ASTM A848-01(2011)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Low-Carbon Magnetic Iron
Standard Specification for Low-Carbon Magnetic Iron
ABSTRACT
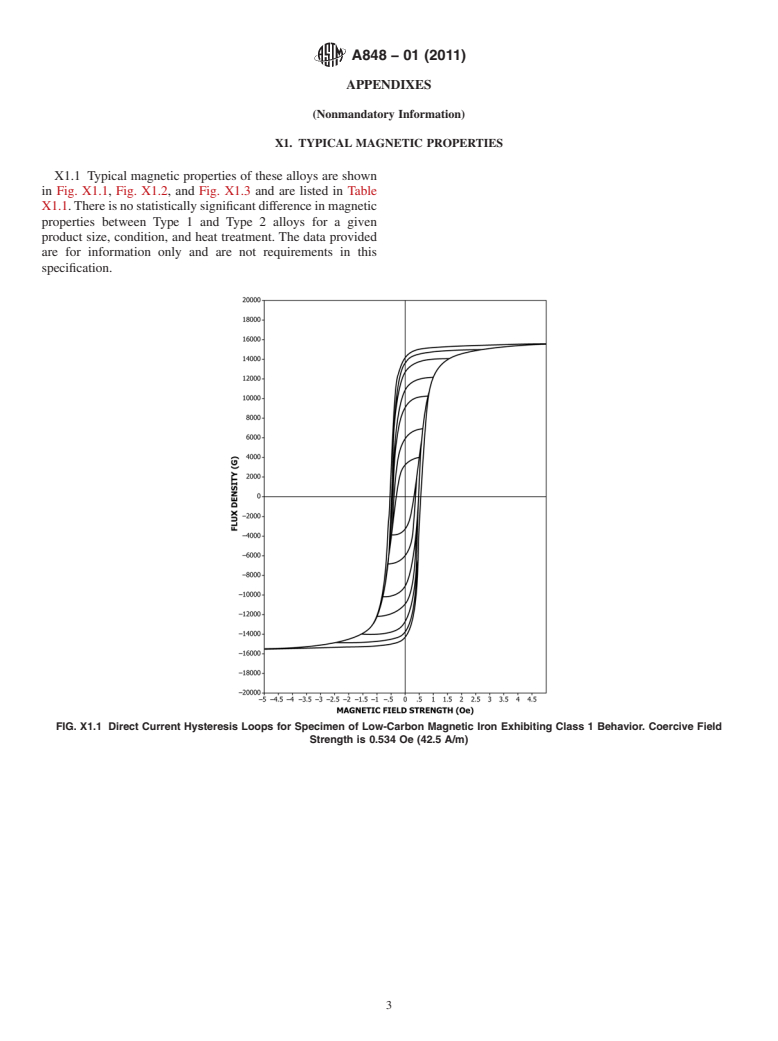
This specification covers the standard requirements for wrought low-carbon iron having a carbon content of 0.015% or less with the remainder of the analysis being substantially iron. These alloys are not electrical steels such as are described in Specifications A 726 and A 840 but are instead primarily used in dc magnetic applications and are produced in a wide variety of mill forms such as forging billet and cold finished bar and wire as well as strip. Two alloy types are covered: Type 1 is a low-phosphorus grade and Type 2 contains a phosphorus addition to improve machinability. Apart from chemical requirements, alloy produced to this specification must exhibit guaranteed maximum values of coercive field strength when heat treated according to this specification. This specification has several useful appendices dealing with typical magnetic, physical and mechanical properties, heat treatment and magnetic aging.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for wrought low-carbon iron having a carbon content of 0.015 % or less with the remainder of the analysis being substantially iron.
1.1.1 Two alloy types are covered: Type 1 is a low-phosphorous grade and Type 2 contains a phosphorous addition to improve machinability.
1.2 This specification also covers alloys supplied by a producer or converter in the form and condition suitable for fabrication into parts which will be subsequently heat treated to create the desired magnetic characteristics. It covers alloys supplied in the form of forging billets, hot-rolled products, and cold-finished bar, wire, and strip.
