ASTM D4815-15b(2019)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of MTBE, ETBE, TAME, DIPE, tertiary-Amyl Alcohol and C1 to C4 Alcohols in Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of MTBE, ETBE, TAME, DIPE, tertiary-Amyl Alcohol and C<inf>1</inf> to C<inf>4</inf> Alcohols in Gasoline by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Ethers, alcohols, and other oxygenates can be added to gasoline to increase octane number and to reduce emissions. Type and concentration of various oxygenates are specified and regulated to ensure acceptable commercial gasoline quality. Drivability, vapor pressure, phase separation, exhaust, and evaporative emissions are some of the concerns associated with oxygenated fuels.
5.2 This test method is applicable to both quality control in the production of gasoline and for the determination of deliberate or extraneous oxygenate additions or contamination.
SCOPE
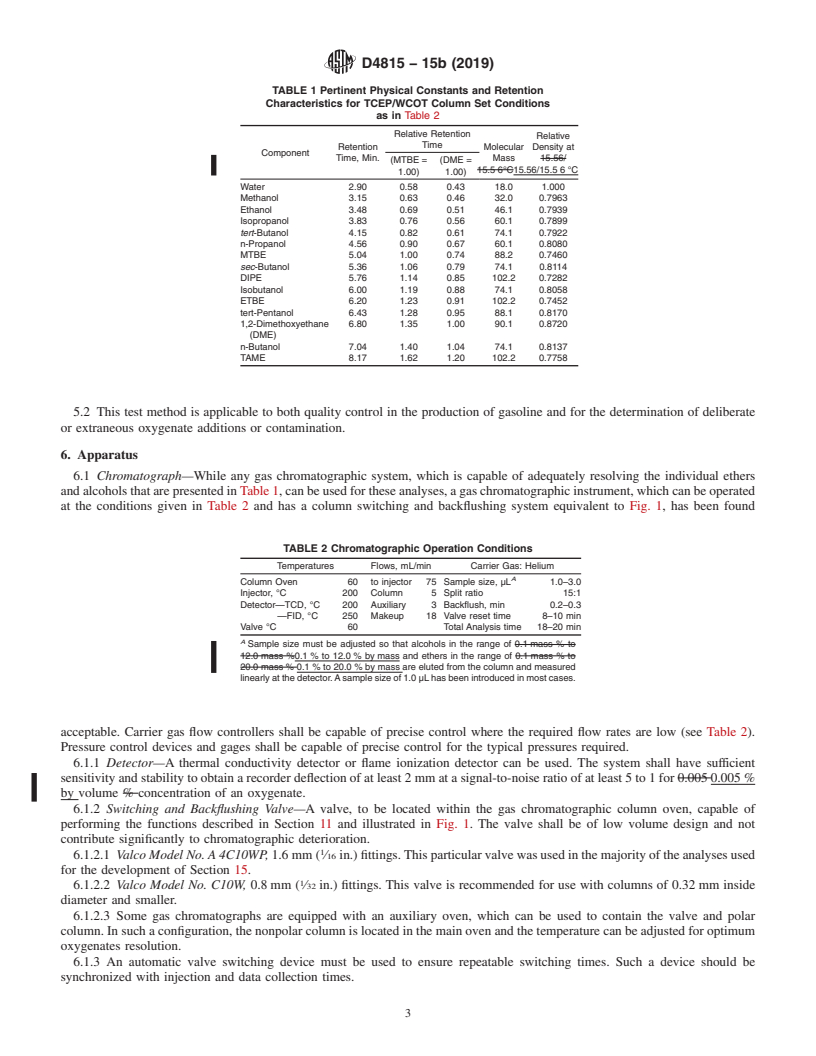
1.1 This test method covers the determination of ethers and alcohols in gasolines by gas chromatography. Specific compounds determined are methyl tert-butylether (MTBE), ethyl tert-butylether (ETBE), tert-amylmethylether (TAME), diisopropylether (DIPE), methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-propanol, isobutanol, tert-butanol, sec-butanol, n-butanol, and tert-pentanol (tert-amylalcohol).
