ASTM D6371-05(2010)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Cold Filter Plugging Point of Diesel and Heating Fuels
Standard Test Method for Cold Filter Plugging Point of Diesel and Heating Fuels
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The CFPP of a fuel is suitable for estimating the lowest temperature at which a fuel will give trouble-free flow in certain fuel systems.
In the case of diesel fuel used in European light duty trucks, the results are usually close to the temperature of failure in service except when the fuel system contains, for example, a paper filter installed in a location exposed to the weather or if the filter plugging temperature is more than 12°C below the cloud point value in accordance with Test Method D2500, D5771, D5772, or D5773. Domestic heating installations are usually less critical and often operate satisfactorily at temperatures somewhat lower than those indicated by the test results.
The difference in results obtained from the sample as received and after heat treatment at 45°C for 30 min can be used to investigate complaints of unsatisfactory performance under low temperature conditions.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the cold filter plugging point (CFPP) temperature of diesel and domestic heating fuels using either manual or automated apparatus.
Note 1—This test method is technically equivalent to test methods IP 309 and EN 116.
1.2 The manual apparatus and automated apparatus are both suitable for referee purposes.
1.3 This test method is applicable to distillate fuels, including those containing a flow-improving or other additive, intended for use in diesel engines and domestic heating installations.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 WARNINGMercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause central nervous system, kidney and liver damage. Mercury, or its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Caution should be taken when handling mercury and mercury containing products. See the applicable product Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for details and EPA’s websitehttp://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htmfor additional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury and/or mercury containing products into your state or country may be prohibited by law.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6371 − 05 (Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
1
Cold Filter Plugging Point of Diesel and Heating Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6371; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the cold
D2500Test Method for Cloud Point of Petroleum Products
filter plugging point (CFPP) temperature of diesel and domes-
D4057Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
tic heating fuels using either manual or automated apparatus.
Petroleum Products
NOTE 1—This test method is technically equivalent to test methods
D4177Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
IP309 and EN116.
Petroleum Products
1.2 Themanualapparatusandautomatedapparatusareboth
D5771Test Method for Cloud Point of Petroleum Products
suitable for referee purposes.
(Optical Detection Stepped Cooling Method)
D5772Test Method for Cloud Point of Petroleum Products
1.3 This test method is applicable to distillate fuels, includ-
(Linear Cooling Rate Method)
ing those containing a flow-improving or other additive,
D5773Test Method for Cloud Point of Petroleum Products
intended for use in diesel engines and domestic heating
(Constant Cooling Rate Method)
installations.
E1Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
3
2.2 IP Standards:
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
IP309Diesel and domestic heating fuels - Determination of
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
cold filter plugging point
standard.
Specifications for IP Standard Thermometers
4
1.5 WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many
2.3 ISO Standards:
regulatory agencies as a hazardous material that can cause
IP3310Test sieves - Technical requirements and testing -
central nervous system, kidney and liver damage. Mercury, or
Part 1: Metal cloth
5
its vapor, may be hazardous to health and corrosive to
2.4 European Standards:
materials.Cautionshouldbetakenwhenhandlingmercuryand
EN116Diesel and domestic heating fuels - Determination
mercury containing products. See the applicable product Ma-
of cold filter plugging point
terial Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for details and EPA’s
website—http://www.epa.gov/mercury/faq.htm—for addi-
tional information. Users should be aware that selling mercury
and/or mercury containing products into your state or country
may be prohibited by law.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
warning statements, see Section 7.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
1 3
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London, WIG 7AR,
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of U.K., http://www.energyinst.org.uk.
4
Subcommittee D02.07 on Flow Properties. Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2010. Published November 2010. Originally 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
5
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D6371–05. DOI: Available from European Committee for Standardization (CEN), 36 rue de
10.1520/D6371-05R10. Stassart, B-1050, Brussels, Belgium, http://www.cenorm.be.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6371 − 05 (2010)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 certified reference material, n—a stable petroleum
product with a method-specific nominal CFPP value estab-
lished by a method-specific interlaboratory study following
6 4
RR:D02-1007 guidelines or ISO Guides 34 and 35.
3.1.2 cold filter plugging point, n—highest temperature,
expressed in multiples of 1°C, at which a given volume of fuel
fails to pass through a standardized filtration device in a
specified time when cooled under the conditions prescribed in
this test method.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A specimen of the sample is cooled under specified
conditions and, at intervals
...







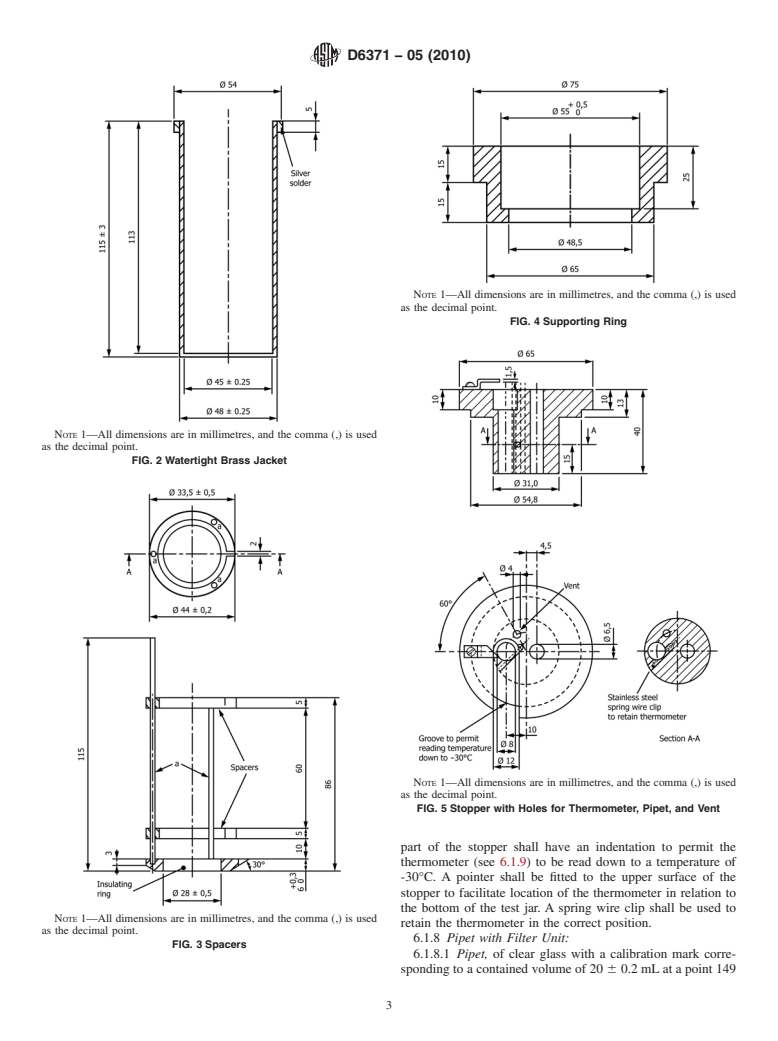
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.