ASTM G119-93(1998)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Determining Synergism Between Wear and Corrosion
Standard Guide for Determining Synergism Between Wear and Corrosion
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides a means for computing the increased wear loss rate attributed to synergism or interaction that may occur in a system when both wear and corrosion processes coexist. The guide applies to systems in liquid solutions or slurries and does not include processes in a gas/solid system.
1.2 This guide applies to metallic materials and can be used in a generic sense with a number of wear/corrosion tests. It is not restricted to use with approved ASTM test methods.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
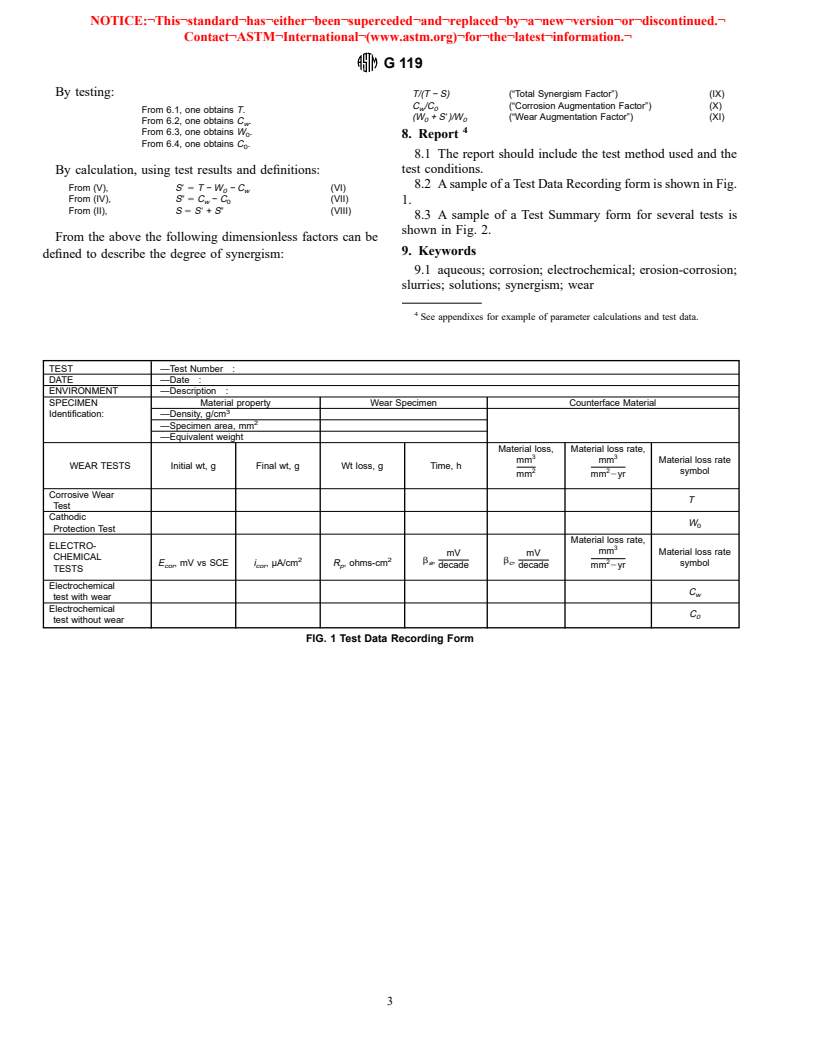
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Contact
ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: G 119 – 93 (Reapproved 1998)
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Guide for
1
Determining Synergism Between Wear and Corrosion
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G 119; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.2 corrosion current density, i —The corrosion current
cor
density measured by electrochemical techniques, as described
1.1 This guide provides a means for computing the in-
in Practice G 102.
creased wear loss rate attributed to synergism or interaction
3.2.3 electrochemical corrosion rate, C—The electrochemi-
that may occur in a system when both wear and corrosion
cal corrosion rate as determined by Practice G 59 and con-
processes coexist. The guide applies to systems in liquid
verted to a penetration rate in accordance with Practice G 102.
solutions or slurries and does not include processes in a
This penetration rate is equivalent to the volume loss rate per
gas/solid system.
area. The term C is the electrochemical corrosion rate during
1.2 This guide applies to metallic materials and can be used w
the corrosive wear process, and the term C designates the
0
in a generic sense with a number of wear/corrosion tests. It is
electrochemical corrosion rate when no mechanical wear is
not restricted to use with approved ASTM test methods.
allowed to take place.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.4 mechanical wear rate, W —The rate of material loss
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 0
from a specimen when the electrochemical corrosion rate has
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
been eliminated by cathodic protection during the wear test.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.2.5 total material loss rate, T—The rate of material loss
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
from a specimen exposed to the specified conditions, including
2. Referenced Documents
contributions from mechanical wear, corrosion, and interac-
tions between these two.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.6 wear/corrosion synergism, S—The rate of material
G 3 Practice for Conventions Applicable to Electrochemical
2
loss resulting from the interaction of wear and corrosion
Measurements in Corrosion Testing
processes, given by T minus the sum of W and C . The
G 5 Reference Test Method for Making Potentiostatic and 0 0
2
component S8 is the increase of mechanical wear rate due to
Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarization Measurements
corrosion, and S9 is the increase of the electrochemical corro-
G 15 Terminology Relating to Corrosion and Corrosion
2
sion rate due to mechanical wear.
Testing
2
G 40 Terminology Relating to Wear and Erosion
4. Summary of Guide
G 59 Practice for Conducting Potentiodynamic Polarization
2
4.1 A wear test is carried out under the test conditions of
Resistance Measurements
interest and T is measured.
G 102 Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and
2
4.2 Additional experiments are conducted to isolate the
Related Information from Electrochemical Measurements
mechanical and corrosion components of the corrosive wear
3. Terminology
process. These are as follows:
4.2.1 A repeat of the experiment in 4.1 with measurement of
3.1 Definitions—For general definitions relating to corro-
C ,
sion see Terminology G 15. For definitions relating to wear see w
4.2.2 A test identical to the initial experiment in 4.1, except
Terminology G 40.
that cathodic protection is used to obtain W , and
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard: 0
4.2.3 Measurement of C , the corrosion rate in the absence
3.2.1 cathodic protection current density, i —The electri- 0
cp
of mechanical wear.
cal current density needed during the wear/corrosion experi-
4.3 S, S 8 and S9 are calculated from the values measured in
ment to maintain the specimen at a potential which is 1 volt
the experiments described in 4.1 and 4.2.
cathodic to the open circuit potential.
5. Significance and Use
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G-2 on Wear and
5.1 Wear and corrosion can involve a number of mechanical
Erosion and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G02.40 on Non-Abrasive
and chemical processes. The combined action of these pro-
Wear.
cesses can result in significant mutual interaction beyond the
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 1993. Published October 1993.
2
individual contributions of mechanical wear and corrosion
Annual Book of ASTM Standards,
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.