ASTM E2469-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Chloride in Mono-, Di- and Tri-ethylene Glycol by Ion Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Chloride in Mono-, Di- and Tri-ethylene Glycol by Ion Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method provides for the quantitative determination of inorganic chloride (chloride ion) in monoethylene glycol (MEG), diethylene glycol (DEG) and triethylene glycol (TEG) using ion chromatography with conductivity detection. The analysis time is less than 5 min with little or no sample preparation required. Conductivity detection is a universal detection mode and is linear over the range of the method. Acceptable levels of chloride in polyester-grade and low-conductivity-grade MEG vary with the manufacturer’s specifications but are normally in the low mg/kg range. Knowledge of the chloride content in polyester-grade and low-conductivity-grade MEG is required to establish whether the MEG product meets specification requirements.
4.2 Glycols have high viscosities and a dilution with high quality deionized water may be required depending on the capability of the autosampler, if used, to deliver the injection. All standards and samples, whether diluted or not should be treated in the same manner.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of inorganic chloride (chloride ion) in monoethylene glycol (MEG), diethylene glycol (DEG) and triethylene glycol (TEG) in the range of 0.01 to 1.0 mg/kg by ion chromatography (IC).
1.2 Ethylene glycol can be analyzed directly by this test method without any sample preparation or diluted with high quality deionized water if an autosampler is used and dilution is necessary (that is, 50:50 or other suitable ratio).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3.1 The exception is the additional information of (psi) in 9.3.3, 11.1.1, and 11.2.1.
1.4 Review the current Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first-aid procedures and safety precautions.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 9.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2469 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Chloride in Mono-, Di- and Tri-ethylene Glycol by Ion
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2469; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of inorganic
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
chloride (chloride ion) in monoethylene glycol (MEG), dieth-
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance
ylene glycol (DEG) and triethylene glycol (TEG) in the range
and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical
of 0.01 to 1.0 mg/kg by ion chromatography (IC).
Measurement System Performance
1.2 Ethylene glycol can be analyzed directly by this test
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
method without any sample preparation or diluted with high
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
3
quality deionized water if an autosampler is used and dilution
cialty Chemicals (Withdrawn 2009)
is necessary (that is, 50:50 or other suitable ratio).
E300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3. Summary of Test Method
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1 An aliquot of the glycol sample is injected directly
standard.
(manually) or diluted (via autosampler) into an ion chromato-
1.3.1 The exception is the additional information of (psi) in
graph consisting of an injector with a fixed sample loop, two
9.3.3, 11.1.1, and 11.2.1.
anion exchange columns (guard and separator column), an
anion suppressor and a conductivity detector. Ions are sepa-
1.4 Review the current Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for de-
rated based on their affinity for the ion exchange sites of the
tailed information concerning toxicity, first-aid procedures and
resin with respect to the resin’s affinity for the eluent. The
safety precautions.
suppressor increases the sensitivity of the test method by both
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
increasing the conductivity of the analytes and decreasing the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
conductivity of the eluent. The suppressor converts the eluent
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
and the analytes to the corresponding hydrogen form acids.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and to
The chloride is detected by conductivity detection and identi-
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to
fied by retention time. Quantitation is by peak area using an
use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 9.
external standard calibration curve. Instructions are provided
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor- for two equivalent IC systems.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4. Significance and Use
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.1 This test method provides for the quantitative determi-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical nation of inorganic chloride (chloride ion) in monoethylene
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
glycol (MEG), diethylene glycol (DEG) and triethylene glycol
(TEG) using ion chromatography with conductivity detection.
The analysis time is less than 5 min with little or no sample
preparation required. Conductivity detection is a universal
detection mode and is linear over the range of the method.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Aromatic, Industrial, Specialty and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsi- contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
bility of Subcommittee D16.14 on Alcohols & Glycols. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2016. Published March 2016. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2006. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as E2469 – 08a. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/E2469-16. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2469 − 08a E2469 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Chloride in Mono-, Di- and Tri-ethylene Glycol by Ion
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2469; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of inorganic chloride (chloride ion) in monoethylene glycol (MEG), diethylene
glycol (DEG) and triethylene glycol (TEG) in the range of 0.01 to 1.0 mg/kg by ion chromatography (IC).
