ASTM E1221-96(2002)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Plane-Strain Crack-Arrest Fracture Toughness, KIa, of Ferritic Steels
Standard Test Method for Determining Plane-Strain Crack-Arrest Fracture Toughness, K<sub>Ia</sub>, of Ferritic Steels
SCOPE
1.1 This test method employs a side-grooved, crack-line-wedge-loaded specimen to obtain a rapid run-arrest segment of flat-tensile separation with a nearly straight crack front. This test method provides a static analysis determination of the stress intensity factor at a short time after crack arrest. The estimate is denoted K a. When certain size requirements are met, the test result provides an estimate, termed KIa, of the plane-strain crack-arrest toughness of the material.
1.2 The specimen size requirements, discussed later, provide for in-plane dimensions large enough to allow the specimen to be modeled by linear elastic analysis. For conditions of plane-strain, a minimum specimen thickness is also required. Both requirements depend upon the crack arrest toughness and the yield strength of the material. A range of specimen sizes may therefore be needed, as specified in this test method.
1.3 If the specimen does not exhibit rapid crack propagation and arrest, Ka cannot be determined.
1.4 Values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standards. SI units are provided for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E1221–96 (Reapproved 2002)
Standard Test Method for
Determining Plane-Strain Crack-Arrest Fracture Toughness,
1
K , of Ferritic Steels
Ia
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1221; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
2
1. Scope E616 Terminology Relating to Fracture Testing
E1304 Test Method for Plane-Strain (Chevron Notch)
1.1 This test method employs a side-grooved, crack-line-
2
Fracture Toughness of Metallic Materials
wedge-loadedspecimentoobtainarapidrun-arrestsegmentof
flat-tensile separation with a nearly straight crack front. This
3. Terminology
test method provides a static analysis determination of the
3.1 Definitions:
stress intensity factor at a short time after crack arrest. The
3.1.1 Definitions in Terminology E616 are applicable to
estimate is denoted K . When certain size requirements are
a
this test method.
met, the test result provides an estimate, termed K ,ofthe
Ia
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
plane-strain crack-arrest toughness of the material.
3.2.1 conditional value of the plane-strain crack-arrest
1.2 The specimen size requirements, discussed later, pro-
−3/2
fracture toughness, K (FL )—the conditional value of K
Qa Ia
vide for in-plane dimensions large enough to allow the speci-
calculated from the test results and subject to the validity
men to be modeled by linear elastic analysis. For conditions of
criteria specified in this test method.
plane-strain, a minimum specimen thickness is also required.
3.2.1.1 Discussion—In this test method, side-grooved
Both requirements depend upon the crack arrest toughness and
specimens are used. The calculation of K is based upon
Qa
the yield strength of the material. A range of specimen sizes
measurements of both the arrested crack length and of the
may therefore be needed, as specified in this test method.
crack-mouth opening displacement prior to initiation of a
1.3 Ifthespecimendoesnotexhibitrapidcrackpropagation
fast-running crack and shortly after crack arrest.
and arrest, K cannot be determined.
a
−3/2
3.2.2 crack-arrest fracture toughness, K (FL )—the
a
1.4 Values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as
value of the stress intensity factor shortly after crack arrest.
the standards. SI units are provided for information only.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—The in-plane specimen dimensions
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
must be large enough for adequate enclosure of the crack-tip
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
plastic zone by a linear-elastic stress field.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.3 plane-strain crack-arrest fracture toughness, K
Ia
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
−3/2
(FL )—the value of crack-arrest fracture toughness, K , for
a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
acrackthatarrestsunderconditionsofcrack-frontplane-strain.
2. Referenced Documents 3.2.3.1 Discussion—The requirements for attaining condi-
tions of crack-front plane-strain are specified in the procedures
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
of this test method.
E8 TestMethodsforTensionTestingofMetallicMaterials
−3/2
3.2.4 stressintensityfactoratcrackinitiation,K (FL )—
o
E23 Test Methods for Notched Bar Impact Testing of
2
the value of K at the onset of rapid fracturing.
