ASTM D178-01(2005)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Rubber Insulating Matting
Standard Specification for Rubber Insulating Matting
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the acceptance testing of insulating rubber matting that are used as a floor covering for the personal protection of workers. The sheeting shall be made from any elastomer or combination of elastomeric compounds. Two types of matting, differing in chemical and physical characteristics, are provided and are designated as Type I, which has been properly vulcanized, and Type II, which has one or more of the following special properties: (A) ozone resistance; (B) flame resistance; and (C) oil resistance. Five classes of matting, designated as Classes 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4, are assigned according to electrical protection characteristics. When evaluated in accordance with the test procedures detailed herein, the matting shall adhere to the following property requirements: electrical properties such as phase-phase maximum use voltage, AC and DC proof-test voltages, AC and DC dielectric breakdown test voltages, and AC and DC electrode clearances; an physical and chemical properties such as moisture absorption, oil resistance, tensile strength, tension set, elongation, resistance to accelerated heat aging, and flame resistance.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers acceptance testing of rubber insulating matting for use as a floor covering for protection of workers.
1.2 Two types of matting, differing in chemical and physical characteristics, are provided and are designated as Type I and Type II matting.
The following safety hazards caveat applies only to the test method portion, Sections to , of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Note 1
Rubber insulating matting should remain flexible for use through normal temperature ranges.Note 2
Rubber as used in this specification is a generic term that includes elastomers and elastomer compounds, regardless of origin.
1.3 This test method covers a small-scale horizontal laboratory screening procedure for measuring the rate, extent, or time, or a combination thereof, of burning of rigid or flexible cellular plastics in accordance with this test procedure.
1.4 Materials that exhibit pronounced shrinking, curling, or melting away upon heating cannot be evaluated by this test method.
1.5 This test method is not applicable to materials that cannot be ignited under the conditions of this test, or to materials that exhibit progressive combustion without flame (continued glowing or charring).Note 3
The rate of burning or extent of burning of rigid cellular plastics also may be determined by Test Method D 3014 where the specimen is supported vertically.
1.5.1 Warning-During the course of combustion, gases or vapors, are evolved that may be hazardous to personnel. Adequate precautions should be taken to protect the operator.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D178 – 01 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Specification for
Rubber Insulating Matting
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D178; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope D570 Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics
D573 Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air
1.1 This specification covers acceptance testing of rubber
Oven
insulating matting for use as a floor covering for protection of
D1692 Discontinued 1978; Method of Test for Rate of
workers.
BurningorExtentandTimeofBurningofCellularPlastics
1.2 Twotypesofmatting,differinginchemicalandphysical
Using a Specimen Supported by a Horizontal Screen
characteristics, are provided and are designated as Type I and
2.2 American National Standard:
Type II matting.
ANSI C84.1 Voltage Ratings for Electric Power Systems
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat applies only to the
and Equipment (60 Hz)
test method portion, Sections 17 to 19, of this specification:
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety
3. Terminology
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
3.1 Definitions:
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and
3.1.1 user, n—as used in 4.3.1, the entity employing the
health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
actual worker(s) utilizing the equipment; if no separate em-
limitations prior to use.
ployer, then the individual.
NOTE 1—Rubber insulating matting should remain flexible for use
3.1.2 voltage, maximum retest, n—voltage, either ac rms or
through normal temperature ranges.
dc avg, which is equal to the proof-test voltage for new
NOTE 2—Rubber as used in this specification is a generic term that
protective equipment.
includes elastomers and elastomer compounds, regardless of origin.
3.1.3 voltage, retest, n—voltage, either ac rms or dc avg,
2. Referenced Documents that used protective equipment must be capable of withstand-
ing for a specified test period without breakdown.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.4 voltage, nominal design, n—a nominal value consis-
D149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
tent with the latest revision of ANSI C84.1, assigned to the
Dielectric Strength of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials
circuit or system for the purpose of conveniently designating
at Commercial Power Frequencies
its voltage class.
D297 TestMethodsforRubberProducts—ChemicalAnaly-
3.1.5 voltage, maximum use, n—the ac voltage (rms) clas-
sis
sification of the protective equipment that designates the
D412 Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermo-
maximum nominal design voltage of the energized system that
plastic Elastomers—Tension
may be safely worked. The nominal design voltage is equal to
D471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
phase-to-phase voltage on multiphase circuits.
