ASTM E2141-01
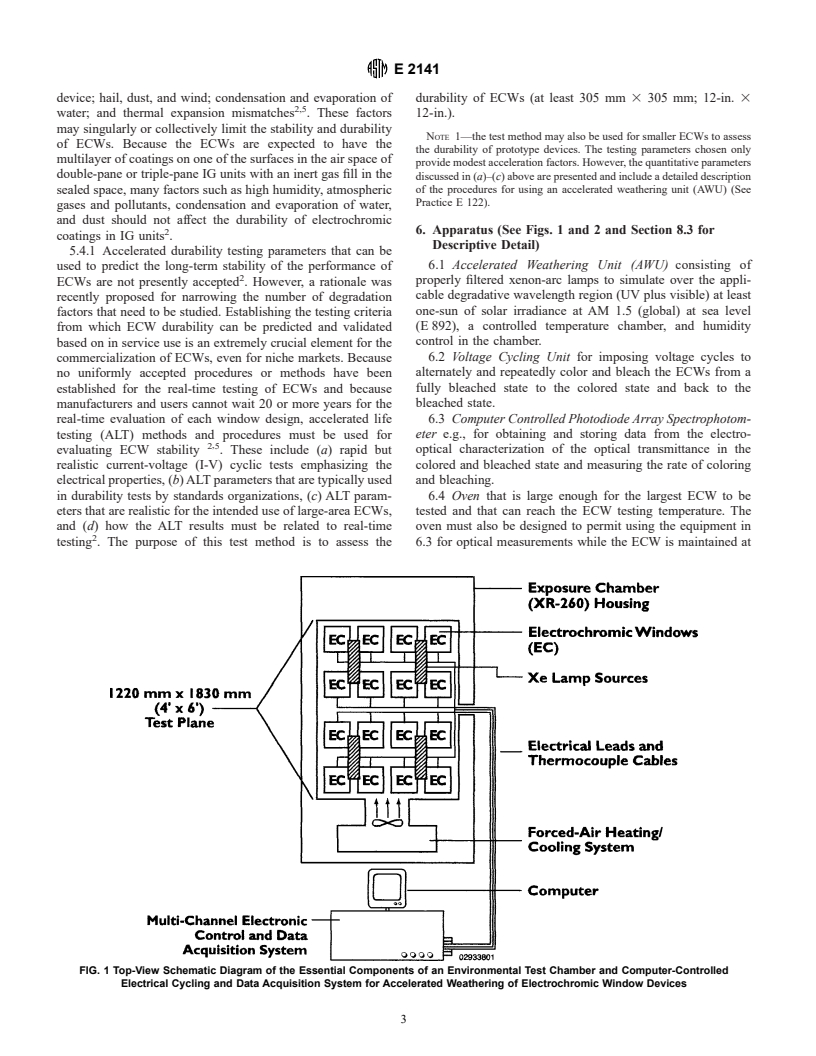
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Assessing the Durability of Absorptive Electrochromic Coatings on Sealed Insulating Glass Units
Standard Test Methods for Assessing the Durability of Absorptive Electrochromic Coatings on Sealed Insulating Glass Units
SCOPE
1.1 The tests described are methods for the accelerated aging and monitoring of the time-dependent performance of electrochromic windows. Cross sections of typical electrochromic windows are shown in which devices have four or five-layers of coatings that include the two or three active layers sandwiched between transparent conducting electrodes (TCEs, see Section 3).
1.2 The test methods are applicable only for multilayered (two or more coatings between the TCEs) absorptive electrochromic coatings on sealed insulating glass (IG) units fabricated for vision glass (superstrate and substrate) areas for use in buildings, such as sliding doors, windows, skylights, and exterior wall systems. The multilayers used for electrochromically changing the optical properties may be inorganic or organic materials between the superstrate and substrate.
1.3 The electrochromic coatings used in this test method are exposed to solar radiation and are deployed to control the amount of radiation by absorption and reflection and thus, limit the solar heat gain and amount of solar radiation that is transmitted into the building.
1.4 The test methods are not applicable to other chromogenic devices, e.g., photochromic and thermochromic devices.
1.5 The test methods are not applicable to electrochromic devices consisting of three layers of coatings including the two transparent conducting electrodes (see Section 3 ).
1.6 The test methods are not applicable to electrochromic windows that are constructed from superstrate or substrate materials other than glass.
