ASTM D8083-16(2023)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Total Nitrogen, and Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) by Calculation, in Water by High Temperature Catalytic Combustion and Chemiluminescence Detection
Standard Test Method for Total Nitrogen, and Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) by Calculation, in Water by High Temperature Catalytic Combustion and Chemiluminescence Detection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is used for determination of the total or dissolved nitrogen content of water from a variety of natural, domestic, and industrial sources. In its most common form, this test method is used to measure nitrogen as a means of monitoring nutrient pollutant in industrial wastewater, domestic wastewater, and ambient water. These measurements may also be used in monitoring waste treatment processes.
5.2 This test method measures oxidized ammonia and organic nitrogen (as nitrate) and soluble nitrate simultaneously, subtracting the nitrate + nitrite value from a non-digested sample gives total Kjeldhal nitrogen (TKN).
When using this test method:
where:
TN = total nitrogen, and TKN = total Kjeldahl nitrogen.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total nitrogen (TN) and total dissolved nitrogen (TDN) in surface water, seawater, groundwater, wastewater, and wastewater effluents in the range from 0.2 mg/L N to 10 mg/L N. Concentrations from 10 mg/L to 500 mg/L are possible when used in conjunction with manual or automatic dilution, or automatic injection of less sample volume. The EPA 40 CFR Part 136 Appendix B Method Detection Limit (MDL) is 0.05 mg/L N. Higher concentrations may be determined by sample dilution. Lower concentrations may be possible by injecting larger sample volumes. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
1.2 The sample is injected onto a platinum catalyst heated at ≥720 °C. The sample converts into a gaseous phase and is forced through a layer of catalyst ensuring conversion of all nitrogen containing compounds to nitrogen oxide (NO). Reaction with ozone converts the NO to an exited NO2. As the excited NO2 returns to the ground state, it emits radiation that is measured photo-electrically.
1.3 Total and dissolved organic carbon analysis by Test Method D7573 can be analyzed at the same time on the same sample simultaneously using a properly equipped analyzer. (See Appendix X1 for an example of simultaneous TOC data.)
1.4 This test method quantitatively recovers nitrogen from a large range of organic and inorganic nitrogen compounds (see Table 1 and Table 2). The test method does not measure nitrogen gas (N2). It is the user's responsibility to ensure the validity of this test method for waters of untested matrices.
1.5 This test method is applicable only to nitrogenous matter in the sample that can be introduced into the reaction zone. The syringe needle or injector opening size generally limits the maximum size of particles that can be so introduced. Optional automatic sample homogenization may be used.
1.6 This test method is performance based. You may make modifications that improve the test method’s performance but do not change the oxidation or detection technique.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D8083 − 16 (Reapproved 2023)
Standard Test Method for
Total Nitrogen, and Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen (TKN) by
Calculation, in Water by High Temperature Catalytic
Combustion and Chemiluminescence Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D8083; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope limits the maximum size of particles that can be so introduced.
Optional automatic sample homogenization may be used.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of total
1.6 This test method is performance based. You may make
nitrogen (TN) and total dissolved nitrogen (TDN) in surface
modifications that improve the test method’s performance but
water, seawater, groundwater, wastewater, and wastewater
do not change the oxidation or detection technique.
effluents in the range from 0.2 mg ⁄L N to 10 mg ⁄L N.
Concentrations from 10 mg ⁄L to 500 mg ⁄L are possible when
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
used in conjunction with manual or automatic dilution, or
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
automatic injection of less sample volume. The EPA 40 CFR
standard.
Part 136 Appendix B Method Detection Limit (MDL) is
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
0.05 mg ⁄L N. Higher concentrations may be determined by
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
sample dilution. Lower concentrations may be possible by
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
injecting larger sample volumes. Follow the manufacturer’s
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
instructions.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.2 The sample is injected onto a platinum catalyst heated at
1.9 This international standard was developed in accor-
≥720 °C. The sample converts into a gaseous phase and is
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
forced through a layer of catalyst ensuring conversion of all
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
nitrogen containing compounds to nitrogen oxide (NO). Reac-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
tion with ozone converts the NO to an exited NO . As the
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
excited NO returns to the ground state, it emits radiation that Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
is measured photo-electrically.
2. Referenced Documents
1.3 Total and dissolved organic carbon analysis by Test
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Method D7573 can be analyzed at the same time on the same
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
sample simultaneously using a properly equipped analyzer.
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
(See Appendix X1 for an example of simultaneous TOC data.)
