ASTM C688-22
(Specification)Standard Specification for Functional Additions for Use in Hydraulic Cements
Standard Specification for Functional Additions for Use in Hydraulic Cements
ABSTRACT
This specification covers methods to investigate the effectiveness of a material to beneficially change the properties of hydraulic cements when the material is interground with the clinker during manufacture of the cement. Cement, mortar, and concrete shall be tested and the individual grades shall conform to specified values of autoclave expansion, drying shrinkage, normal consistency, standard consistency, setting time, compressive strength, false set, water content, flexural strength, bond to steel, volume change, resistance to freezing and thawing, and bleeding. Accelerating addition, retarding addition, set-control addition, water-reducing addition, water-reducing and accelerating addition are detailed.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers methods to investigate the effectiveness of a material to beneficially change the properties of hydraulic cements when the material is incorporated during manufacture of the cement.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
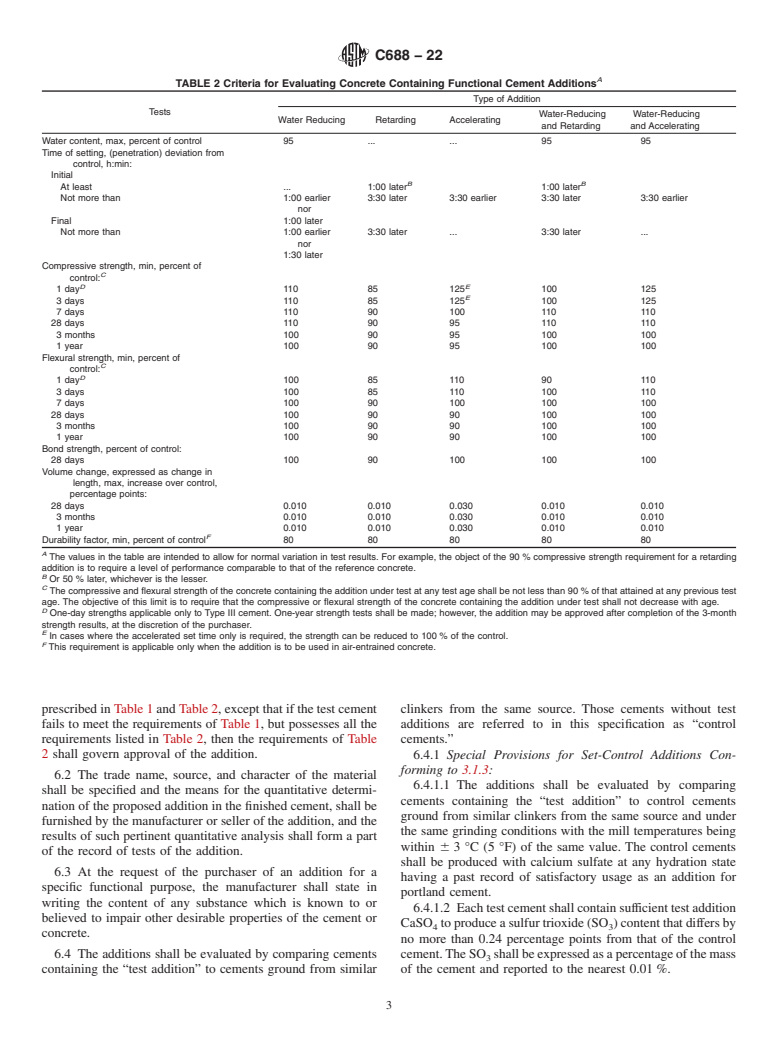
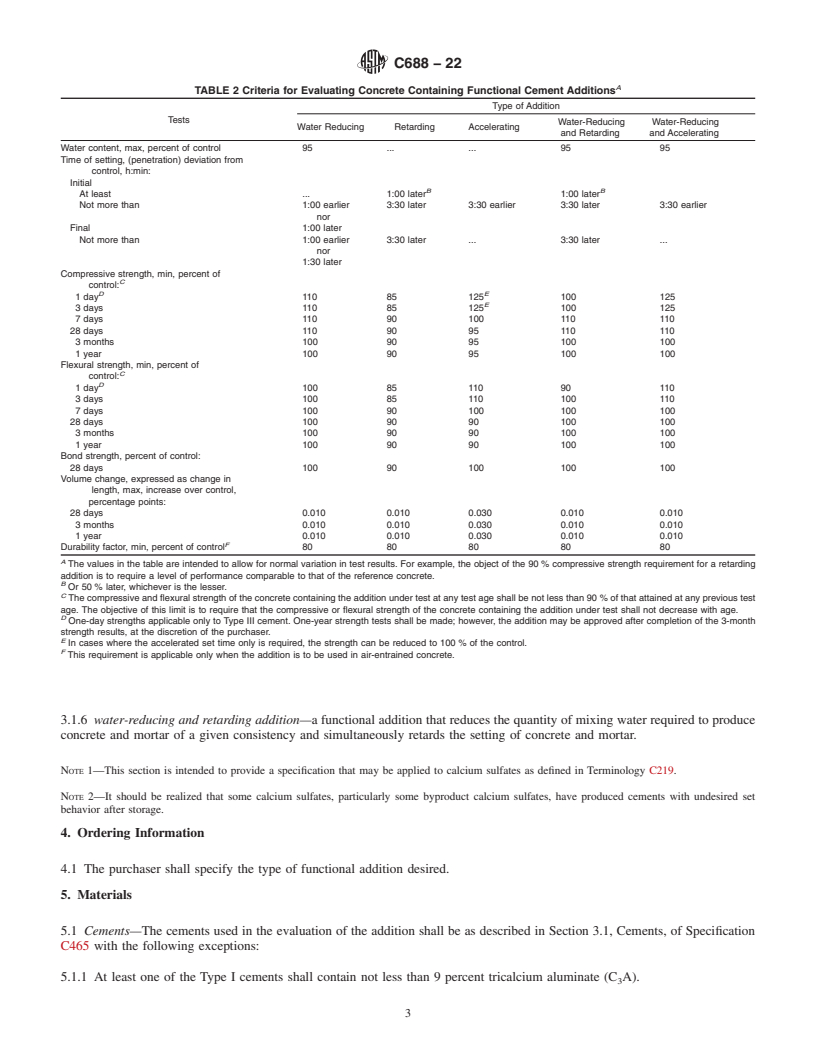
1.3 The effect of additions in cement may markedly change properties other than those they are intended to modify. This specification is designed to test for such changes. Table 1 sets forth values for those properties of cement pastes and mortars that would permit a judgment of the changes effected by an addition. Likewise, Table 2 sets forth similar criteria for concrete. Certain additions may be found effective for more than one purpose as indicated in 3.1.4 and 3.1.5.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:C688 −22
Standard Specification for
1
Functional Additions for Use in Hydraulic Cements
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C688; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* C143/C143M Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement
Concrete
1.1 This specification covers methods to investigate the
C150 Specification for Portland Cement
effectiveness of a material to beneficially change the properties
C151 Test Method for Autoclave Expansion of Hydraulic
of hydraulic cements when the material is incorporated during
Cement
manufacture of the cement.
C157/C157M Test Method for Length Change of Hardened
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Hydraulic-Cement Mortar and Concrete
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
