ASTM D3799-95
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Purity of Styrene by Freezing Point Method (Withdrawn 2000)
Standard Test Method for Purity of Styrene by Freezing Point Method (Withdrawn 2000)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is used for determining the purity of styrene expressed as weight percent. All impurities are considered to be ethylbenzene.
1.2 The following applies to all specified limits in this standard: for purposes of determining conformance with this standard, an observed value or a calculated value shall be rounded off "to the nearest unit" in the last right-hand digit used in expressing the specification limit, in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E29.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 5 and 7.5.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
~
ASTM D3799 95 m 0759510 0556849 273 m
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
Designation: D 3799 - 95
191 6 Race St Philadelphia. Pa 191 03
#Tb
Reprinted from the Annual Book of Ash Standards. Copyright ASTM
If not Iited in the current combined inde? will appear in the ne>d edition.
Standard Test Method for
Purity of Styrene by Freezing Point Method'
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3799; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope of impurities causes a depression of the freezing point which
is proportional to the molal concentration of the contami-
1.1 This test method is used for determining the purity of
nating substances. The freezing point is the highest tempera-
styrene expressed as weight percent. All impunties are
ture obtained after the supercooling of the liquid. For
considered to be ethylbenzene.
purities over 99 % it is not necessary to plot a time-
1.2 The following applies to all specified limits in this
temperature curve.
standard: for purposes of determining conformance with this
3.2 The freezing point methods, Test Methods D 1015
standard, an observed value or a calculated value shall be
and D 1016, specified a platinum resistance thermometer for
rounded off "to the nearest unit" in the last right-hand digit
measuring the temperature. For routine work, mercury-
used in expressing the specification limit, in accordance with
in-glass thermometers are used. Other temperature-mea-
the rounding-off method of Practice E 29.
suring devices can be utilized in this method provided that
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
they have temperature resolution to 0.0i"C or better. They
standard. The values given in parentheses are for informa-
must be calibrated since small differences in the temperature
tion only.
readings are significant. They must be recalibrated about
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
once per week to correct for differences which may develop
safity concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
with age and handling. To simplify the multiple calibrations
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the freezing point of a large sample of styrene is determined
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
with a platinum resistance thermometer and the mercury-
of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
bility
in-glass or other thermometers calibrated against the stan-
statements are given in Section 5 and 7.5.
dard styrene. Styrene may be kept in a deep freeze for several
months with no appreciable change in the freezing point.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards: 4. Significance and Use
D 1015 Test Method for Freezing Points of High-Purity
4.1 Purity can be calculated by measuring the freezing
Hydrocarbons2
point and relating to a freezing point for zero impurities.
D1016 Test Method for Punty of Hydrocarbons from
4.2 This test method is in wide use for both producer and
Freezing Points2
consumer for determining purity and is suitable for estab-
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water3
lishing specifications.
D 3437 Practice for Sampling and Handling Liquid Cyclic
4.3 All impurities are considered to be ethylbenzene.
Products4
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
5. Hazards
Determine Conformance with Specifications5
5.1 Consult current OSHA regulations, supplier's Mate-
2.2 Other Document:
rial Safety Data Sheets, and local regulations for all materials
OSHA Regulations, 29 CFR, paragraphs 19 10.1000 and
used in this test method.
19 10.1 2006
6. Apparatus
3. Summary of Test Method
6.1 Temperature-Measuring Devices-Temperature-mea-
3.1 The purity of the styrene is determined by a measure-
suring devices can be used, provided they have temperature
ment of the freezing point of the sample in equilibrium with
resolution to 0.01"C or better, are operable in the range from
air at atmospheric pressure. The presence of small amounts
-20 to -40"C, and are calibrated against a platinum
resistance thermometer.
6.2 Styrene Freezing Point Thermometer'-Special de-
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-i6 on
sign for determination of the freezing point of styrene as
Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of
shown in Fig. I and described in Table 1 specification.
Subcommittee D16.OH on Styrene, Ethylbenzene, and C9 and Cio Aromatic
Hydrocarbons.
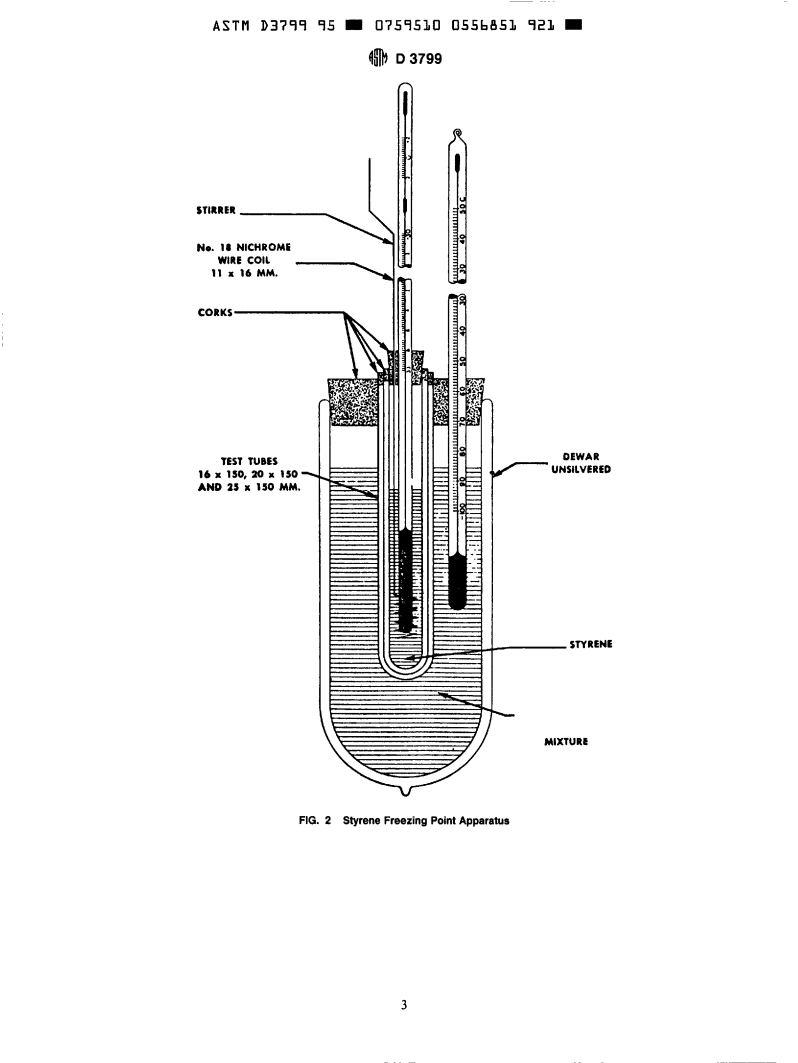
6.3 Freezing Point Apparatus-See Fig. 2 which consists
Current edition approved April 15, 1995. Published June 1995. Originally
of a 665-mL Dewar flask of borosilicate glass, a nest of
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.