ASTM E394-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Iron in Trace Quantities Using the 1,10-Phenanthroline Method
Standard Test Method for Iron in Trace Quantities Using the 1,10-Phenanthroline Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method is suitable for determining trace concentrations of iron in a wide variety of products, provided that appropriate sample preparation has rendered the iron and sample matrix soluble in water or other suitable solvent (see 10.1 and Note 5).
4.2 This test method assumes that the amount of color developed is proportional to the amount of iron in the test solution. The calibration curve is linear over the specified range. Possible interferences are described in Section 5.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of iron in the range from 1 to 100 μg.
1.2 This test method is intended to be general for the final steps in the determination of iron and does not include procedures for sample preparation.
1.3 This test method is applicable to samples whose solutions have a pH less than 2. It is assumed that the pH is adjusted to within this range in the sample preparation.
1.4 Review the current Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first-aid procedures, handling, and safety precautions.
1.5 The values given in SI units are the standard. Values in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E394 − 15
Standard Test Method for
Iron in Trace Quantities Using the 1,10-Phenanthroline
1
Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E394; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
1.1 This test method covers the determination of iron in the
3
cialty Chemicals (Withdrawn 2009)
range from 1 to 100 µg.
E200 Practice for Preparation, Standardization, and Storage
1.2 This test method is intended to be general for the final
of Standard and Reagent Solutions for ChemicalAnalysis
steps in the determination of iron and does not include
E275 Practice for Describing and Measuring Performance of
procedures for sample preparation.
Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometers
1.3 This test method is applicable to samples whose solu-
3. Summary of Test Method
tions have a pH less than 2. It is assumed that the pH is
adjusted to within this range in the sample preparation.
3.1 This test method is based upon a photometric determi-
nation of the 1,10-phenanthroline complex with the iron(II)
1.4 Review the current Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for de-
ion. The sample is dissolved in a suitable solvent and the iron
tailed information concerning toxicity, first-aid procedures,
is reduced to the divalent state by the addition of hydroxylam-
handling, and safety precautions.
ine hydrochloride.The color is then developed, by the addition
1.5 The values given in SI units are the standard. Values in
of 1,10-phenanthroline. After a short reaction period, the
parentheses are for information only.
absorbance of the solution is measured at approximately 510
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
nm using a suitable photometer. The absorbance of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
solution, once the color is developed, is stable for at least
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
several months.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4. Significance and Use
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.1 This test method is suitable for determining trace
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
concentrations of iron in a wide variety of products, provided
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
that appropriate sample preparation has rendered the iron and
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
sample matrix soluble in water or other suitable solvent (see
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
10.1 and Note 5).
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.2 This test method assumes that the amount of color
developed is proportional to the amount of iron in the test
2. Referenced Documents
solution. The calibration curve is linear over the specified
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
range. Possible interferences are described in Section 5.
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
E60 Practice for Analysis of Metals, Ores, and Related
5. Interferences
Materials by Spectrophotometry
4
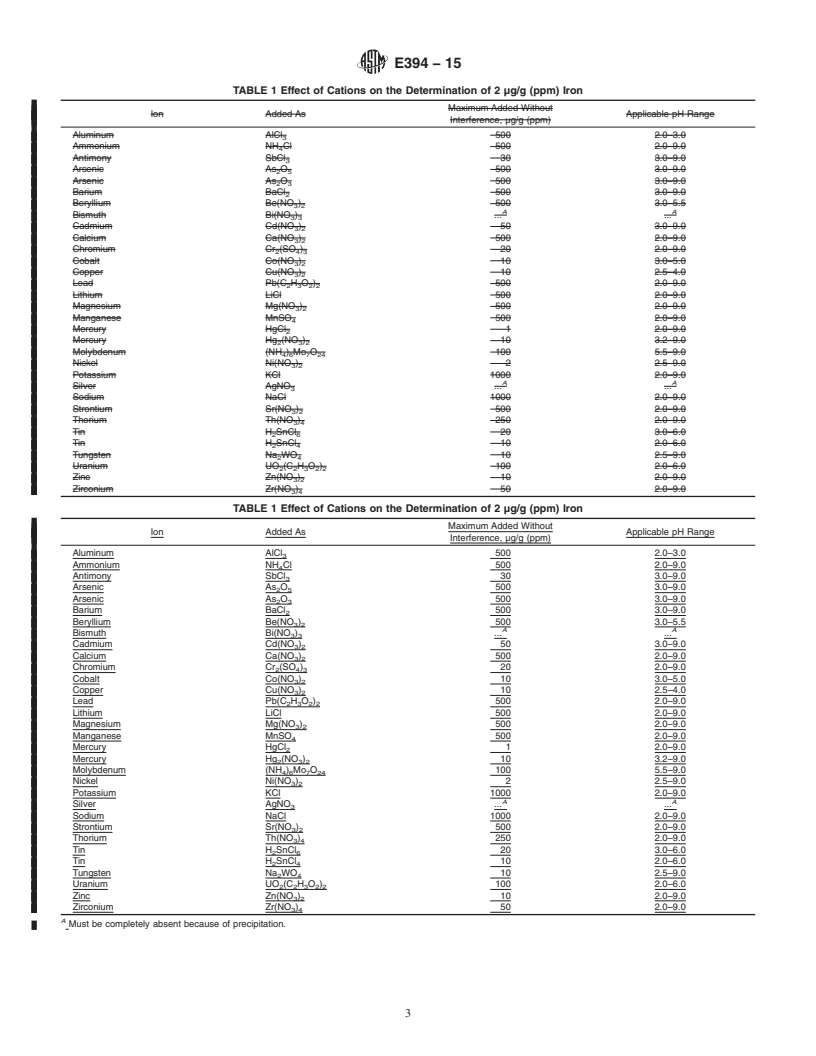
5.1 Fortune and Mellon have made a comprehensive study
