ASTM D4737-10
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation
Standard Test Method for Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation is useful for estimating ASTM cetane number when a test engine is not available for determining this property directly and when cetane improver is not used. It may be conveniently employed for estimating cetane number when the quantity of sample available is too small for an engine rating. In cases where the ASTM cetane number of a fuel has been previously established, the Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation is useful as a cetane number check on subsequent batches of that fuel, provided the fuel's source and mode of manufacture remain unchanged.
Note 2—Test Methods D6890 and D7170 may be used to obtain a Derived Cetane Number (DCN) when the quantity of sample is too small for an engine test. These methods do measure the effect of cetane improver.
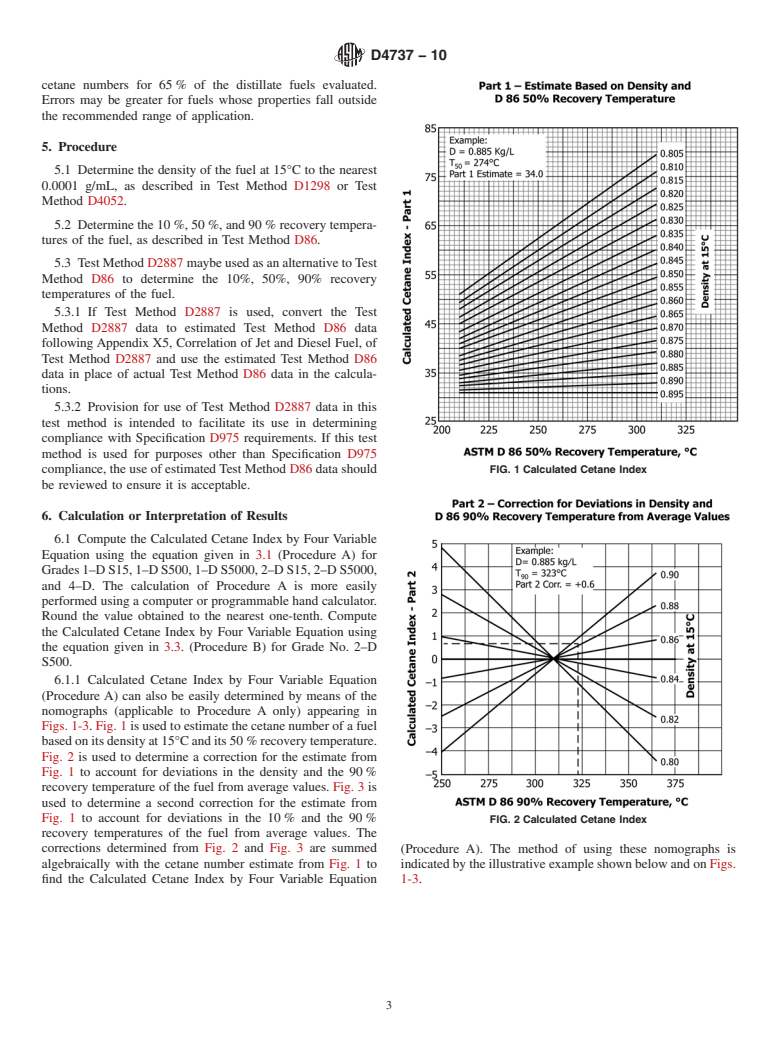
Within the range from 32.5 to 56.5 cetane number, the expected error of prediction of Procedure A of the Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation will be less than ±2 cetane numbers for 65 % of the distillate fuels evaluated. Errors may be greater for fuels whose properties fall outside the recommended range of application.
SCOPE
1.1 The calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation provides a means for estimating the ASTM cetane number (Test Method D613) of distillate fuels from density and distillation recovery temperature measurements. The value computed from the equation is termed the Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation.
1.2 The Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation is not an optional method for expressing ASTM cetane number. It is a supplementary tool for estimating cetane number when a result by Test Method D613 is not available and if cetane improver is not used. As a supplementary tool, the Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable equation must be used with due regard for its limitations.