D518 Test Method for Rubber Deterioration—Surface
3.1.5.1 If there is no multiphase exposure in a system area,
Cracking
and the voltage exposure is limited to phase (polarity on dc
systems) to ground potential, the phase (polarity on dc sys-
1 tems) to ground potential shall be considered to be the nominal
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F18 on
Electrical Protective Equipment for Workers and is the direct responsibility of design voltage.
Subcommittee F18.25 on Insulating Cover-Up Equipment. This standard replaces
3.1.5.2 If electrical equipment and devices are insulated, or
ANSI Standard J 6.7, which is no longer available.
isolated, or both, such that the multiphase exposure on a
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2005. Published November 2005. Originally
´2.
grounded wye circuit is removed, then the nominal design
approved in 1923. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D178 – 01 DOI:
10.1520/D0178-01R05.
voltage may be considered as the phase-to-ground voltage on
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
that circuit.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd Street,
on www.astm.org. 13th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D178 – 01 (2005)
4. Significance and Use 6. Ordering Information
4.1 This specification covers the minimum electrical,
6.1 Orders for matting under this specification should in-
chemical, and physical properties guaranteed by the manufac-
clude the following information:
turer and the detailed procedures by which such properties are
6.1.1 Type,
to be determined. The purchaser may at his option perform or
6.1.2 Class,
have performed any of these tests in order to verify the
6.1.3 Thickness,
guarantee. Claims for failure to meet the specification are
6.1.4 Width,
subject to verification by the manufacturer.
6.1.5 Length, and
4.2 Rubber insulating matting is used for personal protec-
6.1.6 Color.
tion; therefore when authorizing its use a margin of safety
6.2 The listing of types, classes, thicknesses, widths,
should be allowed between the maximum voltage at which it is
lengths, and colors is not intended to mean that all shall
used and the proof-test voltage at which it is tested. The
necessarily be available from manufacturers; it signifies only
relationship between proof-test and the maximum voltage at
that, if made, they shall conform to the details of this
which matting shall be used is shown in Table 1.
specification.
4.3 Work practices vary from user to user, depending upon
many factors. These may include, but are not limited to,
7. Manufacture and Marking
operating system voltages, construction design, work proce-
dures and techniques, weather conditions etc. Therefore, ex- 7.1 The matting shall consist of a rubber compound with a
ceptfortherestrictionssetforthinthisspecificationbecauseof smooth,corrugated,ordiamonddesignononesurfaceandmay
design limitations, the use and maintenance of this equipment be backed with fabric, or may have one or more fabric inserts.
is beyond the scope of this specification The back of the matting may be finished with cloth imprint or
4.3.1 Itiscommonpracticeandtheresponsibilityoftheuser other slip-resistant material. Any such fabric insert shall not
of this type of protective equipment to prepare complete affect adversely the dielectric characteristics of the matting.
instructions and regulations to govern the correct and safe use
7.2 Each piece of matting shall be marked clearly and
of such equipment. permanently at a maximum interval of1m(3ft) with the name
of the manufacturer or supplier, ASTM D178, type, and class.
5. Classification
8. Dimensions and Permissible Variations
5.1 Matting covered under this specification shall be desig-
nated as Type I or Type II; Class 0, Class 1, Class 2, Class 3,
8.1 Width—Standard widths shall be 610 6 13 mm (24.0 6
or Class 4.
0.5 in.), 760 6 13 mm (30.0 6 0.5 in.), 914 6 25 mm (36 6
5.1.1 Type I, made of any elastomer or combination of
1 in.) and 12206 25 mm (48 6 1 in.).
elastomer compounds, properly vulcanized.
8.2 Thickness—The thickness of the matting shall be as
5.1.2 Type II, made of any elastomer or combination of
specified in Table 3. Measurements shall be made over the
elastomeric compounds with one or more of the following
corrugations or diamonds. The corrugations shall be not more
special properties:
than3.2mm(0.125in.)deep.Thediamondsshallnotbehigher
5.1.2.1 A—Ozone resistance
than 1.6 mm (0.062 in.).
5.1.2.2 B—Flame resistance
5.1.2.3 C—Oil resistance
9. Workmanship and Finish
5.1.3 The class designation shall be based on the electrical
9.1 The matting shall be free of harmful physical irregulari-
properties as shown in Table 2.
ties, which can be detected by thorough test or inspection.