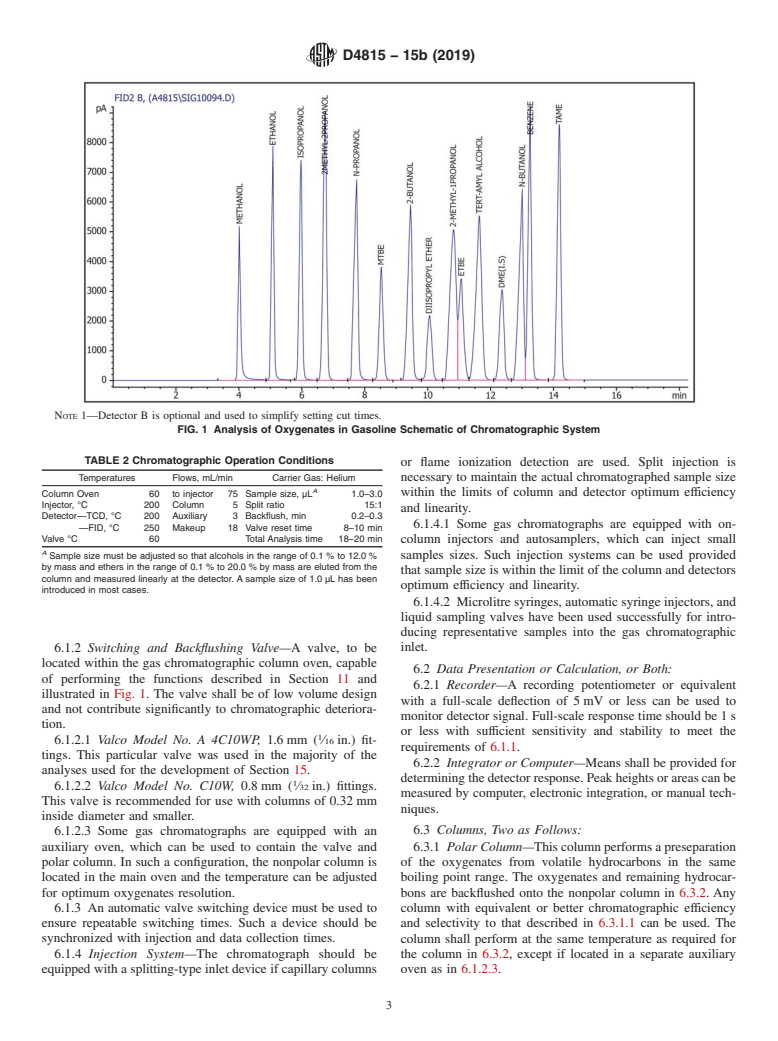
1.2 Individual ethers are determined from 0.20 % to 20.0 % by mass. Individual alcohols are determined from 0.20 % to 12.0 % by mass. Equations used to convert to mass % oxygen and to volume % of individual compounds are provided. At concentrations 10 % by volume olefins, the interference may be >0.20 % by mass. Annex A1 gives a chromatogram showing the interference observed with a gasoline containing 10 % by volume olefins.
1.3 This test method includes a relative bias correlation for ethanol in spark-ignition engine fuels for the U.S. EPA regulations reporting based on Practice D6708 accuracy assessment between Test Method D4815 and Test Method D5599 as a possible Test Method D4815 alternative to Test Method D5599. The Practice D6708 derived correlation equation is only applicable for ethanol in fuels in the concentration range from 2.28 % to 14.42 % by mass as measured by Test Method D4815. The applicable Test Method D5599 range for ethanol is from 2.16 % to 14.39 % by mass as reported by Test Method D5599.
1.4 Alcohol-based fuels, such as M-85 and E-85, MTBE product, ethanol product, and denatured alcohol, are specifically excluded from this test method. The methanol content of M-85 fuel is considered beyond the operating range of the system.
1.5 Benzene, while detected, cannot be quantified using this test method and must be analyzed by alternate methodology (see Test Method D3606).
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Alternate units, in common usage, are also provided to increase clarity and aid the users of this test method.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4815 − 15b (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of MTBE, ETBE, TAME, DIPE, tertiary-Amyl
Alcohol and C to C Alcohols in Gasoline by Gas
1 4
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4815; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope cally excluded from this test method. The methanol content of
M-85 fuel is considered beyond the operating range of the
1.1 This test method covers the determination of ethers and
system.
alcohols in gasolines by gas chromatography. Specific com-
pounds determined are methyl tert-butylether (MTBE), ethyl 1.5 Benzene, while detected, cannot be quantified using this
tert-butylether (ETBE), tert-amylmethylether (TAME), diiso- test method and must be analyzed by alternate methodology
propylether (DIPE), methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, (see Test Method D3606).
n-propanol, isobutanol, tert-butanol, sec-butanol, n-butanol,
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
and tert-pentanol (tert-amylalcohol).
