ASTM E935-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Performance of Permanent Metal Railing Systems and Rails for Buildings
Standard Test Methods for Performance of Permanent Metal Railing Systems and Rails for Buildings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 These test methods are intended to provide information from which applicable design and performance data can be derived for the performance of metal railing systems and rails installed and fastened to structural elements of concrete, masonry, wood, and metal as well as related products.
4.2 These test methods may be used to determine whether railing systems comply with requirements of the applicable performance specifications.
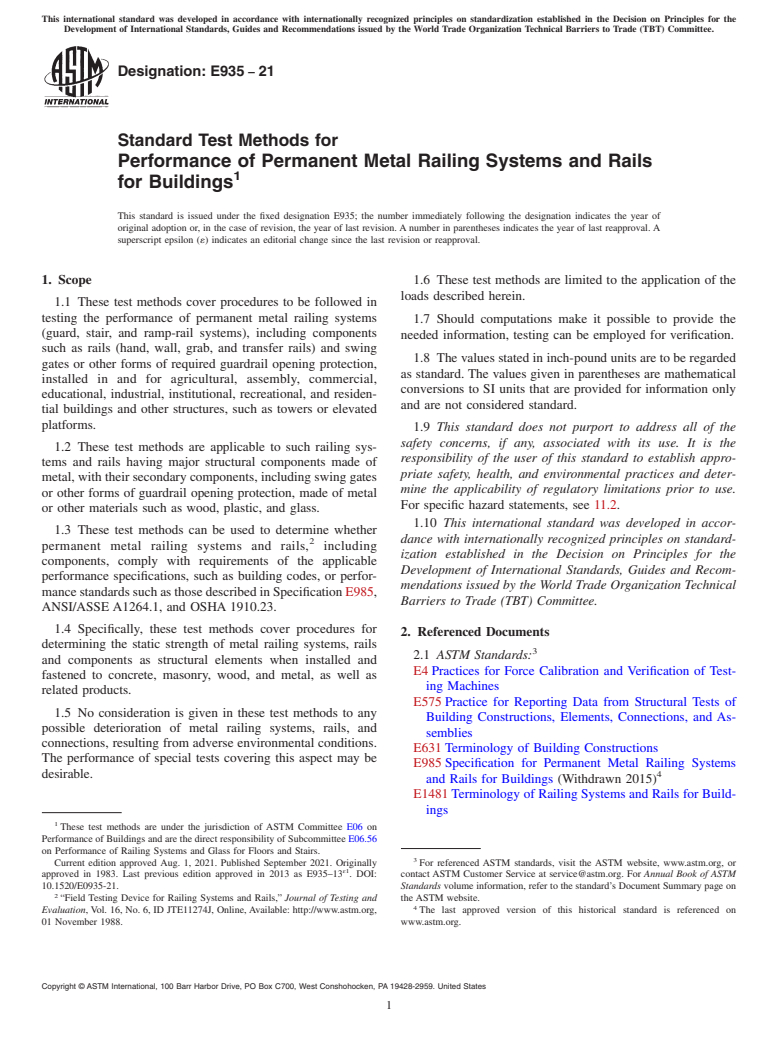
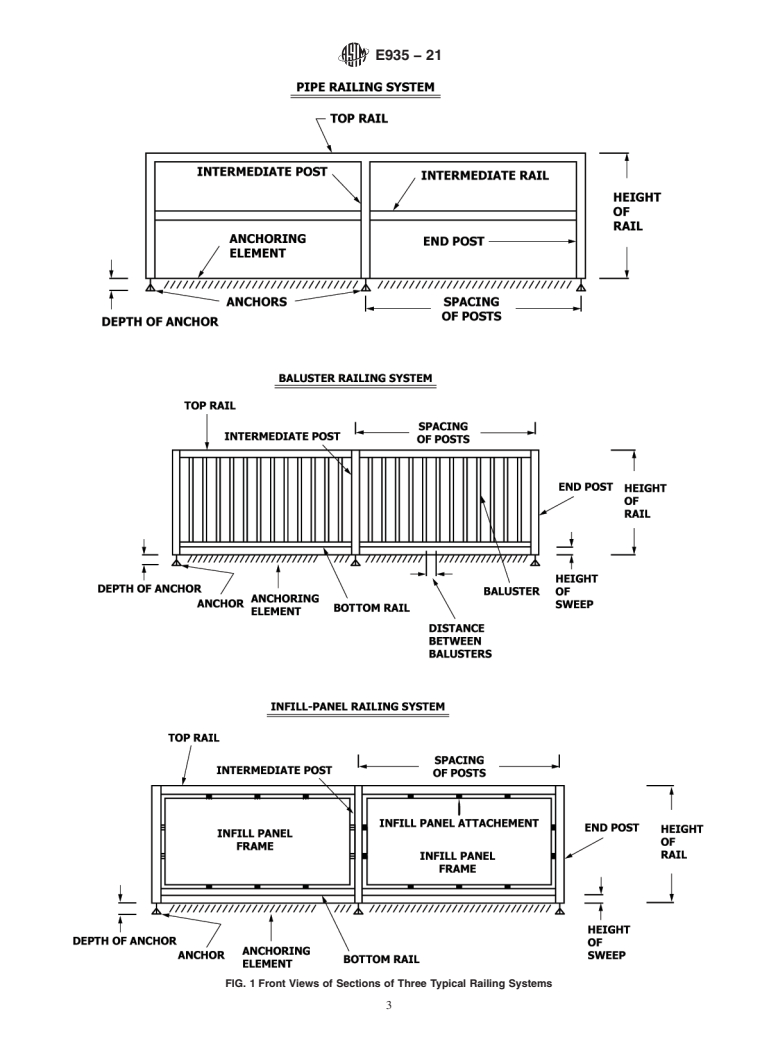
4.3 These test methods are intended for use in the buying and selling of railing systems and components according to performance specifications, for use in product development research, for use in quality assurance and manufacturing process control, for use in developing performance standards, and for use in field and laboratory compliance determination. Typical floor-mounted railings are shown in Fig. 1.
FIG. 1 Front Views of Sections of Three Typical Railing Systems
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover procedures to be followed in testing the performance of permanent metal railing systems (guard, stair, and ramp-rail systems), including components such as rails (hand, wall, grab, and transfer rails) and swing gates or other forms of required guardrail opening protection, installed in and for agricultural, assembly, commercial, educational, industrial, institutional, recreational, and residential buildings and other structures, such as towers or elevated platforms.
1.2 These test methods are applicable to such railing systems and rails having major structural components made of metal, with their secondary components, including swing gates or other forms of guardrail opening protection, made of metal or other materials such as wood, plastic, and glass.
1.3 These test methods can be used to determine whether permanent metal railing systems and rails,2 including components, comply with requirements of the applicable performance specifications, such as building codes, or performance standards such as those described in Specification E985, ANSI/ASSE A1264.1, and OSHA 1910.23.
