ASTM C283-97(2002)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Resistance of Porcelain Enameled Utensils to Boiling Acid
Standard Test Method for Resistance of Porcelain Enameled Utensils to Boiling Acid
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Test Method A provides the producers of porcelain enameled utensils with a quality control method of testing for resistance to boiling acid for parts randomly selected from the production line.
Test Method B provides the supplier of porcelain enamel raw materials with a laboratory method for testing the resistance of different coatings (intended for use on utensils) to boiling acid.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the resistance of porcelain enamel coatings used on utensils to attack by boiling acid.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:C283–97 (Reapproved 2002)
Standard Test Methods for
Resistance of Porcelain Enameled Utensils to Boiling
Acid
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 283; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
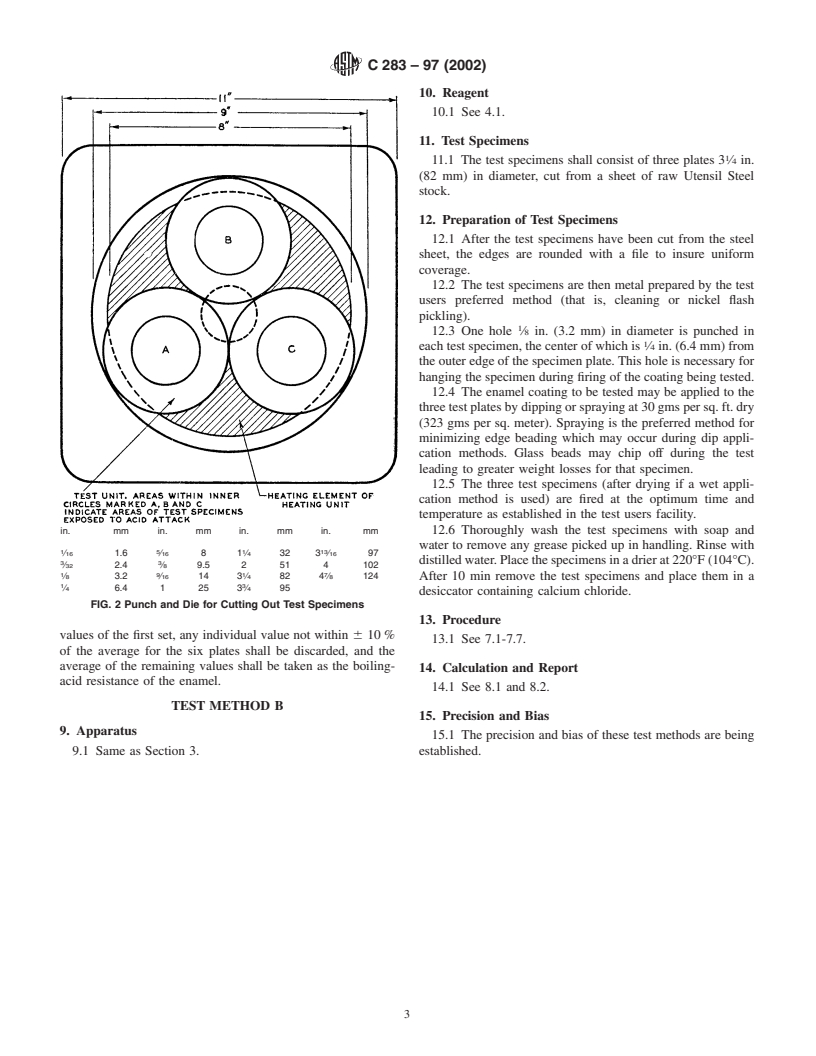
1. Scope 3.5 Cutting Equipment, suitable for cutting a 3 ⁄4-in. (82-
mm) diameter plate from the bottom of a porcelain-enameled
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the
steel utensil, as follows:
resistance of porcelain enamel coatings used on utensils to
3.5.1 Punch and Die (Fig. 2),
attack by boiling acid.