1.3 This specification does not cover iron powders capable of being processed into magnetic components.
1.4 This specification does not cover flat-rolled, low-carbon electrical steels.
1.5 The values stated in customary (cgs-emu and inch-pound) units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units which are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A848 −01 (Reapproved 2011)
Standard Specification for
1
Low-Carbon Magnetic Iron
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A848; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope A773/A773MTest Method for Direct Current Magnetic
Properties of Low Coercivity Magnetic Materials Using
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for wrought
Hysteresigraphs
low-carbon iron having a carbon content of 0.015% or less
2.2 Other:
with the remainder of the analysis being substantially iron.
IEC Publication 60404-7 Ed. 1Method of Measurement of
1.1.1 Two alloy types are covered: Type 1 is a low-
theCoercivityofMagneticMaterialsinanOpenMagnetic
phosphorousgradeandType2containsaphosphorousaddition
3
Circuit
to improve machinability.
1.2 This specification also covers alloys supplied by a
3. Ordering Information
producer or converter in the form and condition suitable for
3.1 Orders to this specification shall include as much of the
fabricationintopartswhichwillbesubsequentlyheattreatedto
following information as is required to describe the desired
create the desired magnetic characteristics. It covers alloys
material:
suppliedintheformofforgingbillets,hot-rolledproducts,and
3.1.1 ASTM specification number and alloy type.
cold-finished bar, wire, and strip.
3.1.2 Dimensions and Tolerances—The tolerances are to be
1.3 This specification does not cover iron powders capable mutually agreed upon between the user and the producer.
of being processed into magnetic components. 3.1.3 Quantity (weight or number of pieces).
3.1.4 Form and condition.
1.4 This specification does not cover flat-rolled, low-carbon
3.1.5 Magnetic property requirements if they are other than
electrical steels.
stated herein.
1.5 The values stated in customary (cgs-emu and inch-
3.1.6 Certification of chemical analysis or magnetic prop-
pound) units are to be regarded as standard. The values given
erty evaluation, or both.
in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units which
3.1.7 Marking and packaging.
are provided for information only and are not considered
3.1.8 EndUse—Whenever possible, the user should specify
standard.
whethertheproductwillbemachined,blankedintoflatpieces,
blanked and formed, or deep drawn to shape.This information
2. Referenced Documents
willhelptheproducerprovidethemostsuitableproductforthe
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
user’s fabrication practice.
A34/A34MPractice for Sampling and Procurement Testing
3.1.9 Exceptions to this specification or special require-
of Magnetic Materials
ments.
A341/A341MTest Method for Direct Current Magnetic
Properties of Materials Using D-C Permeameters and the 4. Chemical Composition
Ballistic Test Methods
4.1 Alloyssuppliedtothisspecificationshallconformtothe
A596/A596MTest Method for Direct-Current Magnetic
requirements in Table 1. Three of the elements listed in Table
Properties of Materials Using the Ballistic Method and
1, namely vanadium, titanium, and aluminum, are not required
Ring Specimens
but may be added to suppress magnetic aging. If present, they
must be analyzed and reported.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A06 on
5. Form and Condition
Magnetic Properties and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A06.02 on
Material Specifications.
5.1 These two alloys are capable of being produced in a
Current edition approved May 1, 2011. Published May 2011. Originally
wide variety of forms and conditions for fabrication into
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as A848–01 (2006).
DOI: 10.1520/A0848-01R11. magneticcomponents.Thedesiredformandconditionshallbe
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from American National Standards Institute, 25 W. 43rd St., 4th
the ASTM website. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A848−01 (2011)
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements (Weight Percent)
shape from the product, specimen shape and size shall be
Alloy Type 1 Alloy Type 2 mutually agreed upon by the user and the producer.
Carbon, max 0.020 0.020
6.3 Heat Treatment—It is recommended that the user
Manganese, max 0.35 0.35
specify the desired heat treatment method to be applied to the
Silicon, max 0.15 0.15
Phosphorous 0.030 max 0.10/0.18
test specimens.
Sulfur, max 0.025 0.025
6
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.