ASTM D5167-03
(Practice)Standard Practice for Melting of Hot-Applied Joint and Crack Sealant and Filler for Evaluation
Standard Practice for Melting of Hot-Applied Joint and Crack Sealant and Filler for Evaluation
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
It is intended that this practice be used by manufacturers, users, and testing agencies. The use of this practice establishes a uniform procedure for the melting or heating of hot-applied sealants and fillers. It is not intended to establish test procedures or conditions of test which are associated with each of the joint sealants and fillers.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice establishes the procedure for melting or heating, or both, of hot-applied joint and crack sealants and fillers in preparation for the making of test specimens used in the laboratory evaluations of the sealants and fillers. Refer to the specific standard material specification for sampling requirements, test sample quantity, temperatures and times for melting and heating, and the number of specimens required for testing.
1.2 This practice is applicable to the hot-applied joint and crack sealants and fillers used in both portland cement and asphaltic-concrete pavements.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautions see Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5167–03
Standard Practice for
Melting of Hot-Applied Joint and Crack Sealant and Filler for
1
Evaluation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5167; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E171 Specification for Atmospheres for Conditioning and
Testing Flexible Barrier Materials
1.1 This practice establishes the procedure for melting or
heating, or both, of hot-applied joint and crack sealants and
3. Terminology
fillers in preparation for the making of test specimens used in
3.1 Definitions—Refer to Terminology D5535 for defini-
the laboratory evaluations of the sealants and fillers. Refer to
tions of the following terms used in this specification: maxi-
the specific standard material specification for sampling re-
mum heating temperature, minimum application temperature.
quirements, test sample quantity, temperatures and times for
melting and heating, and the number of specimens required for
4. Significance and Use
testing.
4.1 It is intended that this practice be used by manufactur-
1.2 This practice is applicable to the hot-applied joint and
ers, users, and testing agencies. The use of this practice
crack sealants and fillers used in both portland cement and
establishes a uniform procedure for the melting or heating of
asphaltic-concrete pavements.
hot-applied sealants and fillers. It is not intended to establish
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
test procedures or conditions of test which are associated with
standard. The values in parentheses are provided for informa-
each of the joint sealants and fillers.
tion purposes only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5. Standard Conditions
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5.1 The laboratory atmospheric conditions, hereinafter re-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ferred to as standard conditions, shall be as detailed in
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Specification E171171, 23 6 2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 %
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
relative humidity 65 %. The material shall be conditioned for
precautions see Section 7.
24 h at standard conditions before melting or heating.
2. Referenced Documents
6. Apparatus
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6.1 Laboratory Melter:
D5535 Terminology Relating to Formed-in-Place Sealants
6.1.1 The equipment for melting of the joint sealant or filler
3
for Joints and Cracks in Pavements
shall be an oil jacketed melter equipped with a mechanical
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
agitator and thermometers for the oil bath and material in the
E77 Test Method for Inspection and Verification of Ther-
melting vat.
mometers
6.1.2 The heat transfer oil shall be a high flash point oil, that
is, in excess of 315°C (600°F).
6.1.3 The heat source shall be thermostatically controlled
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road and
and capable of maintaining the heat transfer oil temperature
Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.33 on
Formed-In-Place Sealants for Joints and Cracks in Pavements.
within a tolerance of 63°C (65°F) and capable of heating the
Current edition approved July 10, 2003. Published September 2003. Originally
oil to a maximum of 288°C (550°F).
approved in 1991. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as D5167 – 91 (1997).
6.1.4 Themechanicalagitatorspeedforthematerialshallbe
DOI: 10.1520/D5167-03.
2
30 6 5 rpm when fully loaded and the agitator speed for the oil
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
bath shall be such to allow continuous circulation of the oil.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
6.1.5 Except when adding the sealant or filler sample, or
the ASTM website.
3
checking temperature, the melter’s pots shall be covered with
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
on www.astm.org. close fitting lids.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5167–03
must be taken when using this type of melter. Check the manufacturer’s
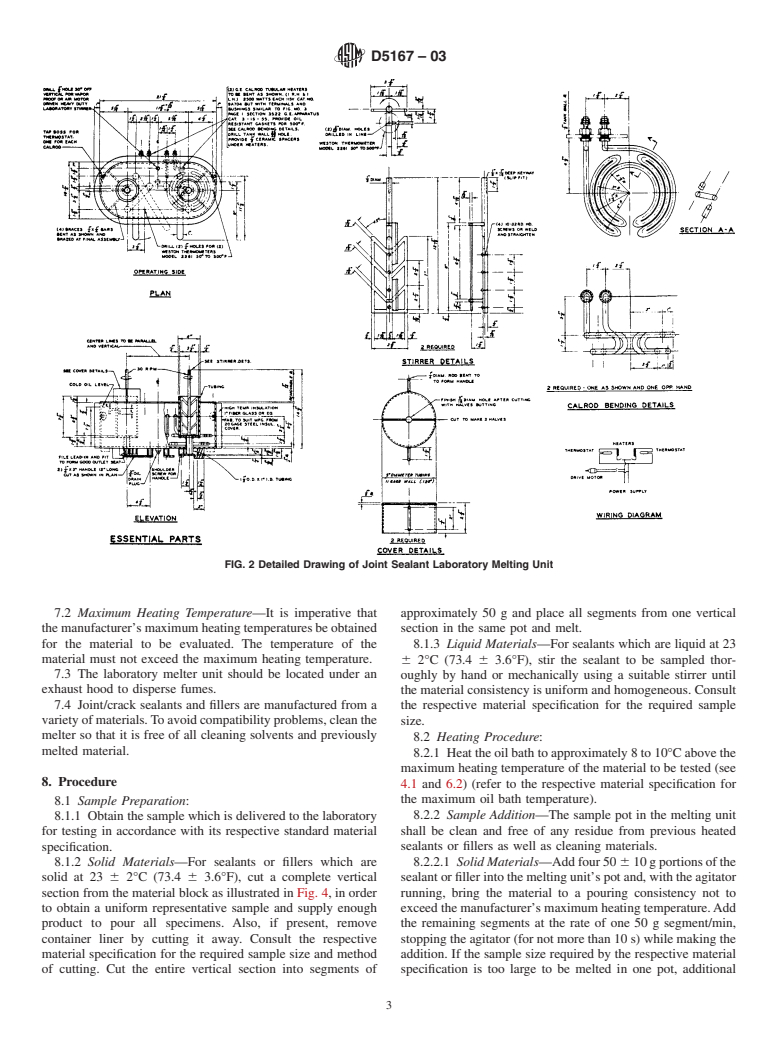
6.1.6 Refer to Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 (bottom discharge type) and
recommended safety procedures before use.
Fig.3(removablecantype)fortypicallaboratorymelters.Also
see Note 1.
7. Precautions
6.2 The thermometers use
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.