1.3 Procedure A is to be used for Specification D975, Grades No. 1–D S15, No. 1–D S500, No. 1–D S5000, No. 2–D S15, No. 2–D S5000, and No. 4–D. This method for estimating cetane number was developed by Chevron Research Co. Procedure A is based on a data set including a relatively small number of No. 1–D fuels. Test Method D4737 Procedure A may be less applicable to No. 1–D S15, No. 1–D S500, and No. 1–D S5000 than to No. 2–D grade S5000 or to No. 4–D fuels.
1.3.1 Procedure A has been verified as applicable to Grade No. 2–D S15 diesel fuels.
1.4 Procedure B is to be used for Specification D975, Grade No. 2–D S500.
1.5 The test method “Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation” is particularly applicable to Grade 1–D S5000, Grade No. 1–D S500, Grade No. 2–D S5000 and Grade No. 2–D S500 diesel fuel oils containing straight-run and cracked stocks, and their blends. It can also be used for heavier fuels with 90 % recovery points less than 382°C and for fuels containing derivatives from oil sands and oil shale.
Note 1—Sxx is the designation for maximum sulfur level specified for the grade. For example, S500 grades are those with a maximum sulfur limit of 500 ppm (μg/g).
1.6 Biodiesel blends are excluded from this test method, because they were not part of the datasets use to develop either Procedure A or B.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4737 − 10
StandardTest Method for
1
Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4737; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* cracked stocks, and their blends. It can also be used for heavier
fuels with 90 % recovery points less than 382°C and for fuels
1.1 The calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation
containing derivatives from oil sands and oil shale.
provides a means for estimating the ASTM cetane number
(Test Method D613) of distillate fuels from density and
NOTE 1—Sxx is the designation for maximum sulfur level specified for
the grade. For example, S500 grades are those with a maximum sulfur
distillation recovery temperature measurements. The value
limit of 500 ppm (µg/g).
computed from the equation is termed the Calculated Cetane
Index by Four Variable Equation.
1.6 Biodiesel blends are excluded from this test method,
because they were not part of the datasets use to develop either
1.2 The Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation
Procedure A or B.
isnotanoptionalmethodforexpressingASTMcetanenumber.
It is a supplementary tool for estimating cetane number when
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
a result by Test Method D613 is not available and if cetane
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
improver is not used. As a supplementary tool, the Calculated
standard.
Cetane Index by Four Variable equation must be used with due
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
regard for its limitations.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.3 Procedure A is to be used for Specification D975,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Grades No. 1–D S15, No. 1–D S500, No. 1–D S5000, No. 2–D
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
S15, No. 2–D S5000, and No. 4–D.This method for estimating
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2
cetane number was developed by Chevron Research Co.
Procedure A is based on a data set including a relatively small
2. Referenced Documents
number of No. 1–D fuels. Test Method D4737 Procedure A
4
2.1 ASTM Standards:
maybelessapplicabletoNo. 1–DS15,No.1–DS500,andNo.
D86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and
1–D S5000 than to No. 2–D grade S5000 or to No. 4–D fuels.
Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure
1.3.1 Procedure A has been verified as applicable to Grade
D613 Test Method for Cetane Number of Diesel Fuel Oil
3
No. 2–D S15 diesel fuels.
D975 Specification for Diesel Fuel Oils
1.4 Procedure B is to be used for Specification D975, Grade
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API
No. 2–D S500.
Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Prod-
ucts by Hydrometer Method
1.5 The test method “Calculated Cetane Index by Four
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Pe-
Variable Equation” is particularly applicable to Grade 1–D
troleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
S5000, Grade No. 1–D S500, Grade No. 2–D S5000 and Grade
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
No. 2–D S500 diesel fuel oils containing straight-run and
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D6751 Specification for Biodiesel Fuel Blend Stock (B100)
for Middle Distillate Fuels
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
D6890 Test Method for Determination of Ignition Delay and
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.E0 on Burner, Diesel, Non-Aviation Gas Turbine, and Marine
Derived Cetane Number (DCN) of Diesel Fuel Oils by
Fuels.