Metallic Materials
3.2.4.1 Discussion—In this test method, only a nominal
E208 Test Method for Conducting Drop-Weight Test to
estimate of the initial driving force is needed. For this reason,
Determine Nil-DuctilityTransitionTemperature of Ferritic
2
K is calculated on the basis of the original (machined) crack
o
Steels
(ornotch)lengthandthecrack-mouthopeningdisplacementat
E399 Test Method for Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness of
2
the initiation of a fast-running crack.
Metallic Materials
4. Summary of Test Method
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeE08onFracture 4.1 This test method estimates the value of the stress
Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E08.07 on Linear-Elastic
intensity factor, K, at which a fast running crack will arrest.
Fracture.
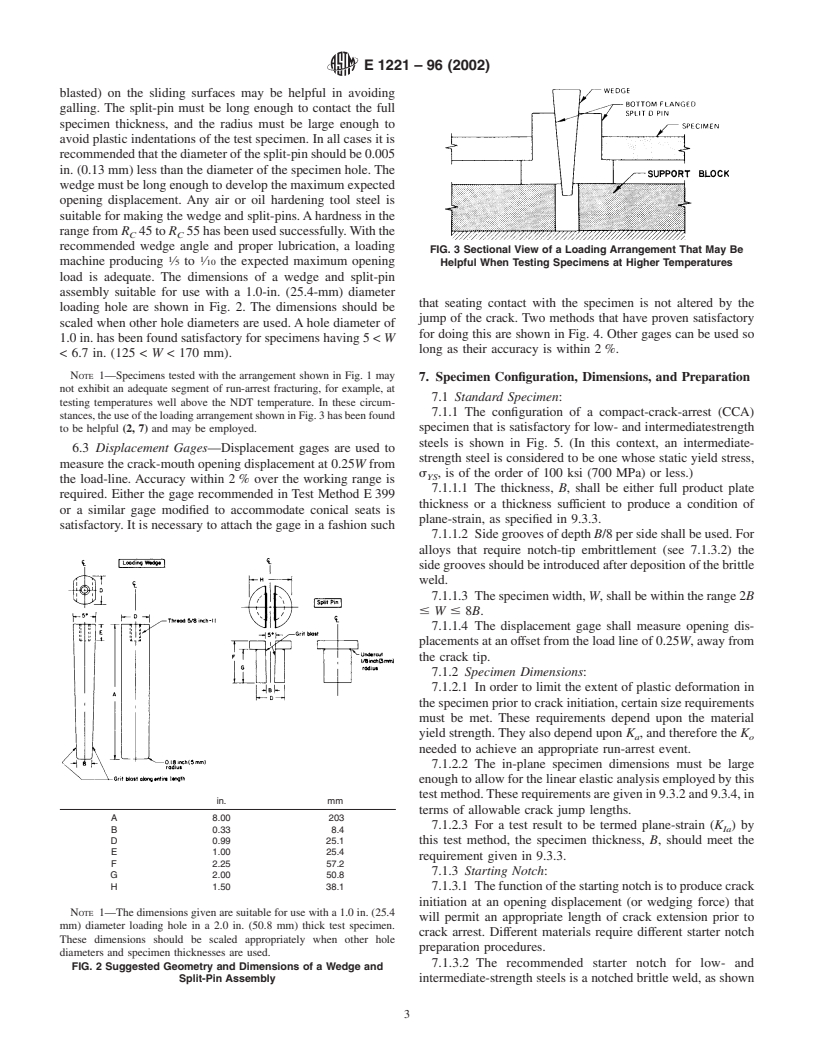
This test method is made by forcing a wedge into a split-pin,
Current edition approved June 10, 1996. Published August 1996. Originally
whichappliesanopeningforceacrossthecrackstarternotchin
published as E1221–88. Last previous edition E1221–88.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 --------------
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.