ASTM E2652-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Assessing Combustibility of Materials Using a Tube Furnace with a Cone-shaped Airflow Stabilizer, at 750 °C
Standard Test Method for Assessing Combustibility of Materials Using a Tube Furnace with a Cone-shaped Airflow Stabilizer, at 750 °C
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 While actual building fire exposure conditions are not duplicated, this test method will assist in indicating those materials which do not act to aid combustion or add appreciable heat to an ambient fire.
5.2 This test method does not apply to laminated or coated materials.
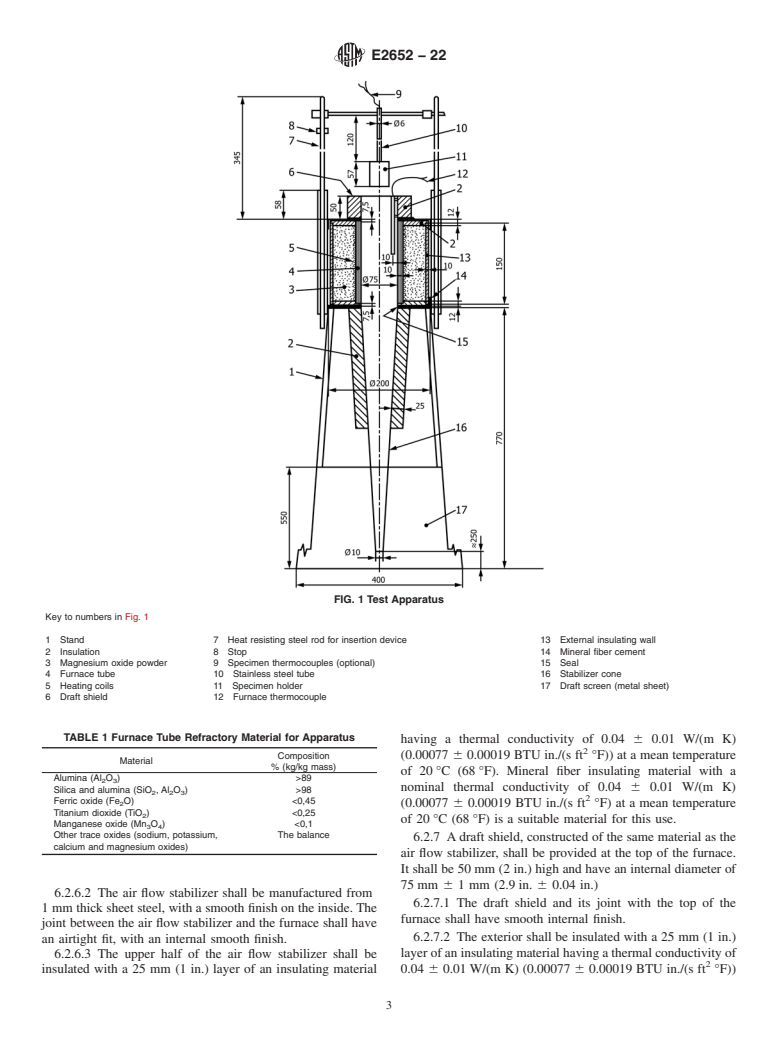
5.3 This test method is technically equivalent to ISO 1182.
5.4 When appropriate pass/fail criteria are applied, materials that are reported as passing this test by complying with those criteria (such as the ones in Appendix X2) are typically classified as noncombustible materials.
SCOPE
1.1 This fire-test-response test method covers the determination under specified laboratory conditions of the combustibility of building materials. Under certain conditions, with the appropriate pass/fail criteria, the results from this test are used to classify materials as noncombustible materials.
1.2 Limitations of this fire-test response test method are shown below.
1.2.1 This test method does not apply to laminated or coated materials.
1.2.2 This test method is not suitable or satisfactory for materials that soften, flow, melt, intumesce or otherwise separate from the measuring thermocouple.
1.2.3 This test method does not provide a measure of an intrinsic property.
1.2.4 This test method does not provide a quantitative measure of heat generation or combustibility; it simply serves as a test method with selected (end point) measures of combustibility.
1.2.5 This test method does not measure the self-heating tendencies of materials.
1.2.6 In this test method materials are not being tested in the nature and form used in building aplications. The test specimen consists of a small, specified volume that is either (1) cut from a thick sheet; (2) assembled from multiple thicknesses of thin sheets; or (3) placed in a container if composed of grarnular powder or loose fiber materials.
1.2.7 Results from this test method apply to the specific test apparatus and test conditions and are likely to vary when changes are made to one or more of the following: (1) the size, shape, and arrangement of the specimen; (2) the distribution of organice content; (3) the exposure temperature; (4) the air supply; (5) the location of thermocouples.
1.3 This test method references notes and footnotes that provide explanatory information. These notes and footnotes, excluding those in tables and figures, shall not be considered as requirements of this test method.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This test method is technically equivalent to ISO 1182:2010 (see also Annex A2 and 6.4.5).
Note 1: While developed as technically equivalent to ISO 1182:2010, a change implemented in ISO 1182:2020 added a second furnace thermocouple to that standard, while this test method continues to use one furnace thermocouple.
