ASTM E720-94
(Guide)Standard Guide for Selection and Use of Neutron-Activation Foils for Determining Neutron Spectra Employed in Radiation-Hardness Testing of Electronics
Standard Guide for Selection and Use of Neutron-Activation Foils for Determining Neutron Spectra Employed in Radiation-Hardness Testing of Electronics
SCOPE
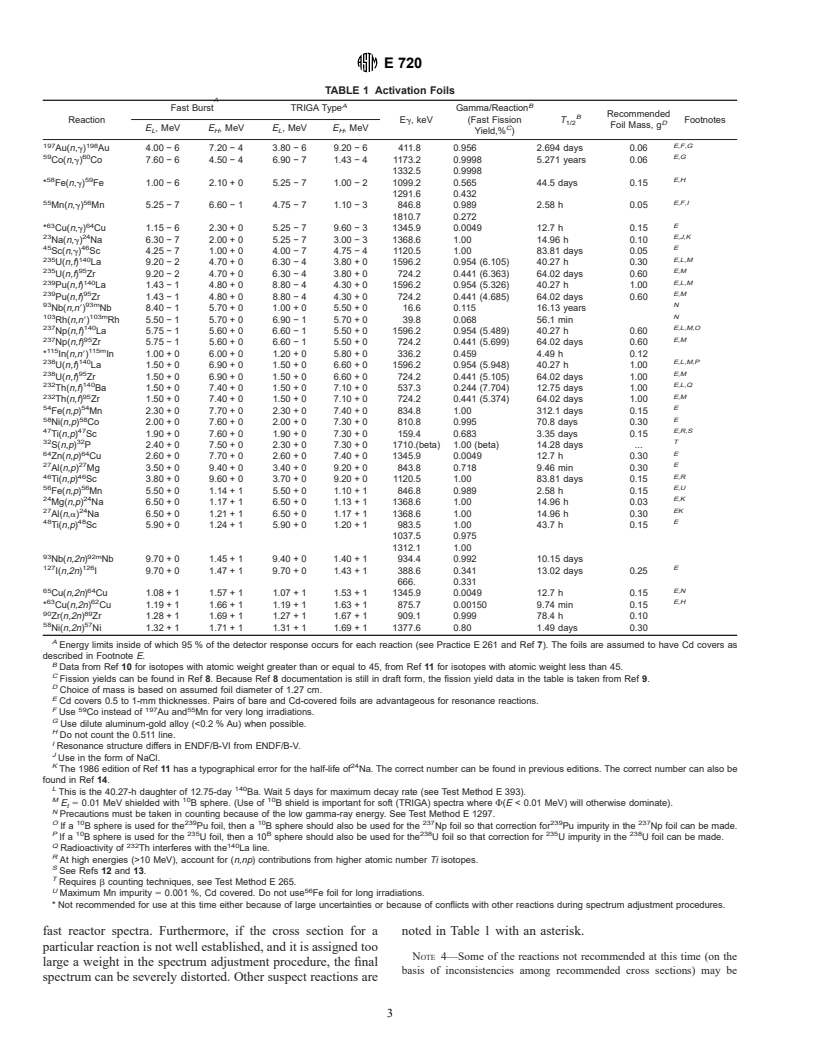
1.1 This guide covers the selection and use of neutron-activation detector materials to be employed in neutron spectra adjustment techniques used for radiation-hardness testing of electronic semiconductor devices. Foils are described that have been used at many radiation hardness-testing facilities, and comments are offered in table footnotes concerning the appropriateness of each reaction as judged by its cross-section accuracy, ease of use as an activation foil, and by past successful application. This guide also discusses the fluence-uniformity, neutron self-shielding, and fluence-depression corrections that need to be considered in choosing the foil thickness, the foil covers, and the foil locations. These considerations are relevant for the determination of neutron spectra from assemblies such as TRIGA- and Godiva-type reactors and from Californium irradiators. This guide may also be applicable to other broad energy distribution sources up to 20 MeV. Note 1-For definitions on terminology used in this guide, see Terminology E170.
1.2 This guide also covers the measurement of the gamma-ray or beta-ray emission rates from the activation foils and the calculation of the absolute specific activities of these foils. The principal measurement technique is high-resolution gamma-ray spectrometry. The activities are used in the determination of the energy-fluence spectrum of the neutron source. See Guide E721.