of the interferences of various inorganic ions in this determi-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on nation. Table 1 and Table 2, taken from their report, show the
Aromatic, Industrial, Specialty and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsi-
effects of various cations and anions on the determination of
bility of Subcommittee D16.04 on Instrumental Analysis.
2.0 µg/g (ppm) iron. If the maximum level of 500 µg/g (ppm)
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2015. Published January 2016. Originally
approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as E394 – 09. DOI:
10.1520/E0394-15.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.astm.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Fortune, W. B., and Mellon, M. G., Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,
the ASTM website. Analytical Edition, IENAA Vol 10, 1938, pp. 60–64.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E394 − 15
TABLE 1 Effect of Cat
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E394 − 09 E394 − 15
Standard Test Method for
Iron in Trace Quantities Using the 1,10-Phenanthroline
1
Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E394; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of iron in the range from 1 to 100 μg.
1.2 This test method is intended to be general for the final steps in the determination of iron and does not include procedures
for sample preparation.
1.3 This test method is applicable to samples whose solutions have a pH less than 2. It is assumed that the pH is adjusted to
within this range in the sample preparation.
1.4 Review the current material safety data sheets (MSDS) Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for detailed information concerning
toxicity, first-aid procedures, handling, and safety precautions.
1.5 The values given in SI units are the standard. Values in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
E60 Practice for Analysis of Metals, Ores, and Related Materials by Spectrophotometry
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Specialty Chemicals
3
(Withdrawn 2009)
E200 Practice for Preparation, Standardization, and Storage of Standard and Reagent Solutions for Chemical Analysis
E275 Practice for Describing and Measuring Performance of Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometers
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 This test method is based upon a photometric determination of the 1,10-phenanthroline complex with the iron(II) ion. The
sample is dissolved in a suitable solvent and the iron is reduced to the divalent state by the addition of hydroxylamine
hydrochloride. The color is then developed, by the addition of 1,10-phenanthroline. After a short reaction period, the absorbance
of the solution is measured at approximately 510 nm using a suitable photometer. The absorbance of the solution, once the color
is developed, is stable for at least several months.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method is suitable for determining trace concentrations of iron in a wide variety of products, provided that
appropriate sample preparation has rendered the iron and sample matrix soluble in water or other suitable solvent (see 10.1 and
Note 65).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E15 on Industrial and Specialty Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E15.01 on
General Standards.
Current edition approved April 1, 2009Nov. 1, 2015. Published May 2009January 2016. Originally approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 20042009 as
E394 – 00E394 – 09.(2004). DOI: 10.1520/E0394-09.10.1520/E0394-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E394 − 15
4.2 This test method assumes that the amount of color developed is proportional to the amount of iron in the test solution. The
calibration curve is linear over the specified range. Possible interferences are described in Section 5.
5. Interferences
4
5.1 Fortune and Mellon have made a comprehensive study of the interferences of various inorganic ions in this determination.
Table 1 and Table 2, taken from their report, show the effects of various cations and anions on the determination of 2.0 μg/g (ppm)
iron. If the maximum level of 500 μg/g (ppm) does not interfere, it is very likely that the ion will not interfere in any quantity.
The data were obtained under slightly different conditions th
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.