1.2 Ethylene glycol can be analyzed directly by this test method without any sample preparation or diluted with high quality
deionized water if an autosampler is used and dilution is necessary (that is, 50:50 or other suitable ratio).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3.1 The exception is the additional information of (psi) in 9.3.3, 11.1.1, and 11.2.1.
1.4 Review the current Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)(SDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first-aid
procedures and safety precautions.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 9.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical Measure-
ment System Performance
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Specialty Chemicals
3
(Withdrawn 2009)
E300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 An aliquot of the glycol sample is injected directly (manually) or diluted (via autosampler) into an ion chromatograph
consisting of an injector with a fixed sample loop, two anion exchange columns (guard and separator column), an anion suppressor
and a conductivity detector. Ions are separated based on their affinity for the ion exchange sites of the resin with respect to the
resin’s affinity for the eluent. The suppressor increases the sensitivity of the test method by both increasing the conductivity of the
analytes and decreasing the conductivity of the eluent. The suppressor converts the eluent and the analytes to the corresponding
hydrogen form acids. The chloride is detected by conductivity detection and identified by retention time. Quantitation is by peak
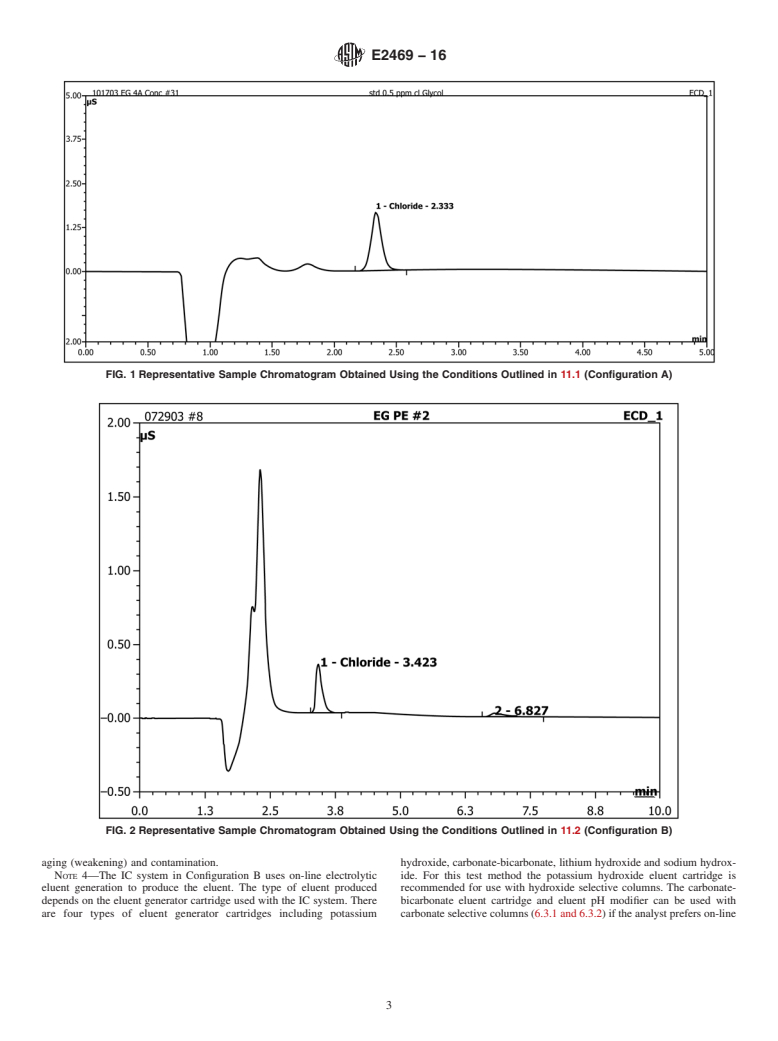
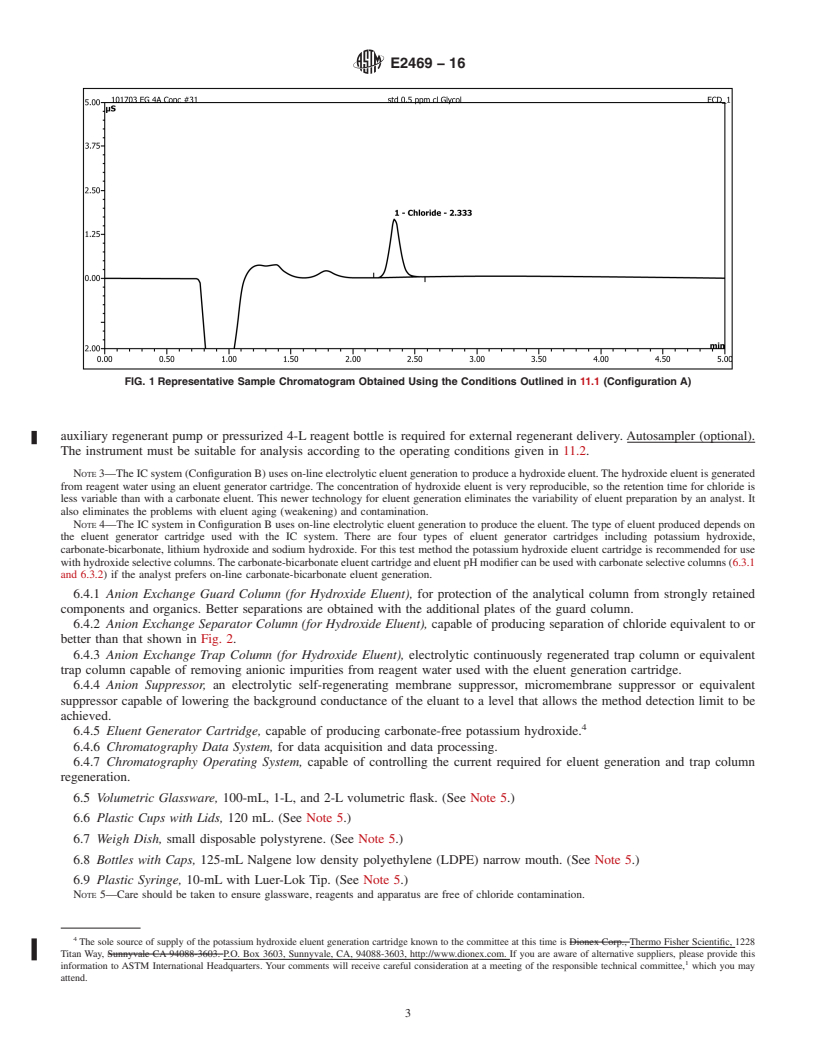
area using an external standard calibration curve. Instructions are provided for two equivalent IC systems.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method provides for the quantitative determination of inorganic chloride (chloride ion) in monoethylene glycol
(MEG), diethylene glycol (DEG) and triethylene glycol (TEG) using ion chromatography with conductivity detection. The analysis
time is less than 5 min with little or no sample preparation required. Conductivity detection is a universal detection mode and is
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E15 on Industrial and Specialty Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E15.02 on
Product Standards.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2008Jan. 1, 2016. Published January 2009March 2016. Originally approved in 2006. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as
E2469 – 08.E2469 – 08a. DOI: 10.1520/E2469-08A.10.1520/E2469-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2469 − 16
linear over the range of the method. Acceptable levels of chloride in polyester-grade and low-conductivity-grade MEG vary with
the manufacturer’s specifications b
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.