ASTM D495-99
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for High-Voltage, Low-Current, Dry Arc Resistance of Solid Electrical Insulation
Standard Test Method for High-Voltage, Low-Current, Dry Arc Resistance of Solid Electrical Insulation
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers, in a preliminary fashion, the differentiation among similar materials with respect to their resistance to the action of a high-voltage, low-current arc close to the surface of insulation, intending to form a conducting path therein or in causing the material to become conducting due to the localized thermal and chemical decomposition and erosion.
1.2 The usefulness of this test method is very severely limited by many restrictions and qualifications, some of which are described in the following paragraphs and in Section 5. Generally, this test method should not be used in material specifications. Whenever possible, alternative test methods should be used, and their development is encouraged.
1.3 This test method will not, in general, permit conclusions to be drawn concerning the relative arc resistance rankings of materials that may be subjected to other types of arcs: for example, high voltage at high currents, and low voltage at low or high currents (promoted by surges or by conducting contaminants).
1.4 The test method is intended, because of its convenience and the short time required for testing, for preliminary screening of material, for detecting the effects of changes in formulation, and for quality control testing after correlation has been established with other types of simulated service arc tests and field experience. Because this test method is usually conducted under clean and dry laboratory conditions rarely encountered in practice, the prediction of a material's relative performance in typical applications and in varying "clean to dirty" environments may be substantially altered (Note 1). Caution is urged against drawing strong conclusions without corroborating support of simulated service tests and field testing. Rather, this test method is useful for preliminary evaluation of changes in structure and composition without the complicating influence of environmental conditions, especially dirt and moisture. Note 1-By changing some of the circuit conditions described herein it has been found possible to rearrange markedly the order of arc resistance of a group of organic insulating materials consisting of vulcanized fiber and of molded phenolic and amino plastics, some containing organic, and some inorganic, filler.
1.5 While this test method uses dry, uncontaminated specimen surfaces, Test Method D2132, Test Method D2303, and Test Method D3638 employ wet, contaminated specimen surfaces. Their use is recommended for engineering purposes and to assist in establishing some degree of significance to this test method for quality control purposes.
1.6 This test method is not applicable to materials that do not produce conductive paths under the action of an electric arc, or that melt or form fluid residues that float conductive residues out of the active test area thereby preventing formation of a conductive path.
1.7 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements, see 6.1.14, 6.1.19, Section 7, and 10.1.1.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D495–99
Standard Test Method for
High-Voltage, Low-Current, Dry Arc Resistance of Solid
1
Electrical Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 495; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (ε) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
it has been found possible to rearrange markedly the order of arc
1. Scope
resistance of a group of organic insulating materials consisting of
1.1 This test method covers, in a preliminary fashion, the
vulcanized fiber and of molded phenolic and amino plastics, some
differentiation among similar materials with respect to their
containing organic, and some inorganic, filler.
resistance to the action of a high-voltage, low-current arc close
1.5 While this test method uses dry, uncontaminated speci-
to the surface of insulation, intending to form a conducting
men surfaces, Test Method D 2132, Test Method D 2303, and
path therein or in causing the material to become conducting
Test Method D 3638 employ wet, contaminated specimen
due to the localized thermal and chemical decomposition and
surfaces. Their use is recommended for engineering purposes
erosion.
and to assist in establishing some degree of significance to this
1.2 The usefulness of this test method is very severely
2
test method for quality control purposes.
limited by many restrictions and qualifications, some of which
1.6 This test method is not applicable to materials that do
are described in the following paragraphs and in Section 5.
not produce conductive paths under the action of an electric
Generally, this test method should not be used in material
arc, or that melt or form fluid residues that float conductive
specifications. Whenever possible, alternative test methods
residues out of the active test area thereby preventing forma-
should be used, and their development is encouraged.
tion of a conductive path.
1.3 This test method will not, in general, permit conclusions
1.7 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
to be drawn concerning the relative arc resistance rankings of
as the standard.
materials that may be subjected to other types of arcs: for
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
example, high voltage at high currents, and low voltage at low
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
or high currents (promoted by surges or by conducting con-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
taminants).