C187 Test Method for Amount of Water Required for Nor-
standard.
mal Consistency of Hydraulic Cement Paste
C219 Terminology Relating to Hydraulic and Other Inor-
1.3 The effect of additions in cement may markedly change
properties other than those they are intended to modify. This ganic Cements
C226 Specification for Air-Entraining Additions for Use in
specification is designed to test for such changes. Table 1 sets
forth values for those properties of cement pastes and mortars the Manufacture of Air-Entraining Hydraulic Cement
C232 Test Method for Bleeding of Concrete
that would permit a judgment of the changes effected by an
addition. Likewise, Table 2 sets forth similar criteria for C234 Test Method for Comparing Concretes on the Basis of
the Bond Developed with Reinforcing Steel (Withdrawn
concrete. Certain additions may be found effective for more
3
than one purpose as indicated in 3.1.4 and 3.1.5. 2000)
C266 Test Method for Time of Setting of Hydraulic-Cement
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
Paste by Gillmore Needles
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
C403/C403M Test Method for Time of Setting of Concrete
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Mixtures by Penetration Resistance
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
C451 Test Method for Early Stiffening of Hydraulic Cement
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
(Paste Method)
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
C465 Specification for Processing Additions for Use in the
Manufacture of Hydraulic Cements
2. Referenced Documents
C595 Specification for Blended Hydraulic Cements
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C596 Test Method for Drying Shrinkage of Mortar Contain-
C10/C10M Specification for Natural Cement
ing Hydraulic Cement
C39/C39M Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylin-
C666/C666M Test Method for Resistance of Concrete to
drical Concrete Specimens
Rapid Freezing and Thawing
C78 Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using
C845 Specification for Expansive Hydraulic Cement
Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading)
C1157 Performance Specification for Hydraulic Cement
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of
Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50 mm] Cube
3. Terminology
Specimens)
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 accelerating addition—a functional addition that ac-
celerates the setting or early strength, or both, of concrete and
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C01 on
mortar.