D1426 Test Methods for Ammonia Nitrogen In Water
1.4 This test method quantitatively recovers nitrogen from a
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
large range of organic and inorganic nitrogen compounds (see
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
Table 1 and Table 2). The test method does not measure
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Flowing Process
nitrogen gas (N ). It is the user’s responsibility to ensure the
Streams
validity of this test method for waters of untested matrices.
D3590 Test Methods for Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen in Water
1.5 This test method is applicable only to nitrogenous D3867 Test Methods for Nitrite-Nitrate in Water
matter in the sample that can be introduced into the reaction D4327 Test Method for Anions in Water by Suppressed Ion
zone. The syringe needle or injector opening size generally Chromatography
D4448 Guide for Sampling Ground-Water Monitoring Wells
D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.06 on Methods for Analysis for
Organic Substances in Water. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2023. Published February 2023. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2016. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D8083 – 16. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D8083-16R23. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D8083 − 16 (2023)
TABLE 1 Nitrogen Recoveries from Various Compounds in
3.2.2 dissolved nitrogen (DN), n—nitrogen determined in a
Presence of Organic Carbon
filtered sample.
Compound Nitrogen ppm Carbon
3.2.3 dissolved organic nitrogen (DON), n—organic nitro-
Potassium Nitrate (100 ppm N) 100 % 0
gen determined in a filtered sample.
Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (0 ppm) ND 100
Acetonitrile (58.6 ppm N) 104 % 100
3.2.4 particulate nitrogen (PN), n—nitrogen bound to par-
Caffeine (58.9 ppm N) 90 % 100
ticulate materials that do not pass through a filter.
Nicotinic Acid (20 ppm N) 99 % 100
Urea (233 ppm) 91 % 100
3.2.5 refractory material, n—that which cannot be com-
Nicotinic Acid (100 ppm N) 97 % 98 %
pletely oxidized under the test method conditions.
3.2.6 total inorganic nitrogen (TIN), n—nitrogen in the form
TABLE 2 Nitrogen Recoveries for a Range of Nitrogen Sources of ammonium ion, nitrite ion, or nitrate ion.
Compound TN (mg/L) Recovery (%)
3.2.7 total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN), n—the sum of nitrogen
Ammonium Chloride 0.01 102
contained in free ammonia and other nitrogen compounds
Ammonium Sulfate 2 102
which are converted to ammonium sulfate [(NH ) SO ] under
4 2 4
Ammonium Sulfate 100 100
the conditions of Test Method D3590.
Aniline 0.014 101
Arginine 0.007 99
3.2.8 total nitrogen (TN), n—the sum of TIN and TON.
Calcium Nitrate 10 99
Glutamic Acid 0.013 98
3.2.9 total organic nitrogen (TON), n—nitrogen in the form
Glycine 0.016 103
of organic compounds.
L-glutamic Acid 2 102
1,6-Hexanediamine 50 101
Imidazole 0.011 100
4. Summary of Test Method
Nitro aniline 50 100
Nitro phenol 50 102 4.1 Fundamentals—Nitrogen can occur in water as inor-
Potassium Nitrate 10 99
ganic or organic compounds, or both. This test method can be
Potassium Nitrate 0.009 99
used to measure TN, and can also determine TON by the
Potassium Nitrate 50 105
Proline 0.01 99 difference of TN and TIN measured by other methods, such as
RNA 0.018 103
Test Method D4327 plus Test Method D6919, Test Method
Sodium Nitrite 0.009 101
D1426 plus Test Method D7781, or Test Methods D1426 plus
Tri-peptide (Glu-Cys-Gly) 0.014 99
Tryptophan 0.009 103 Test Method D3867. DON is determined on samples that have
Urea 0.013 99
been filtered through a quartz fiber filter.
4.2 TON and DON procedures require that samples have
been preserved with acid before it is analyzed for organic
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
nitrogen content.
D6089 Guide for Documenting a Groundwater Sampling
4.3 TN minus nitrate nitrite nitrogen is equivalent to TKN in
Event
most samples.
D6538 Guide for Sampling Wastewater With Automatic
Samplers
5. Significance and Use
D6759 Practice for Sampling Liquids Using Grab and Dis-
crete Depth Samplers
5.1 This test method is used for determination of the total or
D6919 Test Method for Determination of Dissolved Alkali
dissolved nitrogen content of water from a variety of natural,
and Alkaline Earth Cations and Ammonium in Water and
domestic, and industrial sources. In its most common form, this
Wastewater by Ion Chromatography
test method is used to measure nitrogen as a means of
D7573 Test Method for Total Carbon and Organic Carbon in
monitoring nutrient pollutant in industrial wastewater, domes-
Water by High Temperature Catalytic Combustion and
tic wastewater, and ambient water. These measurements may
Infrared Detection
also be used in monitoring waste treatment processes.
