ASTM D4049-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining the Resistance of Lubricating Grease to Water Spray
Standard Test Method for Determining the Resistance of Lubricating Grease to Water Spray
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is used to evaluate the ability of a grease to adhere to a metal surface when subjected to direct water spray. The results obtained from the use of this test method suggest correlation in operations involving direct water spray impingement such as steel mill roll neck bearing service.4 This test method is used for quality control and purchase specifications.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method2 covers the ability of a grease to adhere to a metal surface when subjected to a water spray under prescribed laboratory conditions.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.2.1 Exception—The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4049 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Determining the Resistance of Lubricating Grease to Water
1
Spray
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4049; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
2
3.1 Definitions:
1.1 Thistestmethod coverstheabilityofagreasetoadhere
3.1.1 lubricating grease, n—a semi-fluid to solid product of
to a metal surface when subjected to a water spray under
a dispersion of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
prescribed laboratory conditions.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—The dispersion of the thickener forms a
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by
standard.
surface tension and other physical forces. Other ingredients are
1.2.1 Exception—The values given in parentheses are for
commonly included to impart special properties. D217
information only.
3.1.2 oil separation, n—the appearance of a liquid fraction
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
from an otherwise homogeneous lubricating composition.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
D1742
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.3 thickener, n—in lubricating grease, a substance com-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
posed of finely divided particles dispersed in a liquid lubricant
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
to form the product’s structure.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.3.1 Discussion—The thickeners can be fibers (such as
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
various metallic soaps) or plates or spheres (such as certain
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
non-soapthickeners),whichareinsolubleor,atmost,onlyvery
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
slightly soluble in the liquid lubricant. The general require-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
ments are that the solid particles be extremely small, uniformly
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
dispersed, and capable of forming a relatively stable, gel-like
structure with the liquid lubricant. D217
2. Referenced Documents
3 4. Summary of Test Method
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating 4.1 The grease to be tested is coated on a stainless steel
panel and sprayed with water at the specified test temperature
Grease
D1742 Test Method for Oil Separation from Lubricating and pressure. The amount of grease remaining on the panel
after 5 min 6 15 s is a measure of the resistance of the grease
Grease During Storage
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to to water spray.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is used to evaluate the ability of a
1 grease to adhere to a metal surface when subjected to direct
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
water spray. The results obtained from the use of this test
Subcommittee D02.G0.06 on Functional Tests - Contamination.
methodsuggestcorrelationinoperationsinvolvingdirectwater
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2020. Published November 2020. Originally
spray impingement such as steel mill roll neck bearing ser-
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D4049 – 16. DOI:
4
vice. This test method is used for quality control and purchase
10.1520/D4049-20.
2
The development of this test method is described in Musilli, T. G., “Water
specifications.
Spray-Off Characteristics of Lubricating Grease,” NLGI Spokesman, December
1982, pp. 323–326.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Cichelli, A. E. “Evaluation of Greases for Steel Mill Service,” NLGI
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Spokesman, August 1973, and A. E. Cichelli, “Grease Lubrication in Steel Mills
the ASTM website. with Emphasis on Roll Neck Bearings,” NLGI Spokesman, April 1980.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ---------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4049 − 16 D4049 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Determining the Resistance of Lubricating Grease to Water
1
Spray
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4049; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This test method covers the ability of a grease to adhere to a metal surface when subjected to a water spray under prescribed
laboratory conditions.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.2.1 Exception—The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating Grease
D1742 Test Method for Oil Separation from Lubricating Grease During Storage
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 lubricating grease, n—a semi-fluid to solid product of a dispersion of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—
The dispersion of the thickener forms a two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by surface tension and other
physical forces. Other ingredients are commonly included to impart special properties. D217
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.G0.06 on Functional Tests - Contamination.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2016Nov. 1, 2020. Published January 2017November 2020. Originally approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 20112016
as D4049 – 06 (2011).D4049 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/D4049-16.10.1520/D4049-20.
2
The development of this test method is described in Musilli, T. G., “Water Spray-Off Characteristics of Lubricating Grease,” NLGI Spokesman, December 1982, pp.