1.7 The test methods referenced herein are laboratory tests conducted under specified conditions. These tests are intended to simulate and, in some cases, to also accelerate actual in-service use of the electrochromic windows. Results from these tests cannot be used to predict the performance with time of in-service units unless actual corresponding in-service tests have been conducted and appropriate analyses have been conducted to show how performance can be predicted from the accelerated aging tests.
1.8 The values stated in metric (SI) units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: E 2141 – 01
Standard Test Methods for
Assessing the Durability of Absorptive Electrochromic
1
Coatings on Sealed Insulating Glass Units
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 2141; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope accelerated aging tests.
1.8 The values stated in metric (SI) units are to be regarded
1.1 The tests described are methods for the accelerated
as the standard.
aging and monitoring of the time-dependent performance of
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
electrochromic windows. Cross sections of typical electrochro-
2
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
mic windows are shown in which devices have four or
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
five-layers of coatings that include the two or three active
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
layers sandwiched between transparent conducting electrodes
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
(TCEs, see Section 3).
1.2 The test methods are applicable only for multilayered
2. Referenced Documents
(two or more coatings between the TCEs) absorptive electro-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
chromic coatings on sealed insulating glass (IG) units fabri-
3
C 168 Terminology Relating to Building Materials
cated for vision glass (superstrate and substrate) areas for use
C 1199 Test Method for Measuring the Steady State Ther-
in buildings, such as sliding doors, windows, skylights, and
mal Transmittance of Fenestration Systems Using Hot Box
exterior wall systems. The multilayers used for electrochromi-
3
Methods
cally changing the optical properties may be inorganic or
E 122 Practice for Choice of Sample Size to Estimate a
organic materials between the superstrate and substrate.
4
Measure of Quality for a Lot or Process
1.3 The electrochromic coatings used in this test method are
E 632 Practice to Aid Prediction of Service Life of Building
exposed to solar radiation and are deployed to control the
3
Components and Materials
amount of radiation by absorption and reflection and thus, limit
E 773 Test Method for Accelerated Weathering of Sealed
the solar heat gain and amount of solar radiation that is
3
Insulating Glass Units
transmitted into the building.
E 774 Specification for the Classification of the Durability
1.4 The test methods are not applicable to other chromoge-
3
of Sealed Insulating Glass Units
nic devices, e.g., photochromic and thermochromic devices.
E 891 Tables for Terrestrial Direct Normal Solar Spectral
1.5 The test methods are not applicable to electrochromic
3
Irradiance for Air Mass 1.5
devices consisting of three layers of coatings including the two
E 892 Tables for Terrestrial Solar Spectral Irradiance at Air
transparent conducting electrodes (see Section 3).
3
Mass 1.5 for a 37º Tilted Surface
1.6 The test methods are not applicable to electrochromic
E 903 Test Method for Solar Absorptance, Reflectance, and
windows that are constructed from superstrate or substrate
3
Transmittance of Materials Using Integrating Spheres
materials other than glass.
E 1423 Practice for Determining the Steady State Thermal
1.7 The test methods referenced herein are laboratory tests
3
Transmittance of Fenestration Systems
conducted under specified conditions. These tests are intended
3
E 1887 Test Method for Fog Determination
to simulate and, in some cases, to also accelerate actual
E 2094 Practice for Evaluating the Service Lifetime of
in-service use of the electrochromic windows. Results from
3
Chromogenic Glazings
these tests cannot be used to predict the performance with time
G 113 Terminology Relating to Natural and Artificial
of in-service units unless actual corresponding in-service tests
3
Weathering Tests of Non- Metallic Materials
have been conducted and appropriate analyses have been
G 151 Practice for Exposing Nonmetallic Materials in ac-
conducted to show how performance can be predicted from the
3
celerated Test Devices that Use Laboratory Light Source
G 155 Practice for Operating Xenon Arc Light Apparatus
1 3
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
for Exposure of Non-Metallic Materials
Performance of Building Constructions and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
2.2 Canadian Standards:
mittee E06.22 on Durability of Building Constructions.
Current edition approved April 10, 2001. Published August 2001.
2
A. W. Czanderna and C. M. Lampert, “Evaluation Criteria and Test Methods for
3
Electrochromic Windows,” SERI/PR-255-3537 (July 1990), Golden, CO: Solar Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07.
4
Energy Research Institute. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-29
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.