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.4 The test method is intended, because of its convenience
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
and the short time required for testing, for preliminary screen-
precautionary statements, see 6.1.14, 6.1.19, Section 7, and
ing of material, for detecting the effects of changes in formu-
10.1.1.
lation, and for quality control testing after correlation has been
established with other types of simulated service arc tests and
2. Referenced Documents
field experience. Because this test method is usually conducted
2.1 ASTM Standards:
undercleananddrylaboratoryconditionsrarelyencounteredin 3
D 1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
practice, the prediction of a material’s relative performance in
D 2132 Test Method for Dust-and-Fog Tracking and Ero-
typical applications and in varying “clean to dirty” environ- 4
sion Resistance of Electrical Insulating Materials
ments may be substantially altered (Note 1). Caution is urged
D 2303 Test Method for Liquid-Contaminant, Inclined-
against drawing strong conclusions without corroborating sup- 4
Plane Tracking and Erosion of Insulating Materials
port of simulated service tests and field testing. Rather, this test
D 3638 Test Method for Comparative Tracking Index of
method is useful for preliminary evaluation of changes in 4
Electrical Insulating Materials
structure and composition without the complicating influence
D 6054 Practice for Conditioning Electrical Insulating Ma-
of environmental conditions, especially dirt and moisture. 4
terials for Testing
NOTE 1—By changing some of the circuit conditions described herein
2
Also helpful is Test Method D 2302 for Wet Tracking Resistance of Electrical
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-9 on
Insulating Materials with Controlled Water-to-Metal Discharges. This test method
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
was withdrawn and last appeared in the 1982 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Part
Subco
...







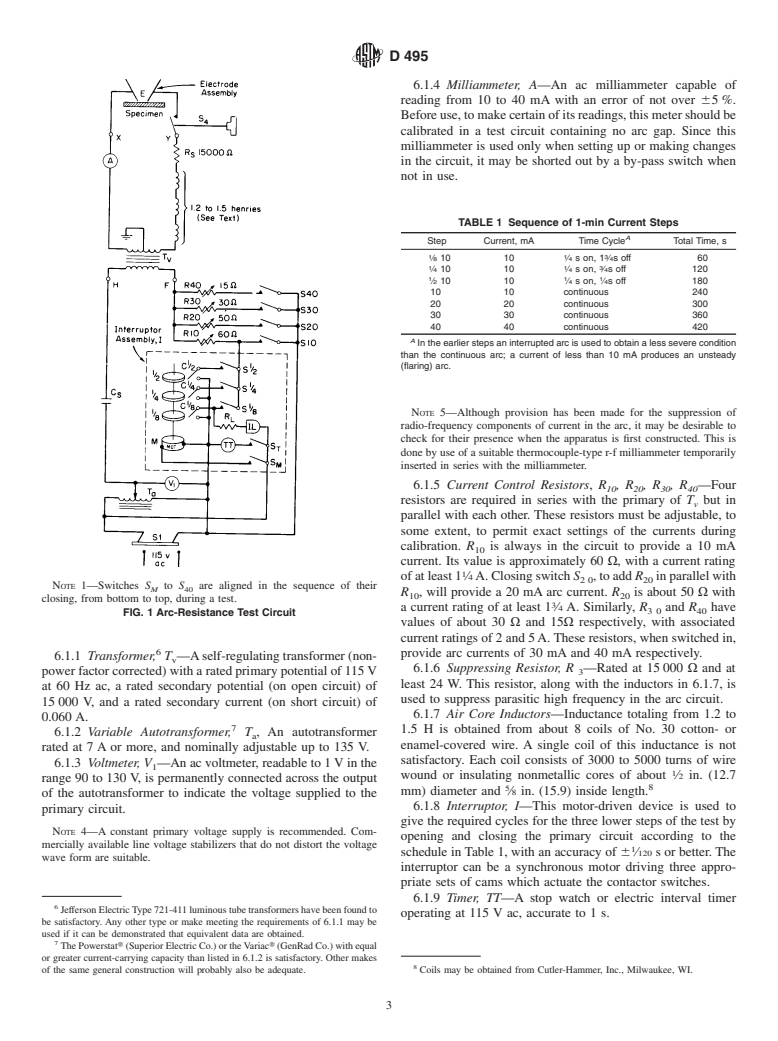
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.