3.5.2 Shears,
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.5.3 Abrasive Cut-off Wheel,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.5.4 Cutting Torch,or
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.5.5 Any Other Suitable Equipment
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.6 Analytical Balance, having a sensitivity of 0.0001 g.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4. Reagent
2. Significance and Use
4.1 The test solution shall contain6gofACS grade citric
2.1 Test Method A provides the producers of porcelain
acid per 94 g of distilled water and shall be prepared fresh for
enameled utensils with a quality control method of testing for
each test.
resistance to boiling acid for parts randomly selected from the
production line.
5. Test Specimens
2.2 Test Method B provides the supplier of porcelain
5.1 The test specimens shall consist of three plates, 3 ⁄4 in.
enamel raw materials with a laboratory method for testing the
(82 mm) in diameter, cut from the bottoms of three identical
resistance of different coatings (intended for use on utensils) to
utensils.
boiling acid.
NOTE 1—“Identical utensils” signifies utensils of the same size, shape,
TEST METHOD A
and finish.
3. Apparatus
6. Preparation of Test Specimens
3.1 Hot Plate, capable of maintaining over its entire surface
6.1 After the test specimens have been cut from the utensils,
a uniform temperature that will keep the test solution at a
file their edges with a triangular file to remove any loose
rolling boil (see section 7.5). The heating element should
enamel chips.
occupy an area at least 8 in. (203 mm) in diameter.
6.2 Thoroughly wash the test specimens with soap and
3.2 Chemical Glassware—Beakers, a desiccator, and a
water to remove any grease picked up in handling. Rinse with
500-mL graduated cylinder.
distilledwater.Placethespecimensinadrierat220°F(104°C).
3.3 Drier, capable of maintaining a temperature of at least
After 10 min, remove the test specimens and place them in a
220°F (104°C).
desiccator containing calcium chloride.
3.4 Boiling Acid Resistance Apparatus, as shown in Fig. 1.
7. Procedure
Three sets will be required.
7.1 Level the hot plate, turn the switch on in the high heat
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B08 on position, and allow to preheat for at least 1 h to obtain a
Metallic and Inorganic Coatings and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
uniform temperature over the entire heating element.
B08.12 on Materials for Porcelain Enamel and Ceramic-Metal Systems.
7.2 Remove the test specimens, one at a time, from the
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1997. Published March 1998. Originally
desiccator, hold at the edges, and inspect the edges for loose
published as C283 – 51. Last previous edition C283 – 54 (1993).
Test Method A is based on the boiling acid resistance test developed by the
chips. Remove any chips found, before the initial weighing.
Enameled Utensil Manufacturers’ Council; see Section 16 of Commercial Standard
7.3 Weigh each specimen on an analytical balance, record-
CS100-47, Porcelain Enameled Steel Utensils, United States Department of Com-
ing its weight to the nearest 0.0001 g.
merce.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C283–97 (2002)
in. mm in. mm in. mm in. mm
1 1 1
⁄16 1.6 1 ⁄4 32 2.5 64 4 ⁄16 103
1 25 1 1
⁄8 3.2 1 ⁄32 45 3 ⁄4 82 4 ⁄8 105
1 1 3 1
⁄4 6.4 2 ⁄4 57 3 ⁄8 86 5 ⁄2 140
⁄8 9.5 2.31 59 4 102 14 356
(a) Assembly (b) Details
FIG. 1 Boiling-Acid Resistance Apparatus
7.4 Place the heat-resistant gasket above the hole in the then rinse the insides of the tubes and the test specimens with
base-plate of the boiling-acid resistance apparatus (Fig. 1). distilled water, and dismantle the apparatus. Remove the test
Place the test specimen over the gasket, with the surface from specimens, rinse again with distilled water scrub the test
the inside of the utensil up. Next, place a rubber jar ring on the specimens gently with a nylon brush (10 to 12 strokes) to
test specimen. This serves as a seal between the test specimen remove loose residue in the attack area, and dry in the drier at
and the heat-resistant glass tube, which shall be placed over it. 220°F (104°C) for 10 min. Place the specimens in a desiccator
Place another rubber jar ring on top of the glass tube, set the and cool to room temperature.
cover-plate on it, and clamp in place by t
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.