ASTM C1479M-16
(Practice)Standard Practice for Installation of Precast Concrete Sewer, Storm Drain, and Culvert Pipe Using Standard Installations (Metric)
Standard Practice for Installation of Precast Concrete Sewer, Storm Drain, and Culvert Pipe Using Standard Installations (Metric)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This practice is useful as a reference by an owner and the owner's engineer in preparing project specifications.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the installation of precast concrete pipe intended to be used for the conveyance of sewage, industrial wastes, and storm water, and for the construction of culverts.
1.2 This practice is the SI companion to Practice C1479.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1479M − 16
Standard Practice for
Installation of Precast Concrete Sewer, Storm Drain, and
1
Culvert Pipe Using Standard Installations (Metric)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1479M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope IEEE/ASTM SI 10 Standard for Use of the International
System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
1.1 This practice covers the installation of precast concrete
3
pipe intended to be used for the conveyance of sewage, 2.2 AASHTO Standards:
industrial wastes, and storm water, and for the construction of
Standard Specifications for Highway Bridges
culverts. M 145 Classification of Soils and Soil—Aggregate Mixtures
for Highway Construction Purposes
1.2 This practice is the SI companion to Practice C1479.
T99 The Moisture-Density Relations of Soils Using a 5.5-lb
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
(2.5-kg) Rammer and a 12-in. (305-mm) Drop
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
T 180 The Moisture-Density Relations of Soils Using a
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
10-lb (4.54-kg) Rammer and an 18-in. (457-mm) Drop
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
T 310 In-Place Density and Moisture Content of Soil and
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Soil-Aggregate by Nuclear Methods (Shallow Depth)
4
2.3 ASCE Standard:
2. Referenced Documents
ASCE 15 Standard Practice for the Direct Design of Buried
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Precast Reinforced Concrete Pipe Using Standard Instal-
C822 Terminology Relating to Concrete Pipe and Related
lations (SIDD)
Products
C1417 Specification for Manufacture of Reinforced Con-
3. Terminology
crete Sewer, Storm Drain, and Culvert Pipe for Direct
3.1 For definitions of terms relating to concrete pipe, see
Design
C1479 Practice for Installation of Precast Concrete Sewer, Terminology C822.
Storm Drain, and Culvert Pipe Using Standard Installa-
3.2 For terminology related to soil classifications, see Prac-
tions
tices D2487 and D2488.
D698 Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Character-
3
istics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12,400 ft-lbf/ft (600 3.3 For terminology and definitions of terms relating to
3
kN-m/m )) structural design, see ASCE 15.
D1557 Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Character-
3.4 Fig. 1 illustrates the definitions and limits of the terms:
3
istics of Soil Using Modified Effort (56,000 ft-lbf/ft
foundation, subgrade, bedding, outer bedding, middle bedding,
3
(2,700 kN-m/m ))
haunch, lower side, backfill or overfill, invert, crown,
D2487 Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering
springline, top of pipe, and bottom of pipe as used in this
Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System)
practice.
D2488 Practice for Description and Identification of Soils
(Visual-Manual Procedure)
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This practice is useful as a reference by an owner and
the owner’s engineer in preparing project specifications.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C13 on Concrete
Pipe and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C13.05 on Special Projects.
