ASTM F637-85(1994)e1
(Specification)Standard Specification for Format, Physical Properties, and Test Methods for 19 and 35 mm Testable Tape Carrier for Perimeter Tape Carrier-Bonded Semiconductor Devices
Standard Specification for Format, Physical Properties, and Test Methods for 19 and 35 mm Testable Tape Carrier for Perimeter Tape Carrier-Bonded Semiconductor Devices
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers standard formats for testable semiconductor lead carrier tape suitable for hybrid applications.
1.2 This standard specifies tape width, configuration, and location of guide perforations ("sprocket holes"), location of lead pattern frames on tape, lead pattern window size, and placement of outer lead bond and electrical test pad areas in the lead pattern.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 The following hazard caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 7 of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
Designation: F 637 – 85 (Reapproved 1994)
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Specification for
Format, Physical Properties, and Test Methods for 19 and
35 mm Testable Tape Carrier for Perimeter Tape Carrier-
Bonded Semiconductor Devices
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 637; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
e NOTE—Editorial changes were made throughout in September 1994.
INTRODUCTION
It is the purpose of this specification to facilitate interchangeability of carrier tape produced by
various manufacturers. Standardization is also intended to promote efficient utilization of equipment
used to test devices on tape and assemble them to hybrid circuits. A complete description of a
particular carrier tape requires specification of a considerable number of parameters not covered by
this standard. This standard specification includes only elements of format design for which substantial
consensus with respect to technically and economically sound commercial practice has been achieved.
1. Scope substrate on the outer end.
2.1.2 outer lead bond area—in tape carrier bonding, that
1.1 This specification covers standard formats for testable
area on each lead which will be connected to a mounting
semiconductor lead carrier tape suitable for hybrid applica-
substrate.
tions.
2.1.3 tape format—in tape carrier bonding, the layout de-
1.2 This standard specifies tape width, configuration, and
sign elements of carrier tape, including the topographical
location of guide perforations (“sprocket holes”), location of
arrangement of lead pattern elements and test contacts in each
lead pattern frames on tape, lead pattern window size, and
frame, description of the placement of frames upon the tape,
placement of outer lead bond and electrical test pad areas in the
and the specification of tape width and the placement of
lead pattern.
mechanical handling aids, such as guide perforations.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
2.1.4 testable tape carrier—in microelectronic fabrication,
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
a continuous length of plastic/metal composite film, superfi-
information only.
cially resembling motion picture film, which carries at each
1.4 The following hazard caveat pertains only to the test
frame position a repetitive pattern of electrically conducting
method portion, Section 7 of this specification. This standard
leads and test contacts.
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this 2.1.4.1 Discussion—The lead arrangement is designed so as
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices to electrically interconnect points on a microelectronic device
with contacts on the mounting substrate of the device. The test
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
to use. contacts permit static or dynamic evaluation, or both, of each
microelectronic device prior to assembly to a mounting sub-
2. Terminology
strate.
2.1 Definitions:
2.1.5 test pads—in tape carrier bonding, conducting areas in
2.1.1 lead pattern window—in tape carrier bonding, the area
each tape frame position that can be contacted electrically by
in each frame in which plastic backing of plastic/metal
probes in order to test devices attached to the tape.
composite tape is totally or partially removed to expose
appropriate areas of bare conducting leads for attachment to a
3. Classification
microelectronic device on the inner end and a mounting
3.1 A wide variety of formats are covered under this
standard. Tape format style is classified according to the
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-1 on following code:
Electronics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F01.16 on Tape
“ Style A–B–C–D–E–F–G–H–I–J”
Automated Bonding.
Current edition approved Aug. 30, 1985. Published October 1985. Originally
where:
published as F 637 – 79. Last previous edition F 637 – 79.
F 637
4. Ordering Information
A 5 nominal tape width in millimeters (see Table 1),
B 5 pattern pitch expressed as an integral multiple of the
4.1 The purchase order or contract shall specify the tape
standard sprocket pitch of 0.1870 inch (for example,
format style classification (see 2.1).
4 5 4 sprocket pitch 5 0.7480 inch) (see Table 1),
4.2 Additional details of tape design and manufacture not
C 5 side dimension of square lead pattern window in
covered by this specification shall be as agreed between the
millimeters (see Table 1),
purchaser and the supplier as part of the purchase contract.
D 5 base film material: K 5 Polyimide M 5 Polyester,
5. Dimensions
E 5 base film thickness expressed in mils (for example,
5 5 0.005 in.), 5.1 Figs. 1-3, and Table 1 specify standard tape widths,
F 5 copper type: ED 5 Electrodeposited AR 5 As-
frame placement on tape, guide perforation, outer lead bond
Rolled,
pad, lead pattern window size, and test pad format options.