Combustion in a Constant Volume Chamber
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2010. Published September 2010. Originally
D7170 Test Method for Determination of Derived Cetane
approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D4737–09a. DOI:
10.1520/D4737-10.
2
Ingham, M. C., et al., “Improved Predictive Equations for Cetane Number,”
SAE Paper No 860250, Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Common-
4
wealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
Supporting data (the analysis leading to the use of ProcedureAfor No. 2-D S15 contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
diesel fuels and to Procedure B) have been filed at ASTM International Headquar- Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
ters and may be obtained by requesting Research Report RR:D02-1699. the ASTM website.
*A S
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D4737–09a Designation: D4737 – 10
Standard Test Method for
1
Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4737; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 The calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation provides a means for estimating the ASTM cetane number (Test
Method D613) of distillate fuels from density and distillation recovery temperature measurements. The value computed from the
equation is termed the Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation.
1.2 The Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable Equation is not an optional method for expressingASTM cetane number. It
is a supplementary tool for estimating cetane number when a result by Test Method D613 is not available and if cetane improver
is not used.As a supplementary tool, the Calculated Cetane Index by Four Variable equation must be used with due regard for its
limitations.
1.3 ProcedureAis to be used for Specification D975, Grades No. 1–D S15, No. 1–D S500, No. 1–D S5000, No. 2–D S15, No.
2
2–D S5000, and No. 4–D. This method for estimating cetane number was developed by Chevron Research Co. Procedure A is
based on a data set including a relatively small number of No. 1–D fuels. Test Method D4737 ProcedureAmay be less applicable
to No. 1–D S15, No. 1–D S500, and No. 1–D S5000 than to No. 2–D grade S5000 or to No. 4–D fuels.
3
1.3.1 Procedure A has been verified as applicable to Grade No. 2–D S15 diesel fuels.
1.4 Procedure B is to be used for Specification D975, Grades No. 2–D S15 and No. 2–D S500. , Grade No. 2–D S500.
1.5 Thetestmethod“CalculatedCetaneIndexbyFourVariableEquation”isparticularlyapplicabletoGrade1–DS5000,Grade
No. 1–D S500, Grade No. 2–D S5000 and Grade No. 2–D S500 diesel fuel oils containing straight-run and cracked stocks, and
their blends. It can also be used for heavier fuels with 90 % recovery points less than 382°C and for fuels containing derivatives
from oil sands and oil shale.
NOTE 1—Sxx is the designation for maximum sulfur level specified for the grade. For example, S500 grades are those with a maximum sulfur limit
of 500 ppm (µg/g).
1.6 Biodiesel blends are excluded from this test method, because they were not part of the datasets use to develop either
Procedure A or B.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
4
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at Atmospheric Pressure
D613 Test Method for Cetane Number of Diesel Fuel Oil
D975 Specification for Diesel Fuel Oils
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density (Specific Gravity), orAPI Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum
Products by Hydrometer Method
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.E0.02
on Diesel Fuel Oils.
Current edition approved Dec.Aug. 1, 2009.2010. Published December 2009.September 2010. Originally approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as
D4737–09a. DOI: 10.1520/D4737-09a.10.1520/D4737-10.
2
Ingham, M. C., et al., “Improved Predictive Equations for Cetane Number,” SAE Paper No 860250, Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr.,
Warrendale, PA 15096-0001.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book ofASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Supporting data (the analysis leading to the use of Procedure A for No. 2-D S15 diesel fuels and to Procedure B) have been filed at ASTM International Headquarters
and may be obtained by requesting Research Report RR:D02-1699.
4
Available from the National CEN members listed on the CEN website (www.cenorm.be) or from the CEN/TC 19 Secretariat (astm@nen.nl).
4
For referencedASTM standards, visit theA
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.