to Practice D 3739.
dissolved solids, calcium ion content, total alkalinity, pH, and
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
temperature of the feed solution and the recovery of the reverse
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
osmosis system.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.2 This practice also presents techniques to lower the S &
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
DSI by decreasing the recovery; decreasing the calcium and
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
alkalinity concentrations; or by changing the ratio of total
2. Referenced Documents alkalinity to free carbon dioxide in the feedwater.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Significance and Use
D 511 Test Methods for Calcium and Magnesium in Water
5.1 In the design and operation of reverse osmosis installa-
D 1067 Test Methods for Acidity or Alkalinity of Water
tions, it is important to predict the calcium carbonate scaling
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
properties of the concentrate stream. Because of the increase in
D 1293 Test Methods for pH of Water
total dissolved solids in the concentrate stream and the differ-
D 1888 Test Methods for Particulate and Dissolved Matter
ences in salt passages for calcium ion, bicarbonate ion, and free
in Water
CO , the calcium carbonate scaling properties of the concen-
D 3739 Practice for Calculation and Adjustment of Lange-
trate stream will generally be quite different from those of the
lier Saturation Index for Reverse Osmosis
feed solution. This practice permits the calculation of the S &
D 4194 Test Methods for Operating Characteristics of Re-
DSI for the concentrate stream from the feed water analyses
verse Osmosis Devices
and the reverse osmosis operating parameters.
D 4195 Guide for Water Analysis for Reverse Osmosis
5.2 A positive S & DSI indicates the tendency to form a
Application
calcium carbonate scale, which can be damaging to reverse
3. Terminology osmosis performance. This practice gives procedures for the
adjustment of the S & DSI.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in the prac-
tice, refer to Terminology D 1129.
6. Procedure
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
6.1 Determine the calcium concentration in the feed solu-
3.2.1 For description of terms relating to reverse osmosis,
tion in accordance with Test Methods D 511 and express as
CaCO .
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-19 on Water and
6.2 Determine the total dissolved solids of the feed solution
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.08 on Membranes and Ion
using Test Methods D 1888.
Exchange Materials.
Current edition approved June 28, 1991. Published September 1991. Originally
published as D 4582 – 86. Last previous edition D 4582 – 86 (1991).
2 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01. Stiff, H. A. and Davis, L. E., “A Method for Predicting the Tendency of Oil
Discontinued; see 1990 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01. Field Waters to Deposit Calcium Carbonate,” Petroleum Transactions, Vol 195,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.02. 1952.
D 4582
6.3 Determine the total alkalinity of the feed solution using
where:
Test Methods D 1067 and express as CaCO .
Alk 5 alkalinity in concentrate as CaCO , mg/L,
c 3
6.4 Measure the pH of the feed solution using Test Methods
Alk 5 alkalinity in feed as CaCO , mg/L,
f 3
D 1293. y 5 recovery of the reverse osmosis system,
6.5 Measure the temperature of the feed solution. expressed as a decimal, and
SP 5 alkalinity passage, expressed as a decimal.
6.6 Measure the concentration of all major ions using the
Alk
methods cited in Guide D 4195. At a minimum, measure the
NOTE 2—SP may be dependent on the pH of the feed solution, and
++ + + 5 2 Alk
concentration of Mg ,Na ,K , SO , and Cl .
its value should be obtained from the supplier of the specific reverse
osmosis system.
7. Calculation
7.1 Calculate the calcium concentration in the concentrate 7.3 Calculate the ionic strength of the feed stream by:
stream from the calcium concentration in the feed solution, the
I 5 ½ ( m z
f i i
recovery of the reverse osmosis system, and the calcium ion
passage as follows:
where:
I 5 ionic strength of the feed stream,
f
1 2 y~SP !
Ca
Ca 5 Ca 3
m 5 molal concentration of ion, i (moles/1000 g of water)
c f
i
1 2 y
in the feed solution, and
where: z 5 ionic charge of
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.