1.6 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire-hazard or fire-risk assessment of the materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.7 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting these tests.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Orga...
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:E2652 −22 An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Assessing Combustibility of Materials Using a Tube Furnace
1
with a Cone-shaped Airflow Stabilizer, at 750°C
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2652; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* excludingthoseintablesandfigures,shallnotbeconsideredas
requirements of this test method.
1.1 This fire-test-response test method covers the determi-
nation under specified laboratory conditions of the combusti- 1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
bility of building materials. Under certain conditions, with the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
appropriate pass/fail criteria, the results from this test are used only.
to classify materials as noncombustible materials.
1.5 This test method is technically equivalent to ISO
1.2 Limitations of this fire-test response test method are 1182:2010 (see also Annex A2 and 6.4.5).
shown below.
NOTE 1—While developed as technically equivalent to ISO 1182:2010,
1.2.1 Thistestmethoddoesnotapplytolaminatedorcoated
a change implemented in ISO 1182:2020 added a second furnace
materials.
thermocouple to that standard, while this test method continues to use one
furnace thermocouple.
1.2.2 This test method is not suitable or satisfactory for
materials that soften, flow, melt, intumesce or otherwise
1.6 This standard is used to measure and describe the
separate from the measuring thermocouple.
response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and
1.2.3 This test method does not provide a measure of an
flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself
intrinsic property.
incorporate all factors required for fire-hazard or fire-risk
1.2.4 This test method does not provide a quantitative
assessment of the materials, products, or assemblies under
measure of heat generation or combustibility; it simply serves
actual fire conditions.
as a test method with selected (end point) measures of
1.7 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safe-
combustibility.
guards for personnel and property shall be employed in
1.2.5 This test method does not measure the self-heating
conducting these tests.
tendencies of materials.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
1.2.6 Inthistestmethodmaterialsarenotbeingtestedinthe
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
natureandformusedinbuildingaplications.Thetestspecimen
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
consists of a small, specified volume that is either (1) cut from
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
a thick sheet; (2) assembled from multiple thicknesses of thin
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
sheets; or (3) placed in a container if composed of grarnular
1.9 This international standard was developed in accor-
powder or loose fiber materials.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.2.7 Results from this test method apply to the specific test
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
apparatus and test conditions and are likely to vary when
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
changes are made to one or more of the following: (1) the size,
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
shape, and arrangement of the specimen; (2) the distribution of
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
organice content; (3) the exposure temperature; (4) the air
supply; (5) the location of thermocouples.
2. Referenced Documents
1.3 This test method references notes and footnotes that
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
provide explanatory information. These notes and footnotes,
E136 TestMethodforAssessingCombustibilityofMaterials
Using a Vertical Tube Furnace at 750 °C
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E05 on Fire
Standards and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E05.23 on Combustibil-
2
ity. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2022. Published November 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as E2652–18. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/E2652-22. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2652 − 18 E2652 − 22 An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Assessing Combustibility of Materials Using a Tube Furnace
1
with a Cone-shaped Airflow Stabilizer, at 750°C750 °C
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2652; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This fire-test-response test method covers the determination under specified laboratory conditions of the combustibility of
building materials. Under certain conditions, with the appropriate pass/fail criteria, the results from this test are used to classify
materials as noncombustible materials.
1.2 Limitations of this fire-test response test method are shown below.
1.2.1 This test method does not apply to laminated or coated materials.
1.2.2 This test method is not suitable or satisfactory for materials that soften, flow, melt, intumesce or otherwise separate from the
measuring thermocouple.
1.2.3 This test method does not provide a measure of an intrinsic property.
1.2.4 This test method does not provide a quantitative measure of heat generation or combustibility; it simply serves as a test
method with selected (end point) measures of combustibility.
1.2.5 This test method does not measure the self-heating tendencies of materials.
1.2.6 In this test method materials are not being tested in the nature and form used in building aplications. The test specimen
consists of a small, specified volume that is either (1) cut from a thick sheet; (2) assembled from multiple thicknesses of thin sheets;
or (3) placed in a container if composed of grarnular powder or loose fiber materials.
1.2.7 Results from this test method apply to the specific test apparatus and test conditions and are likely to vary when changes
are made to one or more of the following: (1) the size, shape, and arrangement of the specimen; (2) the distribution of organice
content; (3) the exposure temperature; (4) the air supply; (5) the location of thermocouples.
1.3 This test method references notes and footnotes that provide explanatory information. These notes and footnotes, excluding
those in tables and figures, shall not be considered as requirements of this test method.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This test method is technically equivalent to ISO 11821182:2010 (see also Annex A2 and 6.4.5).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E05 on Fire Standards and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E05.23 on Combustibility.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2018Nov. 1, 2022. Published January 2019November 2022. Originally approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 20162018
as E2652–16.–18. DOI: 10.1520/E2652-18.10.1520/E2652-22.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2652 − 22
NOTE 1—While developed as technically equivalent to ISO 1182:2010, a change implemented in ISO 1182:2020 added a second furnace thermocouple
to that standard, while this test method continues to use one furnace thermocouple.
1.6 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under
controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire-hazard or fire-risk assessment of the materials,
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.7 FIreFire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting
these tests.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.