D7781 Test Method for Nitrite-Nitrate in Water by Nitrate
5.2 This test method measures oxidized ammonia and or-
Reductase (Withdrawn 2023)
ganic nitrogen (as nitrate) and soluble nitrate simultaneously,
subtracting the nitrate + nitrite value from a non-digested
3. Terminology
sample gives total Kjeldhal nitrogen (TKN).
3.1 Definitions:
TN 5 TKN1 NO 2 N 1 NO 2 N
~ ! ~ !
3 2
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to
TKN 5 NH 2 N1Organic N
Terminology D1129. 3
When using this test method:
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN), n—nitrogen in the
TN 5 Digested Sample 2 Non-Digested Sample
form of ammonium, nitrate ion, or nitrite ion determined in a
TKN 5 TN 2 @NO 2 N 1 NO 2 N#
3 2
filtered sample.
where:
TN = total nitrogen, and
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.ast-
TKN = total Kjeldahl nitrogen.
m.org.
D8083 − 16 (2023)
6. Interferences 7.2.2 Ozone Generator, converts NO gas emerging from the
combustion chamber to NO .
6.1 The conversion of dissolved inorganic and organic
7.2.3 Detector—The excited NO in the gas stream relaxing
nitrogen to NO is brought about at high temperatures
to ground state NO is detected by a NO -specific chemilumi-
2 2
(≥720 °C) in the presence of oxygen. A catalyst promotes the
nescence detector.
process and the resulting nitrogen oxide is converted by ozone
7.2.4 Detector Response—Area integration accurately quan-
to nitrogen dioxide (NO ). The NO is measured by a chemi-
2 2
tifies nitrogen content in the event of split or overlapping peaks
luminescence detector. Suspended and refractory materials are
that result from furnace cooling or variable combustion rates of
completely oxidized under these conditions.
different organic molecules contained in a sample.
6.2 Acid preservation minimizes interference that can cause
7.2.5 Presentation of Results—The detector output is related
results to be low.
to stored calibration data and then displayed as milligrams of
6.3 Total organic carbon (TOC) up to 300 mg/L does not nitrogen per litre.
interfere. Dissolved salts up to 31 000 mg/L do not interfere.
8. Reagents and Materials
6.4 Homogenizing may be necessary for samples with a
8.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
high particulate loading.
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
6.5 Inorganics dissolved in the sample are not volatilized
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the commit-
into gas and remain on the catalyst or quartz surface of the
tee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society,
combustion tube. High amounts of solids eventually react with
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
the quartz causing devitrification, or solidify in the catalyst bed
used, provided it is pure enough to be used without lessening
decreasing flow rates. Limit sample volume injected to reduce
the accuracy of the determination.
the amount of soluble salts and to reduce cooling of the
8.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references
reaction chamber. Buildup of salts; reduction of flow rate, or
to water shall be understood to mean reagent water conforming
large injection volumes could result in peak splitting.
to Specification D1193, Type I or Type II.
7. Apparatus
8.3 Acid—Acid is used for sample preservation and inter-
ference removal. Follow the manufacturer’s suggestions for
7.1 Sampling Devices, manually operated or automatically
acid and acid concentration. Do not use nitric acid.
operated sampling valves, or syringes are typically used with
this test method.