323–326.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
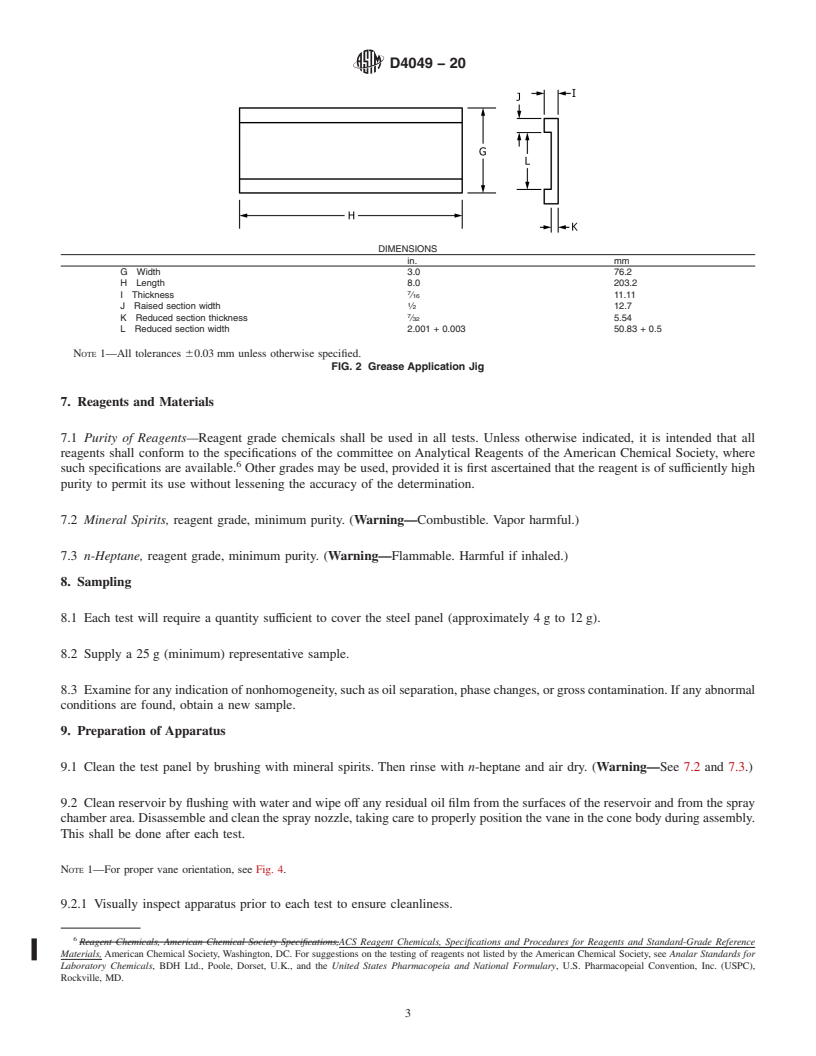
D4049 − 20
DIMENSIONS
in. mm
A Overall panel length 6.0 152.4
B Raised section length 4.0 101.6
C Width 2.000 - 0.002 50.8 - 0.05
03
D Thickness ⁄16 ± 0.003 4.76 ± 0.08
1
E Reduced section thickness ⁄16 1.59
F Reduced section length 1.0 25.4
NOTE 1—All tolerances 60.03 mm unless otherwise specified.
FIG. 1 Stainless Steel Test Panel
3.1.2 oil separation, n—the appearance of a liquid fraction from an otherwise homogeneous lubricating composition. D1742
3.1.3 thickener, n—in lubricating grease, a substance composed of finely divided particles dispersed in a liquid lubricant to form
the product’s structure.
3.1.3.1 Discussion—
The thickeners can be fibers (such as various metallic soaps) or plates or spheres (such as certain non-soap thickeners), which are
insoluble or, at most, only very slightly soluble in the liquid lubricant. The general requirements are that the solid particles be
extremely small, uniformly dispersed, and capable of forming a relatively stable, gel-like structure with the liquid lubricant. D217
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The grease to be tested is coated on a stainless steel panel and sprayed with water at the specified test temperature and pressure.
The amount of grease remaining on the panel after 5 min 6 15 s is a measure of the resistance of the grease to water spray.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is used
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.