G 5 copper thickness expressed in ounces (for example,
6. Sampling
1 51oz 5 0.0014 in.),
6.1 Unless otherwise agreed to between the purchaser and
H 5 lead configuration: P 5 Planar B 5 Bumped,
I 5 lead finish: CU 5 Copper (no finish) SN 5 Tin the supplier, conformance with Section 5 shall be determined
by sampling and testing specimens from each lot.
AU 5 Gold
J 5 pattern style: S 5 all leads electrically connected to a
6.1.1 A lot shall consist of all material processed in one
common conductor for plating, static grounding, etc. essentially continuous production operation, and delivered in
O 5 all leads electrically isolated. one shipment from one supplier against one order description.
6.1.2 Sampling Plan:
NOTE 1—Example of a tape format style classification, as follows:
6.1.2.1 The sampling plan shall be agreed upon between the
“Style 35–4–7–K–5–ED–1–P–SN–O”
purchaser and the supplier.
This tape format style identifies a 1.4-in. (35-mm) wide tape carrier with
6.1.2.2 Samples chosen shall be representative of the lot.
patterns on a 4-sprocket pitch, having a 0.28 by 0.28-in. 7 by 7-mm lead
pattern window, fabricated on a polyimide film, 0.005 in.-thick (127-μm)
7. Test Methods
with electrodeposited copper, 1-oz thick (0.0014 in.), (35.6μ m) having
planar leads tin-plated with all leads electrically isolated. 7.1 Dimensional Tolerances:
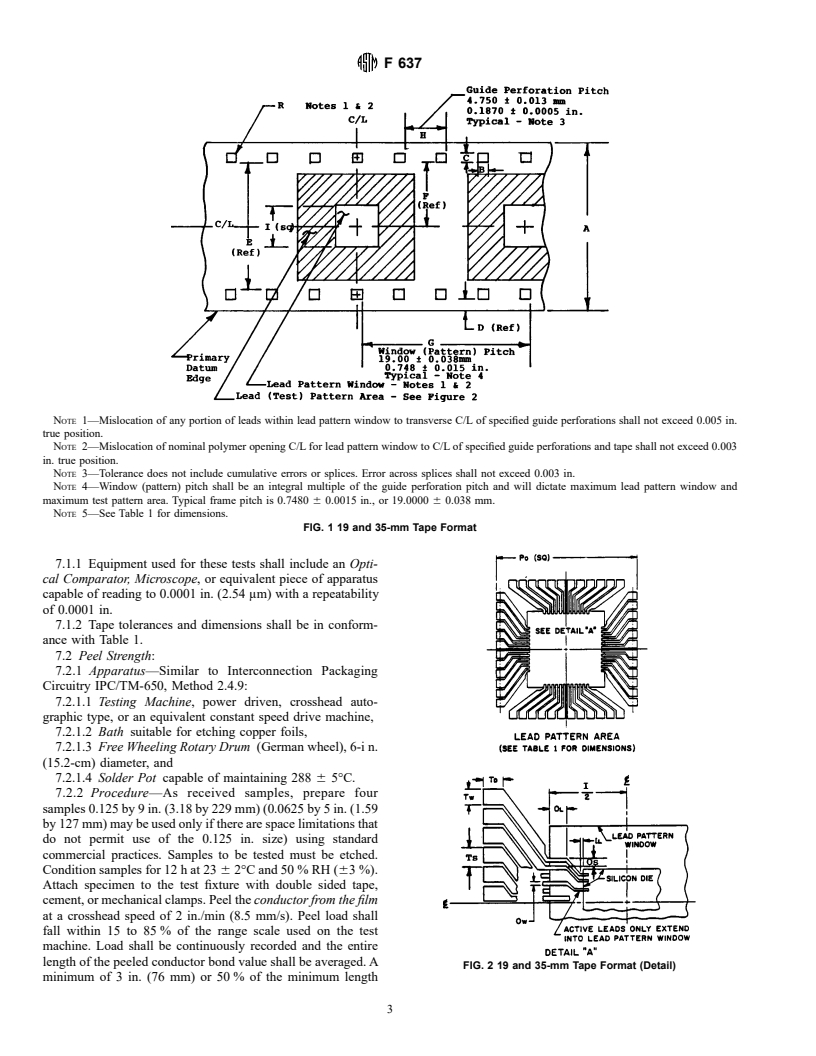
TABLE 1 Dimensions for 19 and 35-mm Tape Format (see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2)
NOTE 1—For smaller die or fewer leads, Dimension I may be reduced in increments of 1.000 mm (0.0394 in.). The selection of an appropriate I for
any specific die requires consideration of parameters not covered by this Standard such as die size, number and location of leads, assembly equipment
and processes, minimum spacing between windows for film strength, etc.