9.1.1 Nonharmful Irregularities—Surfaceirregularitiesmay
TABLE 1 Proof Test/Use Voltage Relationship
be present on all rubber matting due to imperfections in molds
and inherent difficulties in the manufacturing processes. These
NOTE 1—The ac voltage (rms) classification of the protective equip-
irregularities may appear as indentations, protuberances, or
ment designates the maximum nominal design voltage of the energized
imbedded foreign material that are acceptable provided that:
systemthatmaybesafelyworked.Thenominaldesignvoltageisequalto:
a. The phase to phase on multiphase circuits or
9.1.1.1 The indentation or protuberance tends to blend into
b. The phase to ground voltage on single phase grounded circuits.
a smooth slope upon stretching of the material.
Nominal Maximum
9.1.1.2 The rubber thickness at any irregularity conforms to
A
Class of Insulat- Use Voltage AC Proof-Test Volt- DC Proof-Test Volt-
the thickness requirements.
ing Matting Phase-Phase age, rms V age, avg, V
ac rms, max 9.1.1.3 Foreign material remains in place when the matting
is bent and stretches equally with the material surrounding it.
0 1 000 5 000 20 000
1 7 500 10 000 40 000
2 17 000 20 000 50 000
10. Chemical and Physical Requirements
3 26 500 30 000 60 000
4 36 000 40 000 70 000
10.1 Insulating matting shall conform to the physical re-
A
Except for Class O equipment, the maximum use voltage is based on the
quirements in Table 4. For Type II matting, flame or oil
following formula:
resistance can be determined by conducting the tests in 19.2.5
Maximum use voltage (maximum nominal design voltage) 0.95 ac proof-test
voltage − 2000 or 19.2.6, respectively.
D178 – 01 (2005)
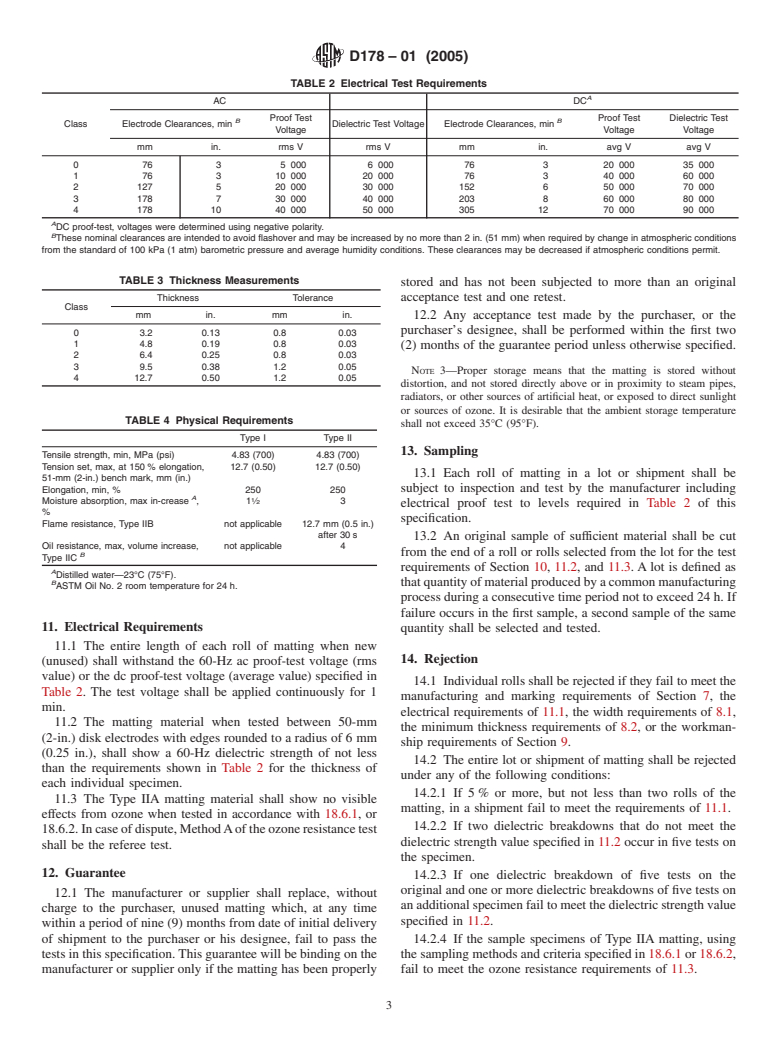
TABLE 2 Electrical Test Requirements
A
AC DC
Proof Test Proof Test Dielectric Test
B B
Class Electrode Clearances, min Dielectric Test Voltage Electrode Clearances, min
Voltage Voltage Voltage
mm in. rms V rms V mm in. avg V avg V
0 76 3 5 000 6 000 76 3 20 000 35 000
1 76 3 10 000 20 000 76 3 40 000 60 000
2 127 5 20 000 30 000 152 6 50 000 70 000
3 178 7 30 000 40 000 203 8 60 000 80 000
4 178 10 40 000 50 000 305 12 70 000 90 000
A
DC proof-test, voltages were determined using negative polarity.