Current edition approved Oct. 15, 2016. Published October 2016. Originally
approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as C1479M - 13. DOI:
3
10.1520/C1479M-16. Available from American Association of State Highway and Transportation
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Officials (AASHTO), 444 N. Capitol St., NW, Suite 249, Washington, DC 20001,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM http://www.transportation.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), 1801 Alexander
the ASTM website. Bell Dr., Reston, VA 20191, http://www.asce.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1479M − 16
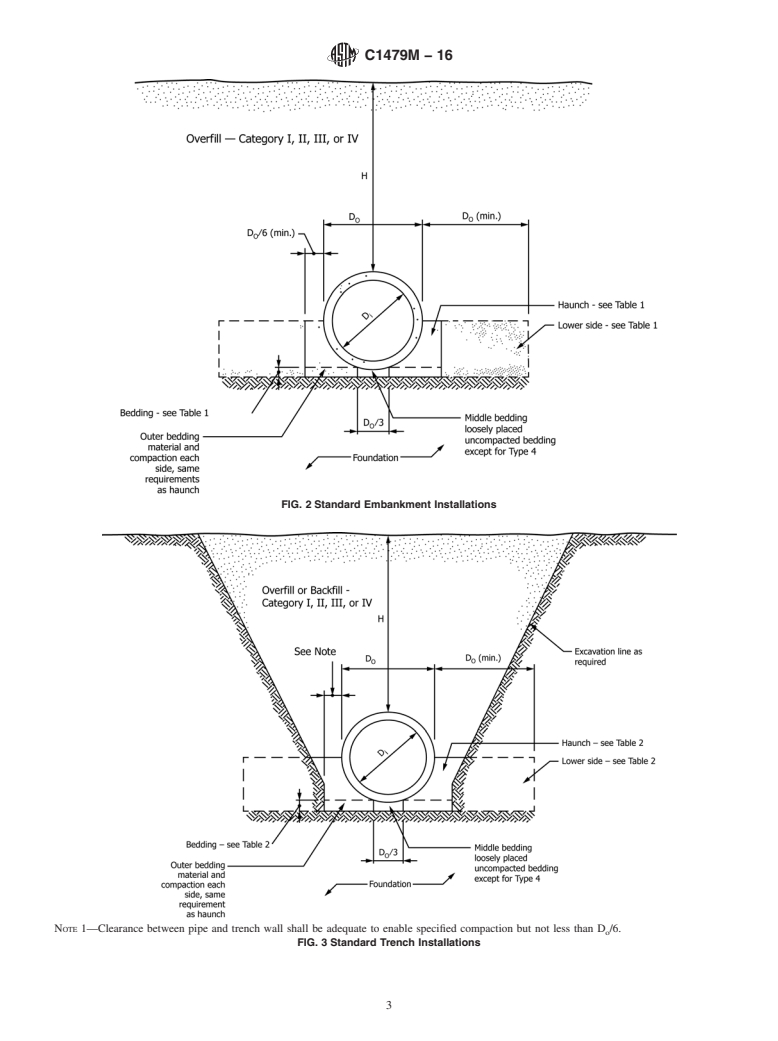
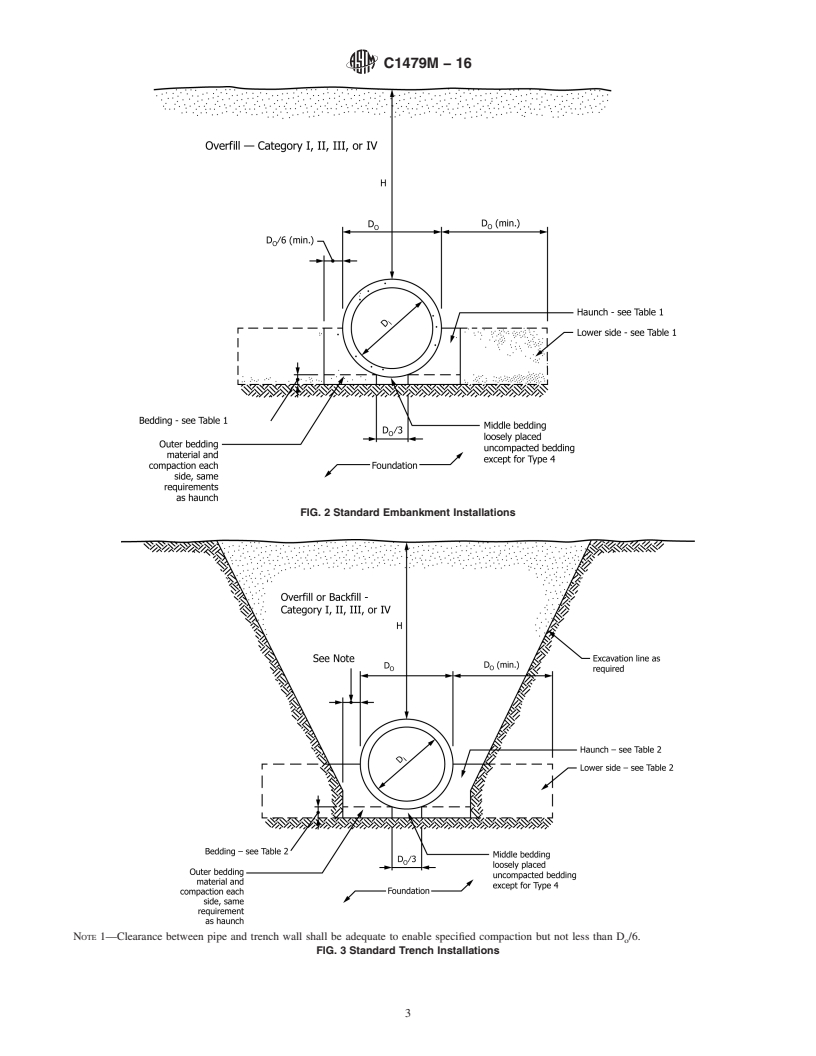
FIG. 1 Pipe/Installation Terminology
5. Notations 8. Foundation
8.1 The foundation shall be moderately firm to hard in situ
D = inside diameter of pipe, mm.
