ASTM A773/A773M-01
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for dc Magnetic Properties of Materials Using Ring and Permeameter Procedures with dc Electronic Hysteresigraphs
Standard Test Method for dc Magnetic Properties of Materials Using Ring and Permeameter Procedures with dc Electronic Hysteresigraphs
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Hysteresigraph testing permits more rapid and efficient collection of dc hysteresis (B-H loop) data as compared to the point by point ballistic Test Methods A 341/A 341M and A 596/A 596M. The accuracy and precision of testing is comparable to the ballistic methods. Hysteresigraphs are particularly desirable for testing of semihard and hard magnetic materials where either the entire second quadrant (demagnetization curve) or entire hysteresis loop is of primary concern.
Provided the test specimen is representative of the bulk sample or lot, this test method is well suited for design, specification acceptance, service evaluation and research and development.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides dc hysteresigraph procedures ( B-H loop methods) for the determination of basic magnetic properties of materials in the form of ring, toroidal, link, double-lapped Epstein cores, or other standard shapes that may be cut, stamped, machined, or ground from cast, compacted, sintered, forged, or rolled materials. It includes tests for normal induction and hysteresis taken under conditions of continuous sweep magnetization. Rate of sweep may be varied, either manually or automatically at different portions of the curves during tracing. Total elapsed time for tracing a hysteresis loop is commonly 10 to 120 s per loop.
1.2 The values stated in either customary (cgs-emu and inch-pound) units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the systems may result in nonconformance with this test method.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A 773/A 773M–01
Standard Test Method for
dc Magnetic Properties of Materials Using Ring and
Permeameter Procedures with dc Electronic
1
Hysteresigraphs
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationA773/A773M;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyear
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope A343/A343M Test Method for Alternating-Current Mag-
netic Properties of Materials at Power Frequencies Using
1.1 This test method provides dc hysteresigraph procedures
Wattmeter-Ammeter-VoltmeterMethodand25-cmEpstein
(B-H loop methods) for the determination of basic magnetic
Test Frame
properties of materials in the form of ring, toroidal, link,
A596/A596M Test Method for Direct-Current Magnetic
double-lappedEpsteincores,orotherstandardshapesthatmay
Properties of Materials Using the Ballistic Method and
be cut, stamped, machined, or ground from cast, compacted,
Ring Specimens
sintered,forged,orrolledmaterials.Itincludestestsfornormal
2.2 Other:
induction and hysteresis taken under conditions of continuous
IEC Publication 404-4: Magnetic Materials—Part 4: Meth-
sweep magnetization. Rate of sweep may be varied, either
odsofMeasurementofdcMagneticPropertiesofIronand
manually or automatically at different portions of the curves
3
Steel (1995)
during tracing. Total elapsed time for tracing a hysteresis loop
is commonly 10 to 120 s per loop.
3. Summary of Test Method
1.2 The values and equations stated in customary (cgs-emu
3.1 Asinmakingmostmagneticmeasurements,aspecimen
and inch-pound) or SI units are to be regarded separately as
is wound with an exciting winding (the primary) and a search
standard.Within th is standard, SI units are shown in brackets.
coil(thesecondary)formeasuringthechangeinflux.Whenan
Thevaluesstatedineachsystemmaynotbeexactequivalents;
exciting current, I, is applied to the primary winding, a
therefore,eachsystemshallbeusedindependentlyoftheother.
magnetic field, H, is produced in the coil, and this in turn
Combiningvaluesfromthetwosystemsmayresultinnoncon-
produces magnetic flux f in the specimen. In uniform speci-
formance with this standard.
mens that do not contain air gaps, such as ring samples, all of
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the exciting current is used to magnetize the specimen, and H
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
is proportional to I in accordance with the following equation:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- H 5 KI
(1)
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
where:
2. Referenced Documents
H = magnetic field strength, Oe [A/m];
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
I = current in the exciting coil A; and
A34/A34M Practice for Sampling and Procurement Test-
K = constant determined by the number of primary turns
ing of Magnetic Materials
the magnetic path length of the specimen and system
A341/A341M Test Method for Direct Current Magnetic
of units.