Cement and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C01.20 on Additions.
3.1.2 retarding addition—a functional addition that retards
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2022. Published January 2023. Originally
approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as C688 – 14. DOI:
the setting of concrete and mortar.
10.1520/C0688-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C688−22
TABLE 1 Criteria for Evaluating Neat Cement and Mortar Containing Functional Cement Additions
Type of Addition
Tests
Water-Reducing Water-Reducing and
Water Reducing Retarding Accelerating Set-Contro
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C688 − 14 C688 − 22
Standard Specification for
1
Functional Additions for Use in Hydraulic Cements
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C688; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers methods to investigate the effectiveness of a material to beneficially change the properties of
hydraulic cements when the material is incorporated during manufacture of the cement.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 The effect of additions in cement may markedly change properties other than those they are intended to modify. This
specification is designed to test for such changes. Table 1 sets forth values for those properties of cement pastes and mortars that
would permit a judgment of the changes effected by an addition. Likewise, Table 2 sets forth similar criteria for concrete. Certain
additions may be found effective for more than one purpose as indicated in 3.1.4 and 3.1.5.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C10/C10M Specification for Natural Cement
C39/C39M Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens
C78 Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading)
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50 mm] Cube Specimens)
C143/C143M Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete
C150 Specification for Portland Cement
C151 Test Method for Autoclave Expansion of Hydraulic Cement
C157/C157M Test Method for Length Change of Hardened Hydraulic-Cement Mortar and Concrete
C187 Test Method for Amount of Water Required for Normal Consistency of Hydraulic Cement Paste
C219 Terminology Relating to Hydraulic and Other Inorganic Cements
C226 Specification for Air-Entraining Additions for Use in the Manufacture of Air-Entraining Hydraulic Cement
C232 Test Method for Bleeding of Concrete
3
C234 Test Method for Comparing Concretes on the Basis of the Bond Developed with Reinforcing Steel (Withdrawn 2000)
C266 Test Method for Time of Setting of Hydraulic-Cement Paste by Gillmore Needles
C403/C403M Test Method for Time of Setting of Concrete Mixtures by Penetration Resistance
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C01 on Cement and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C01.20 on Additions.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2014Dec. 15, 2022. Published March 2014January 2023. Originally approved in 1971. Last previous edition approved in 20082014 as
C688 – 08.C688 – 14. DOI: 10.1520/C0688-14. 10.1520/C0688-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C688 − 22
TABLE 1 Criteria for Evaluating Neat Cement and Mortar Containing Functional Cement Additions
Type of Addition
Tests
Water-Reducing Water-Reducing and
Water Reducing Retarding Accelerating Set-Control
and Retarding Accelerating
Normal consistency, deviation from control, −1.0 min +1.0 max +1.0 max −1.0 min −1.0 mm ±1.0 max
A
percentage points
Standard consistency (flow) deviation from −4.0 min +2.0 max +2.0 max −4.0 min −4.0 min ±2.0 max
A
control, percentage points
Setting time, (Gillmore) deviation from control,
h:min
Initial
B B
At least . 1:00 later 1:00 later .
Not more than 1:00 earlier 3:30 later 1:30 earlier 3:30 later 1:30 earlier 1:00 earlier
nor nor nor nor
1:30 later 1:30 later 1:30 later 1:30 later
C
Setting time, Vicat Initia
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.