1.4 Specifically, these test methods cover procedures for determining the static strength of metal railing systems, rails and components as structural elements when installed and fastened to concrete, masonry, wood, and metal, as well as related products.
1.5 No consideration is given in these test methods to any possible deterioration of metal railing systems, rails, and connections, resulting from adverse environmental conditions. The performance of special tests covering this aspect may be desirable.
1.6 These test methods are limited to the application of the loads described herein.
1.7 Should computations make it possible to provide the needed information, testing can be employed for verification.
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see 11.2.
1.10 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E935 − 21
Standard Test Methods for
Performance of Permanent Metal Railing Systems and Rails
1
for Buildings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E935; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.6 These test methods are limited to the application of the
loads described herein.
1.1 These test methods cover procedures to be followed in
testing the performance of permanent metal railing systems
1.7 Should computations make it possible to provide the
(guard, stair, and ramp-rail systems), including components
needed information, testing can be employed for verification.
such as rails (hand, wall, grab, and transfer rails) and swing
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
gates or other forms of required guardrail opening protection,
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
installed in and for agricultural, assembly, commercial,
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
educational, industrial, institutional, recreational, and residen-
and are not considered standard.
tial buildings and other structures, such as towers or elevated
platforms.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.2 These test methods are applicable to such railing sys-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
tems and rails having major structural components made of
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
metal, with their secondary components, including swing gates
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
or other forms of guardrail opening protection, made of metal
For specific hazard statements, see 11.2.
or other materials such as wood, plastic, and glass.