8.4 Total Nitrogen Stock Calibration Standard Solution
(1000 mg/L)—Weigh 3.609 g of potassium nitrate (KNO ) and
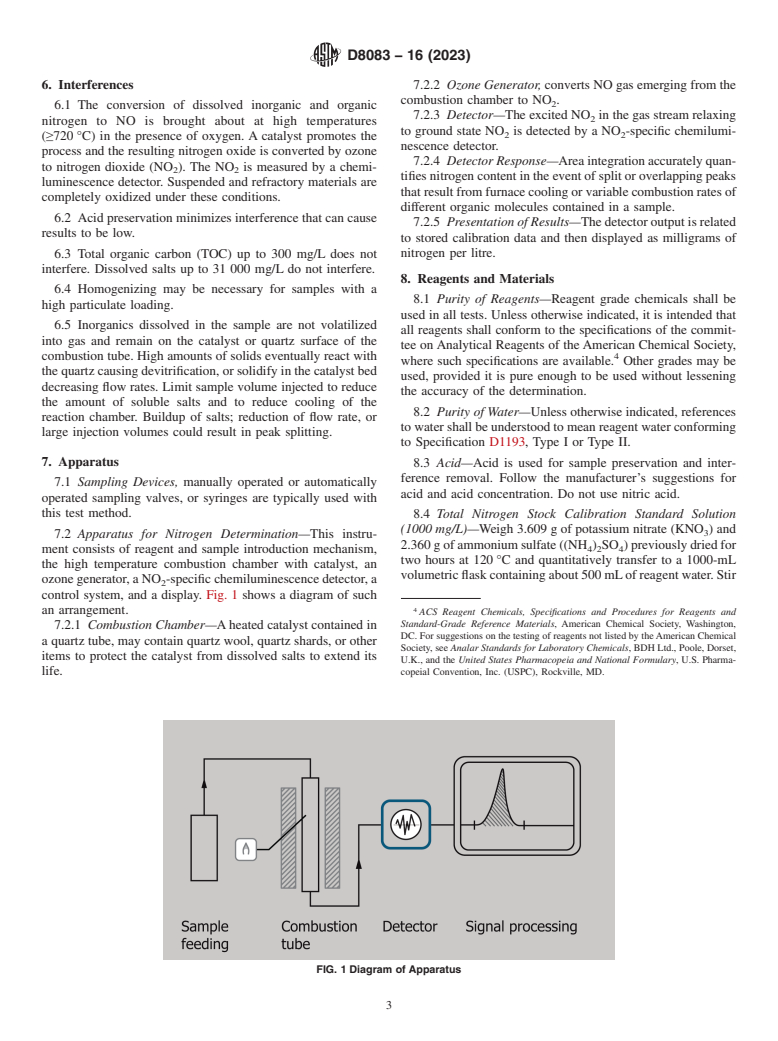
7.2 Apparatus for Nitrogen Determination—This instru-
2.360 g of ammonium sulfate ((NH ) SO ) previously dried for
4 2 4
ment consists of reagent and sample introduction mechanism,
two hours at 120 °C and quantitatively transfer to a 1000-mL
the high temperature combustion chamber with catalyst, an
volumetric flask containing about 500 mL of reagent water. Stir
ozone generator, a NO -specific chemiluminescence detector, a
control system, and a display. Fig. 1 shows a diagram of such
an arrangement.
ACS Reagent Chemicals, Specifications and Procedures for Reagents and
Standard-Grade Reference Materials, American Chemical Society, Washington,
7.2.1 Combustion Chamber—A heated catalyst contained in
DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not listed by the American Chemical
a quartz tube, may contain quartz wool, quartz shards, or other
Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset,
items to protect the catalyst from dissolved salts to extend its
U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia and National Formulary, U.S. Pharma-
life. copeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville, MD.
FIG. 1 Diagram of Apparatus
D8083 − 16 (2023)
to dissolve and add 1 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid 6 °C. Acidify the samples to a pH ≤2 with H SO . Analyze
2 4
(HCl), dilute to the mark with reagent water and mix. Transfer within 28 days of collection.
to an amber glass reagent bottle and cap for storage. This stock
9.3 DON or DN must be filtered in the field or in the
solution, or dilutions of it, is used to calibrate and test
laboratory within 48 h of collection and prior to acidification
performance of the nitrogen analyzer.
and analysis. After filtration, the sample is acidified to a pH ≤
2 and stored at above freezing to 6 °C. The sample must be
NOTE 1—Alternative nitrogen compounds, such as glycine, may be
used as the stock calibrant providing all QC acceptance criteria is met.
analyzed within 28 days of collection.
8.5 Total Nitrogen, Stock Laboratory Control Sample (LCS)
9.4 For monitoring of waters containing solids or immis-
Solution (1000 mg/L)—Weigh 7.218 g of potassium nitrate
cible liquids that are to be injected into the heated reaction zone
(KNO ) previously dried at 120 °C for two hours and quanti-
3 use a mechanical homogenizer or ultrasonic disintegrator.
tatively transfer to a 1000-mL volumetric flask containing
Filtering or screening may be necessary after homogenization
about 500 mL of reagent water. Stir to dissolve and add 1 mL
to reject particle sizes that are too large for injection.
of concentrated hydro
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.