ASTM E223-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Analysis of Sulfuric Acid
Standard Test Methods for Analysis of Sulfuric Acid
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 These test methods provide for the classification of various grades of sulfuric acid and for the determination of various impurities. Acid strength and impurity levels are important factors in many uses of sulfuric acid.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the analysis of sulfuric acid.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
Sections
Total Acidity
8 to 16
Baumé Gravity
17 to 26
Nonvolatile Matter
27 to 33
Iron
34 to 43
Sulfur Dioxide
44 to 51
Arsenic
52 to 61
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazards statements are given in Section 5.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E223 − 16
Standard Test Methods for
1
Analysis of Sulfuric Acid
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E223; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
1.1 These test methods cover the analysis of sulfuric acid.
3
cialty Chemicals (Withdrawn 2009)
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
E200 Practice for Preparation, Standardization, and Storage
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
of Standard and Reagent Solutions for Chemical Analysis
only.
3. Significance and Use
1.3 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
Sections
3.1 These test methods provide for the classification of
Total Acidity 8 to 16
various grades of sulfuric acid and for the determination of
Baumé Gravity 17 to 26
various impurities. Acid strength and impurity levels are
Nonvolatile Matter 27 to 33
Iron 34 to 43 important factors in many uses of sulfuric acid.
Sulfur Dioxide 44 to 51
Arsenic 52 to 61
4. Purity of Reagents
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
tee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society,
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
Specific hazards statements are given in Section 5.
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
accuracy of the determination.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
to water shall be understood to mean Type II or Type III
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
reagent water conforming to Specification D1193.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Hazards
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 Sulfuric acid is a strong corrosive acid and is dangerous
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
if improperly handled. Avoid any skin or eye contact.
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
5.2 Clean up all spills immediately by covering the spill
E60 Practice for Analysis of Metals, Ores, and Related
with vermiculite or some other inert absorbent material and
Materials by Spectrophotometry
sweeping into a pan. Dispose of the absorbent by flooding with
E100 Specification for ASTM Hydrometers
water and discarding in a suitable container. Flush the area with
water.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on
Aromatic, Industrial, Specialty and Related Chemicals and are the direct responsi-
3
bility of Subcommittee D16.10 on Acids. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
Current edition approved April 1, 2016. Published May 2016. Originally www.astm.org.
4
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as E223 – 08. DOI: Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
10.1520/E0223-16. Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USP), Rockville,
the ASTM website. MD.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E223 − 16
TABLE 1 Sample Size for Total Acidity
H SO , % mass (m/m) Sample Size, g
2 4
98 1.9 to
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E223 − 08 E223 − 16
Standard Test Methods for
1
Analysis of Sulfuric Acid
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E223; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 These test methods cover the analysis of sulfuric acid.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The analytical procedures appear in the following order:
Sections
Total Acidity 8 to 16
Total Acidity 8 to 16
Baumé Gravity 17 to 26
Baumé Gravity 17 to 26
Nonvolatile Matter 27 to 33
Nonvolatile Matter 27 to 33
Iron 34 to 43
Iron 34 to 43
Sulfur Dioxide 44 to 51
Sulfur Dioxide 44 to 51
Arsenic 52 to 61
Arsenic 52 to 61
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific hazards statements are given in Section 5.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E60 Practice for Analysis of Metals, Ores, and Related Materials by Spectrophotometry
E100 Specification for ASTM Hydrometers
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Specialty Chemicals
3
(Withdrawn 2009)
E200 Practice for Preparation, Standardization, and Storage of Standard and Reagent Solutions for Chemical Analysis
3. Significance and Use
3.1 These test methods provide for the classification of various grades of sulfuric acid and for the determination of various
impurities. Acid strength and impurity levels are important factors in many uses of sulfuric acid.
4. Purity of Reagents
4.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all
reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E15 on Industrial and Specialty Chemicals and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E15.02
on Product Standards.