1.3 Details of measurement and analysis are covered as follows:
1.3.1 Corrections involved in measuring the foil activities include those for finite foil size and thickness in the calibration of the gamma-ray detector, for pulse-height analyzer deadtime and pulse-pileup losses, and for background radioactivity.
1.3.2 The primary method for detector calibration that uses secondary standard gamma-ray emitting sources is considered in this guide and in General Methods E181. In addition, an alternative method in which the foils are activated in the known spectrum of a benchmark neutron field is discussed in Guide E1018.
1.3.3 A data analysis method is presented which accounts for the following:detector efficiency; background subtraction; irradiation, waiting, and counting times; fission yields and gamma-ray branching ratios; and self-absorption of gamma rays and neutrons in the foils.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: E 720 – 94
Standard Guide for
Selection and Use of Neutron-Activation Foils for
Determining Neutron Spectra Employed in Radiation-
1
Hardness Testing of Electronics
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 720; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope in this guide and in General Methods E 181. In addition, an
alternative method in which the foils are activated in the known
1.1 This guide covers the selection and use of neutron-
spectrum of a benchmark neutron field is discussed in Guide
activation detector materials to be employed in neutron spectra
E 1018.
adjustment techniques used for radiation-hardness testing of
1.3.3 A data analysis method is presented which accounts
electronic semiconductor devices. Foils are described that have
for the following: detector efficiency; background subtraction;
been used at many radiation hardness-testing facilities, and
irradiation, waiting, and counting times; fission yields and
comments are offered in table footnotes concerning the appro-
gamma-ray branching ratios; and self-absorption of gamma
priateness of each reaction as judged by its cross-section
rays and neutrons in the foils.
accuracy, ease of use as an activation foil, and by past
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
successful application. This guide also discusses the fluence-
standard.
uniformity, neutron self-shielding, and fluence-depression cor-
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
rections that need to be considered in choosing the foil
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
thickness, the foil covers, and the foil locations. These consid-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
erations are relevant for the determination of neutron spectra
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
from assemblies such as TRIGA- and Godiva-type reactors and
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
from Californium irradiators. This guide may also be appli-
cable to other broad energy distribution sources up to 20 MeV.
2. Referenced Documents
NOTE 1—For definitions on terminology used in this guide, see Termi-
2.1 General considerations of neutron-activation detectors
nology E 170.
discussed in Practice E 261, Test Method E 262, and Guides
1.2 This guide also covers the measurement of the gamma-
E 721 and E 844 are applicable to this guide. Background
ray or beta-ray emission rates from the activation foils and the
information for applying this guide are given in these and other
calculation of the absolute specific activities of these foils. The
relevant standards as follows:
principal measurement technique is high-resolution gamma-
2.2 ASTM Standards:
ray spectrometry. The activities are used in the determination
E 170 Terminology Relating to Radiation Measurements
2
of the energy-fluence spectrum of the neutron source. See
and Dosimetry
Guide E 721.
E 181 Test Methods for Detector Calibration and Analysis
2
1.3 Details of measurement and analysis are covered as
of Radionuclides
follows:
E 261 Practice for Determining Neutron Fluence Rate, Flu-
2
1.3.1 Corrections involved in measuring the foil activities
ence, and Spectra by Radioactivation Techniques
include those for finite foil size and thickness in the calibration
E 262 Test Method for Determining Thermal Neutron Re-
2
of the gamma-ray detector, for pulse-height analyzer deadtime
action and Fluence Rates by Radioactivation Techniques
and pulse-pileup losses, and for background radioactivity.
E 263 Test Method for Measuring Fast-Neutron Reaction
2
1.3.2 The primary method for detector calibration that uses
Rates by Radioactivation of Iron
secondary standard gamma-ray emitting sources is considered
E 264 Test Method for Measuring Fast-Neutron Reaction
2
Rates by Radioactivation of Nickel
E 265 Test Method for Measuring Reaction Rates and
2
1
Fast-Neutron Fluences by Radioactivation of Sulfur-32
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E-10 on Nuclear
Technology and Applications and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
E 266 Test Method for Measuring Fast-Neutron Reaction
E10.07 on Radiation Effects on Electronic Materials and Devices and Pulsed 2
Rates by Radioactivation of Aluminum
Radiation Effects.
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 1994. Published November 1994. Originally
2
published as E 720 – 80. Last previous edition E 720 – 93. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 12.02.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E 720
E 343 Test Method for Measuring Reac
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.