B
These nominal clearances are intended to avoid flashover and may be increased by no more than 2 in. (51 mm) when required by change in atmospheric conditions
from the standard of 100 kPa (1 atm) barometric pressure and average humidity conditions. These clearances may be decreased if atmospheric conditions permit.
TABLE 3 Thickness Measurements
stored and has not been subjected to more than an original
Thickness Tolerance acceptance test and one retest.
Class
mm in. mm in. 12.2 Any acceptance test made by the purchaser, or the
purchaser’s designee, shall be performed within the first two
0 3.2 0.13 0.8 0.03
1 4.8 0.19 0.8 0.03
(2) months of the guarantee period unless otherwise specified.
2 6.4 0.25 0.8 0.03
3 9.5 0.38 1.2 0.05
NOTE 3—Proper storage means that the matting is stored without
4 12.7 0.50 1.2 0.05
distortion, and not stored directly above or in proximity to steam pipes,
radiators, or other sources of artificial heat, or exposed to direct sunlight
or sources of ozone. It is desirable that the ambient storage temperature
TABLE 4 Physical Requirements
shall not exceed 35°C (95°F).
Type I Type II
13. Sampling
Tensile strength, min, MPa (psi) 4.83 (700) 4.83 (700)
Tension set, max, at 150 % elongation, 12.7 (0.50) 12.7 (0.50)
13.1 Each roll of matting in a lot or shipment shall be
51-mm (2-in.) bench mark, mm (in.)
Elongation, min, % 250 250 subject to inspection and test by the manufacturer including
A
Moisture absorption, max in-crease , 1 ⁄2 3
electrical proof test to levels required in Table 2 of this
%
specification.
Flame resistance, Type IIB not applicable 12.7 mm (0.5 in.)
after 30 s
13.2 An original sample of sufficient material shall be cut
Oil resistance, max, volume increase, not applicable 4
from the end of a roll or rolls selected from the lot for the test
B
Type IIC
requirements of Section 10, 11.2, and 11.3. A lot is defined as
A
Distilled water—23°C (75°F).
B
thatquantityofmaterialproducedbyacommonmanufacturing
ASTM Oil No. 2 room temperature for 24 h.
process during a consecutive time period not to exceed 24 h. If
failure occurs in the first sample, a second sample of the same
11. Electrical Requirements
quantity shall be selected and tested.
11.1 The entire length of each roll of matting when new
14. Rejection
(unused) shall withstand the 60-Hz ac proof-test voltage (rms
value) or the dc proof-test voltage (average value) specified in
14.1 Individual rolls shall be rejected if they fail to meet the
Table 2. The test voltage shall be applied continuously for 1
manufacturing and marking requirements of Section 7, the
min.
electrical requirements of 11.1, the width requirements of 8.1,
11.2 The matting material when tested between 50-mm
the minimum thickness requirements of 8.2, or the workman-
(2-in.) disk electrodes with edges rounded to a radius of 6 mm
ship requirements of Section 9.
(0.25 in.), shall show a 60-Hz dielectric strength of not less
14.2 The entire lot or shipment of matting shall be rejected
than the requirements shown in Table 2 for the thickness of
under any of the following conditions:
each individual specimen.
14.2.1 If 5 % or more, but not less than two rolls of the
11.3 The Type IIA matting material shall show no visible
matting, in a shipment fail to meet the requirements of 11.1.
effects from ozone when tested in accordance with 18.6.1,or
14.2.2 If two dielectric breakdowns that do not meet the
18.6.2.Incaseofdispute,MethodAoftheozoneresistancetest
dielectric strength value specified in 11.2 occur in five tests on
shall be the referee test.
the specimen.
12. Guarantee
14.2.3 If one dielectric breakdown of five tests on the
original and one or more dielectric breakdowns of five tests on
12.1 The manufacturer or supplier shall replace, without
anadditionalspecimenfailtomeetthedielectricstrengthvalue
charge to the purchaser, unused matting which, at any time
specified in 11.2.
within a period of nine (9) months from date of initial delivery
of shipment to the purchaser or his designee, fail to pass the 14.2.4 If the sample specimens of Type IIA matting, using
tests in this specification.This guarantee will be binding on the the sampling methods and criteria specified in 18.6.1 or 18.6.2,
manufacturer or supplier only if the matting
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.