Current edition approved April 1, 2008April 1, 2016. Published May 2008May 2016. Originally approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 20022008 as
ε1
E223 – 96 (2002)E223 – 08. . DOI: 10.1520/E0223-08.10.1520/E0223-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E223 − 16
4
such specifications are available. Other grades may be used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high
purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of the determination.
4.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references to water shall be understood to mean Type II or Type III reagent
water conforming to Specification D1193.
5. Hazards
5.1 Sulfuric acid is a strong corrosive acid and is dangerous if improperly handled. Avoid any skin or eye contact.
5.2 Clean up all spills immediately by covering the spill with vermiculite or some other inert absorbent material and sweeping
into a pan. Dispose of the absorbent by flooding with water and discarding in a suitable container. Flush the area with water.
6. Photometers and Photometric Practice
6.1 Photometers and the photometric practice used in these test methods shall conform to Practice E60.
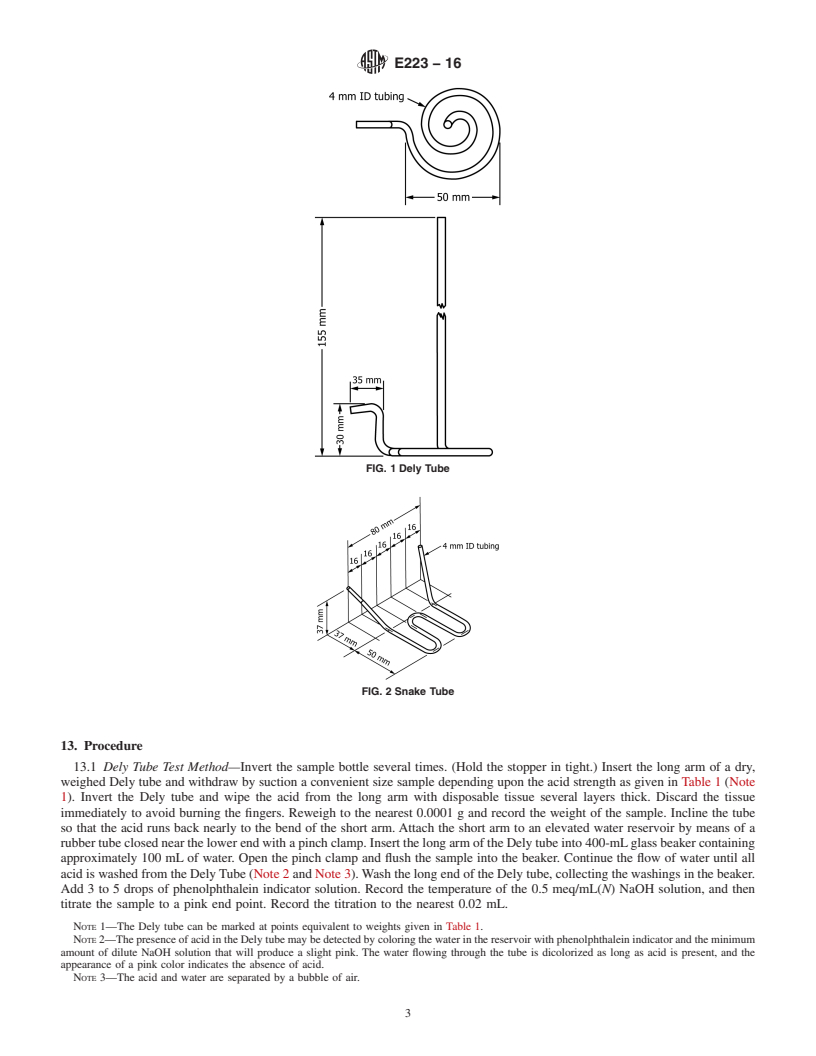
7. Sampling
7.1 Sampling of sulfuric acid is not within the scope of these test methods.
7.2 The sample to be analyzed shall be considered to be that sample in a single bottle submitted to the analytical laboratory.
7.3 The siz
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.