1.10 This international standard was developed in accor-
1.3 These test methods can be used to determine whether
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
2
permanent metal railing systems and rails, including
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
components, comply with requirements of the applicable
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
performance specifications, such as building codes, or perfor-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
mancestandardssuchasthosedescribedinSpecificationE985,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ANSI/ASSE A1264.1, and OSHA 1910.23.
1.4 Specifically, these test methods cover procedures for
2. Referenced Documents
determining the static strength of metal railing systems, rails
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
and components as structural elements when installed and
E4 Practices for Force Calibration and Verification of Test-
fastened to concrete, masonry, wood, and metal, as well as
ing Machines
related products.
E575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of
1.5 No consideration is given in these test methods to any
Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and As-
possible deterioration of metal railing systems, rails, and
semblies
connections, resulting from adverse environmental conditions.
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
The performance of special tests covering this aspect may be
E985 Specification for Permanent Metal Railing Systems
desirable. 4
and Rails for Buildings (Withdrawn 2015)
E1481 Terminology of Railing Systems and Rails for Build-
ings
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.56
on Performance of Railing Systems and Glass for Floors and Stairs.
3
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2021. Published September 2021. Originally For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
ɛ1
approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as E935–13 . DOI: contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
10.1520/E0935-21. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
2
“Field Testing Device for Railing Systems and Rails,” Journal of Testing and the ASTM website.
4
Evaluation, Vol. 16, No. 6, ID JTE11274J, Online, Available: http://www.astm.org, The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
01 November 1988. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: E935 − 13 E935 − 21
Standard Test Methods for
Performance of Permanent Metal Railing Systems and Rails
1
for Buildings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E935; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Section 1.2 was editorially revised in October 2013.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods cover procedures to be followed in testing the performance of permanent metal railing systems (guard,
stair, and ramp-rail systems), including components such as rails (hand, wall, grab, and transfer rails) and swing gates or other
forms of required guardrail opening protection, installed in and for agricultural, assembly, commercial, educational, industrial,
institutional, recreational, and residential buildings and other structures, such as towers or elevated platforms.
1.2 These test methods are applicable to such railing systems and rails having major structural components made of metal, with
their secondary components, including swing gates or other forms of guardrail opening protection, made of metal or other materials
such as wood, plastic, and glass.
2
1.3 These test methods can be used to determine whether permanent metal railing systems and rails, including components,
comply with requirements of the applicable performance specifications, such as building codes, or performance standards such as
those described in Specification E985, ANSI/ASSE A1264.1, and OSHA 1910.23.
1.4 Specifically, these test methods cover procedures for determining the static strength of metal railing systems, rails and
components as structural elements when installed and fastened to concrete, masonry, wood, and metal, as well as related products.
1.5 No consideration is given in these test methods to any possible deterioration of metal railing systems, rails, and connections,
resulting from adverse environmental conditions. The performance of special tests covering this aspect may be desirable.
1.6 These test methods are limited to the application of the loads described herein.
1.7 Should computations make it possible to provide the needed information, testing can be employed for verification.
1.8 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on Performance of Buildings and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.56 on
Performance of Railing Systems and Glass for Floors and Stairs.
Current edition approved April 1, 2013Aug. 1, 2021. Published April 2013September 2021. Originally approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 20062013 as
ɛ1
E935-00(2006).E935–13 . DOI: 10.1520/E0935-13E01.10.1520/E0935-21.
2
“Field Testing Device for Railing Systems and Rails,” Journal of Testing and Evaluation, Vol. 16, No. 6, ID JTE11274J, Online, Available: http://www.astm.org, 01
November 1988.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E935 − 21
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see 11.2.
1.10 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E4 Practices for Force Calibration and Verification of Testing Machines
E575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and Assemblies
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
4
E985 Specification for Permanent Metal Railing Systems and Rails for Buildings (Withdrawn 2015)
E1481 Terminology of Railing Systems and Rails for Buildings
2.2 Othe
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.