Properties of Materials Using D-C Permeameters and the
3.1.1 The magnetic flux may be determined by integration
Ballistic Test Methods
of the instantaneous electromotive force that is induced in the
secondary coil when the flux is increased or decreased by a
varying H. The instantaneous voltage, e, is equal to:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A06 on
MagneticPropertiesandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeA06.01onTest
df
1
e52NK (2)
Methods.
dt
Current edition approved June 10, 2001. Published September 2001. Originally
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 1996 as A773–96. or
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from American National Standards Institute, 25 W. 43rd St., 4th
the ASTM website. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A 773/A 773M–01
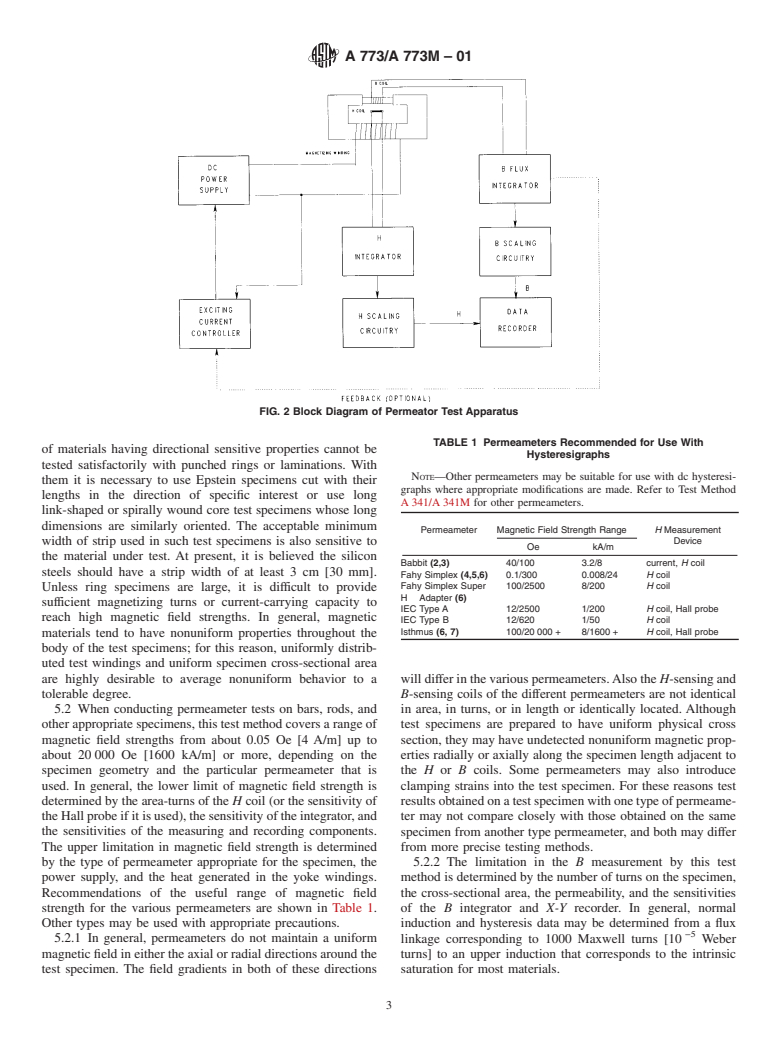
FIG. 1 Block Diagram of Ring Test Apparatus
1
block diagram of Fig. 2. When using permeameters, the value
f5 edt
*
K N
of H in the gap is generally not proportional to I that flows
1
through the exciting coil of the yoke. In these cases, the value
where:
of H is determined by integration of the electromotive force
dt = time differential,
thatisinducedinan Hcoil(orChattockpotentiometer)orfrom
N = number of turns, and
−8
the signal developed by a Hall probe which is placed near the
K =
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.