19mm Tape 35mm Tape
Dimension
in. mm in. mm
A Tape width 0.748 19.00 1.377 34.975
60.003 60.075 60.003 60.075
B Perforation length 0.0560 1.422 0.078 1.98
60.001 60.025 60.001 60.025
C Perforation width 0.0560 1.422 0.1100 2.794
60.001 60.025 60.001 60.025
D Tape edge to perforation edge from 0.034 0.86 0.079 2.01
primary datum edge 60.002 60.05 60.002 60.05
E Width between perforation edges 0.568 14.427 0.999 25.375
60.001 60.025 60.001 60.025
F Perforation edge to window C/L 0.284 7.21 0.4995 12.69
60.001 60.025 60.001 60.025
G Window pitch (typical) 0.748 19.000 0.748 19.000
60.015 60.038 60.015 60.038
H Guide perforation pitch 0.1870 4.750 0.1870 4.750
60.0005 60.013 60.0005 60.013
100 perforations 18.70 475.0 18.70 475.0
60.030 60.762 60.030 60.762
I Lead pattern window maximum di- 0.394 10.0 0.472 12.0
mension (see Note) 60.002 60.05 60.002 60.05
R Maximum radius 0.010 0.25 0.021 0.53
Po Maximum test pad pattern outline 0.498 12.65 0.890 22.50
(square)
Ts Test pad spacing (noncumulative) 0.025 0.64 0.050 1.27
Tw Test pad width 0.020 0.51 0.040 1.02
60.002 60.05 60.002 60.05
Td Test pad depth (min) 0.018 0.46 0.038 0.97
Os Outer lead bond C/L spacing (noncu- 0.020 0.51 0.020 0.51
mulative)
Ow Outer lead bond width (nominal) 0.010 0.25 0.010 0.025
OL Minimum outer lead bond length: 0.015 0.38 0.015 0.58
Flat leads 0.045 1.15 0.045 1.15
Formed leads
IL Minimum straight extension of inner 0.005 0.13 0.005 0.13
lead from edge of silicon die
F 637
NOTE 1—Mislocation of any portion of leads within lead pattern window to transverse C/L of specified guide perforations shall not exceed 0.005 in.
true position.
NOTE 2—Mislocation of nominal polymer opening C/L for lead pattern window to C/L of specified guide perforations and tape shall not exceed 0.003
in. true position.
NOTE 3—Tolerance does not include cumulative errors or splices. Error across splices shall not exceed 0.003 in.
NOTE 4—Window (pattern) pitch shall be an integral multiple of the guide perforation pitch and will dictate maximum lead pattern window and
maximum test pattern area. Typical frame pitch is 0.7480 6 0.0015 in., or 19.0000 6 0.038 mm.
NOTE 5—See Table 1 for dimensions.
FIG. 1 19 and 35-mm Tape Format
7.1.1 Equipment used for these tests shall include an Opti-
cal Comparator, Microscope, or equivalent piece of apparatus
capable of reading to 0.0001 in. (2.54 μm) with a repeatability
of 0.0001 in.
7.1.2 Tape tolerances and dimensions shall be in conform-
ance with Table 1.
7.2 Peel Strength:
7.2.1 Apparatus—Similar to Interconnection Packaging
Circuitry IPC/TM-650, Method 2.4.9:
7.2.1.1 Testing Machine, power driven, crosshead auto-
graphic type, or an equivalent constant speed drive machine,
7.2.1.2 Bath suitable for etching copper foils,
7.2.1.3 Free Wheeling Rotary Drum (German wheel), 6-i n.
(15.2-cm) diameter, and
7.2.1.4 Solder Pot capable of maintaining 288 6 5°C.
7.2.2 Procedure—As received samples, prepare four
samples 0.125 by 9 in. (3.18 by 229 mm) (0.0625 by 5 in. (1.59
by 127 mm) may be used only if there are space limitations that
do not permit use of the 0.125 in. size) using standard
commercial practices. Samples to be tested must be etched.
Condition samples for 12 h at 23 6 2°C and 50 % RH (63 %).
Attach specimen to the test fixture with double sided tape,
cement, or mechanical clamps. Peel the conductor from the film
at a crosshead s
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.