i
soil, stabilized soil, or compacted fill material.
D = outside diameter of pipe, mm.
o
H = design height of earth above top of pipe, m.
8.2 When unsuitable or unstable material is encountered,
3
w = unit weight of soil, N/m .
the foundation shall be stabilized.
8.3 Methods to prevent migration of soil fines shall be
6. Standard Installations
provided when groundwater or exis
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1479M − 13 C1479M − 16
Standard Practice for
Installation of Precast Concrete Sewer, Storm Drain, and
1
Culvert Pipe Using Standard Installations (Metric)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1479M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers the installation of precast concrete pipe intended to be used for the conveyance of sewage, industrial
wastes, and storm water, and for the construction of culverts.
1.2 This practice is the SI companion to Practice C1479.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C822 Terminology Relating to Concrete Pipe and Related Products
C1417 Specification for Manufacture of Reinforced Concrete Sewer, Storm Drain, and Culvert Pipe for Direct Design
C1479 Practice for Installation of Precast Concrete Sewer, Storm Drain, and Culvert Pipe Using Standard Installations
3 3
D698 Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12,400 ft-lbf/ft (600 kN-m/m ))
3
D1557 Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Modified Effort (56,000 ft-lbf/ft (2,700
3
kN-m/m ))
D2487 Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System)
D2488 Practice for Description and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual Procedure)
IEEE/ASTM SI 10 Standard for Use of the International System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
3
2.2 AASHTO Standards:
Standard Specifications for Highway Bridges
M 145 Classification of Soils and Soil—Aggregate Mixtures for Highway Construction Purposes
T 99 The Moisture-Density Relations of Soils Using a 5.5-lb (2.5-kg) Rammer and a 12-in. (305-mm) Drop
T 180 The Moisture-Density Relations of Soils Using a 10-lb (4.54-kg) Rammer and an 18-in. (457-mm) Drop
T 310 In-Place Density and Moisture Content of Soil and Soil-Aggregate by Nuclear Methods (Shallow Depth)
4
2.3 ASCE Standard:
ASCE 15 Standard Practice for the Direct Design of Buried Precast Reinforced Concrete Pipe Using Standard Installations
(SIDD)
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of terms relating to concrete pipe, see Terminology C822.
3.2 For terminology related to soil classifications, see Practices D2487 and D2488.
3.3 For terminology and definitions of terms relating to structural design, see ASCE 15.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C13 on Concrete Pipe and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C13.05 on Special Projects.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2013Oct. 15, 2016. Published February 2013October 2016. Originally approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 20122013
as C1479M – 12.C1479M - 13. DOI: 10.1520/C1479M-13.10.1520/C1479M-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO), 444 N. Capitol St., NW, Suite 249, Washington, DC 20001,
http://www.transportation.org.
4
Available from American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), 1801 Alexander Bell Dr., Reston, VA 20191, http://www.asce.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1479M − 16
3.4 Fig. 1 illustrates the definitions and limits of the terms: foundation, subgrade, bedding, outer bedding, middle bedding,
haunch, lower side, backfill or overfill, invert, crown, springline, top of pipe, and bottom of pipe as used in this practice.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This practice is useful as a reference by an owner and the owner’s engineer in preparing project specifications.
5. Notations
D = inside diameter of pipe, mm
i
D = inside diameter of pipe, mm.
i
D = outside diameter of pipe, mm.
o
H = design height of earth above top of pipe, m.
3
w = unit weight of soil, N/m
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.