standard. Alternate units, in common usage, are also provided
1.2 Individual ethers are determined from 0.20 % to 20.0 %
to increase clarity and aid the users of this test method.
by mass. Individual alcohols are determined from 0.20 % to
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
12.0 % by mass. Equations used to convert to mass % oxygen
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
and to volume % of individual compounds are provided. At
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
concentrations <0.20 % by mass, it is possible that hydrocar-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
bons may interfere with several ethers and alcohols. The
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
reporting limit of 0.20 % by mass was tested for gasolines
1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
containing a maximum of 10 % by volume olefins. It may be
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
possible that for gasolines containing >10 % by volume
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
olefins, the interference may be >0.20 % by mass. Annex A1
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
gives a chromatogram showing the interference observed with
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
a gasoline containing 10 % by volume olefins.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.3 This test method includes a relative bias correlation for
2. Referenced Documents
ethanol in spark-ignition engine fuels for the U.S. EPA
2
regulationsreportingbasedonPracticeD6708accuracyassess-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ment between Test Method D4815 and Test Method D5599 as
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API
a possible Test Method D4815 alternative to Test Method
Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Prod-
D5599. The Practice D6708 derived correlation equation is
ucts by Hydrometer Method
only applicable for ethanol in fuels in the concentration range
D1744 Test Method for Water in Liquid Petroleum Products
3
from 2.28 % to 14.42 % by mass as measured by Test Method
by Karl Fischer Reagent
D4815.TheapplicableTestMethodD5599rangeforethanolis
D3606 Test Method for Determination of Benzene and
from 2.16 % to 14.39 % by mass as reported by Test Method
Toluene in Spark Ignition Fuels by Gas Chromatography
D5599.
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
1.4 Alcohol-based fuels, such as M-85 and E-85, MTBE
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
product, ethanol product, and denatured alcohol, are specifi-
Petroleum Products
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019. Published December 2019. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D4815 – 15b. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D4815-15BR19. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ---------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4815 − 15b D4815 − 15b (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of MTBE, ETBE, TAME, DIPE, tertiary-Amyl
Alcohol and C to C Alcohols in Gasoline by Gas
1 4
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4815; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of ethers and alcohols in gasolines by gas chromatography. Specific compounds
determined are methyl tert-butylether (MTBE), ethyl tert-butylether (ETBE), tert-amylmethylether (TAME), diisopropylether
(DIPE), methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-propanol, isobutanol, tert-butanol, sec-butanol, n-butanol, and tert-pentanol (tert-
amylalcohol).
1.2 Individual ethers are determined from 0.20 mass % to 20.0 mass %. 0.20 % to 20.0 % by mass. Individual alcohols are
determined from 0.20 mass % to 12.0 mass %. 0.20 % to 12.0 % by mass. Equations used to convert to mass % oxygen and to
volume % of individual compounds are provided. At concentrations <0.20 mass %, <0.20 % by mass, it is possible that
hydrocarbons may interfere with several ethers and alcohols. The reporting limit of 0.20 mass % 0.20 % by mass was tested for
gasolines containing a maximum of 10 volume % olefins.10 % by volume olefins. It may be possible that for gasolines containing
>10 volume % >10 % by volume olefins, the interference may be >0.20 mass %. >0.20 % by mass. Annex A1 gives a
chromatogram showing the interference observed with a gasoline containing 10 volume % 10 % by volume olefins.
1.3 This test method includes a relative bias correlation for ethanol in spark-ignition engine fuels for the U.S. EPA regulations
reporting based on Practice D6708 accuracy assessment between Test Method D4815 and Test Method D5599 as a possible Test
Method D4815 alternative to Test Method D5599. The Practice D6708 derived correlation equation is only applicable for ethanol
in fuels in the concentration range from 2.28 % to 14.42 % by mass as measured by Test Method D4815. The applicable Test
Method D5599 range for ethanol is from 2.16 % to14.39 to 14.39 % by mass as reported by Test Method D5599.
1.4 Alcohol-based fuels, such as M-85 and E-85, MTBE product, ethanol product, and denatured alcohol, are specifically
excluded from this test method. The methanol content of M-85 fuel is considered beyond the operating range of the system.
1.5 Benzene, while detected, cannot be quantified using this test method and must be analyzed by alternate methodology (see
Test Method D3606).
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. Alternate units, in common usage, are also provided to increase
clarity and aid the users of this test method.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2015Dec. 1, 2019. Published December 2015December 2019. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as
D4815 – 15a.D4815 – 15b. DOI: 10.1520/D4815-15B.10.1520/D4815-15BR19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshoho
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.