ASTM D3803-91(2022)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Nuclear-Grade Activated Carbon
Standard Test Method for Nuclear-Grade Activated Carbon
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The results of this test method give a conservative estimate of the performance of nuclear-grade activated carbon used in all nuclear power plant HVAC systems for the removal of radioiodine.
SCOPE
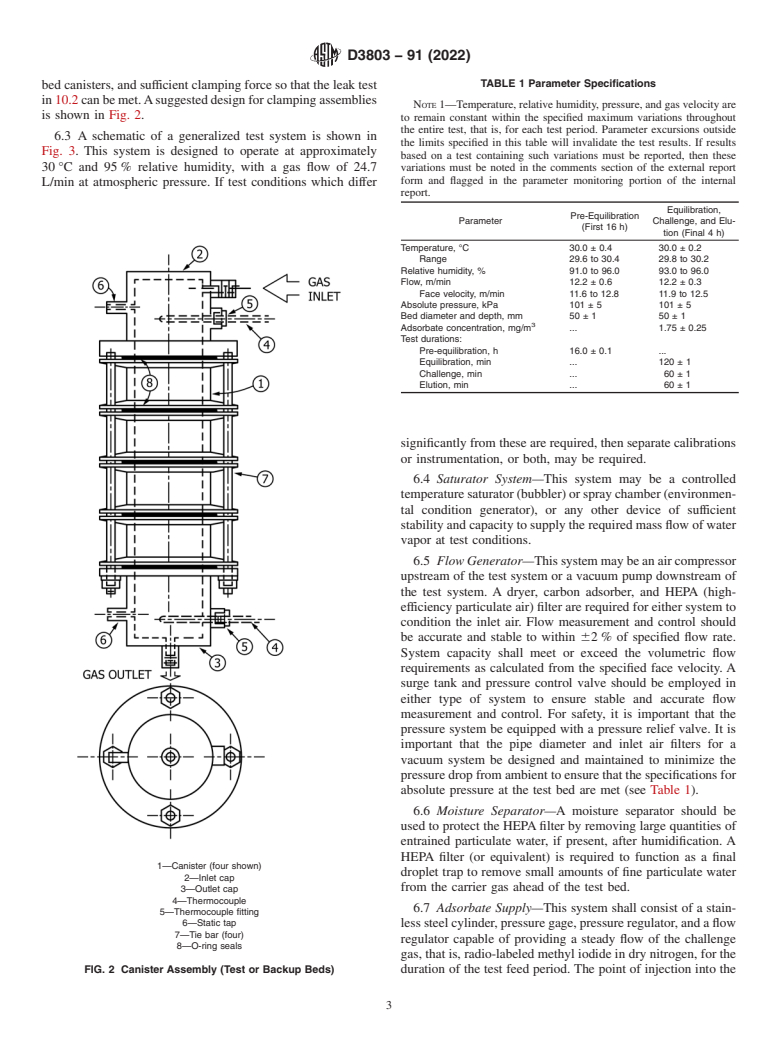
1.1 This test method is a very stringent procedure for establishing the capability of new and used activated carbon to remove radio-labeled methyl iodide from air and gas streams. The single test method described is for application to both new and used carbons, and should give test results comparable to those obtained from similar tests required and performed throughout the world. The conditions employed were selected to approximate operating or accident conditions of a nuclear reactor which would severely reduce the performance of activated carbons. Increasing the temperature at which this test is performed generally increases the removal efficiency of the carbon by increasing the rate of chemical and physical absorption and isotopic exchange, that is, increasing the kinetics of the radioiodine removal mechanisms. Decreasing the relative humidity of the test generally increases the efficiency of methyl iodide removal by activated carbon. The water vapor competes with the methyl iodide for adsorption sites on the carbon, and as the amount of water vapor decreases with lower specified relative humidities, the easier it is for the methyl iodide to be adsorbed. Therefore, this test method is a very stringent test of nuclear-grade activated carbon because of the low temperature and high relative humidity specified. This test method is recommended for the qualification of new carbons and the quantification of the degradation of used carbons.
1.1.1 Guidance for testing new and used carbons using conditions different from this test method is offered in Annex A1.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D3803 − 91 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Test Method for
1
Nuclear-Grade Activated Carbon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3803; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This test method is a very stringent procedure for
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
establishing the capability of new and used activated carbon to
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
remove radio-labeled methyl iodide from air and gas streams.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Thesingletestmethoddescribedisforapplicationtobothnew
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
and used carbons, and should give test results comparable to
those obtained from similar tests required and performed
2. Referenced Documents
throughout the world. The conditions employed were selected
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
to approximate operating or accident conditions of a nuclear
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
reactor which would severely reduce the performance of
D2652Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
activatedcarbons.Increasingthetemperatureatwhichthistest
D2854Test Method for Apparent Density of Activated
is performed generally increases the removal efficiency of the
Carbon
carbon by increasing the rate of chemical and physical absorp-
E300Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
tion and isotopic exchange, that is, increasing the kinetics of
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
the radioiodine removal mechanisms. Decreasing the relative
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
humidityofthetestgenerallyincreasestheefficiencyofmethyl
2.2 Code of Federal Regulations:
iodideremovalbyactivatedcarbon.Thewatervaporcompetes
CFR Title 49,Section 173.34, “Qualification, Maintenance,
with the methyl iodide for adsorption sites on the carbon, and
3
and Use of Cylinders’’
as the amount of water vapor decreases with lower specified
CFR Title 49,Part 178, Subpart C, “Specifications for
relative humidities, the easier it is for the methyl iodide to be
3
Cylinders’’
adsorbed.Therefore, this test method is a very stringent test of
2.3 Military Standards:
nuclear-grade activated carbon because of the low temperature
MIL-F-51068D Filter, Particulate High Efficiency, Fire
and high relative humidity specified. This test method is
4
Resistant
recommended for the qualification of new carbons and the
MIL-F-51079A Filter, Medium Fire Resistant, High Effi-
quantification of the degradation of used carbons.
4
ciency
1.1.1 Guidance for testing new and used carbons using
4
MIL-STD-45662 Calibration Systems Requirements
conditions different from this test method is offered in Annex
2.4 Other Standards:
A1.
ANSI/ASME N45.2.6 Qualifications of Inspection,
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Examination, and Testing Personnel for Nuclear Power
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this 5
Plants
standard.
3. Terminology
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3
Published by the General Service Administration, 18th and “F”’ St., N. W.,
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D28 on Washington, DC 20405.
4
Activated Carbon and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D28.04 on Gas Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
Phase Evaluation Tests. Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2022. Published October 2022. Originally dodssp.daps.dla.mil.
5
approved in 1979. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as D3803–91 (2014). Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
DOI: 10.1520/D3803-91R22. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.