ASTM E190-92(2003)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Guided Bend Test for Ductility of Welds
Standard Test Method for Guided Bend Test for Ductility of Welds
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The guided bend test as described in this test method is used to evaluate the quality of welds as a function of ductility as evidenced by their ability to resist cracking during bending.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a guided bend test for the determination of soundness and ductility of welds in ferrous and nonferrous products. Defects, not shown by X rays, may appear in the surface of a specimen when it is subjected to progressive localized overstressing. This guided bend test has been developed primarily for plates and is not intended to be substituted for other methods of bend testing.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The SI equivalents are in parentheses and may be approximate.
Note 1—For additional information see Terminology E 6, and American Welding Society Standard D 1.1.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:E190–92(Reapproved 2003)
Standard Test Method for
Guided Bend Test for Ductility of Welds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 190; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope having the shape necessary to produce the desired contour.The
convex surface of the bent specimen is examined for cracks or
1.1 This test method covers a guided bend test for the
other open defects.
determination of soundness and ductility of welds in ferrous
and nonferrous products. Defects, not shown by X rays, may
4. Significance and Use
appear in the surface of a specimen when it is subjected to
4.1 The guided bend test as described in this test method is
progressive localized overstressing. This guided bend test has
used to evaluate the quality of welds as a function of ductility
been developed primarily for plates and is not intended to be
as evidenced by their ability to resist cracking during bending.
substituted for other methods of bend testing.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
5. Apparatus
as the standard. The SI equivalents are in parentheses and may
5.1 The guided bend test jig is shown in Fig. 1 (see
be approximate.
Explanatory Notes at end of this test method).
NOTE 1—For additional information see TerminologyE6, and Ameri-
can Welding Society Standard D 1.1.
6. Sampling
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 6.1 Sampling is performed in accordance with the require-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the ments of relevant specifications and codes.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
7. Test Specimens
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. 7.1 The types of specimens generally used for guided bend
testing are rectangular ones machined from plates and pipes.
2. Referenced Documents
Thefacesurfaceoftheflatspecimencontainsthegreaterwidth
2.1 ASTM Standards: of the weld material, while the opposite side is called the root
E6 Terminology Relating to Methods of Mechanical Test- surface.
ing 7.1.1 Transverse Side Bend—The weld is transverse to the
2.2 AWS Standard: longitudinal axis of the specimen which is bent so that either
D1.1 Structural Welding Code, Steel oneofthesidesurfacesbecomestheconvexsurfaceofthebent
specimen (Fig. 2 and Fig. 3).
3. Summary of Test Method
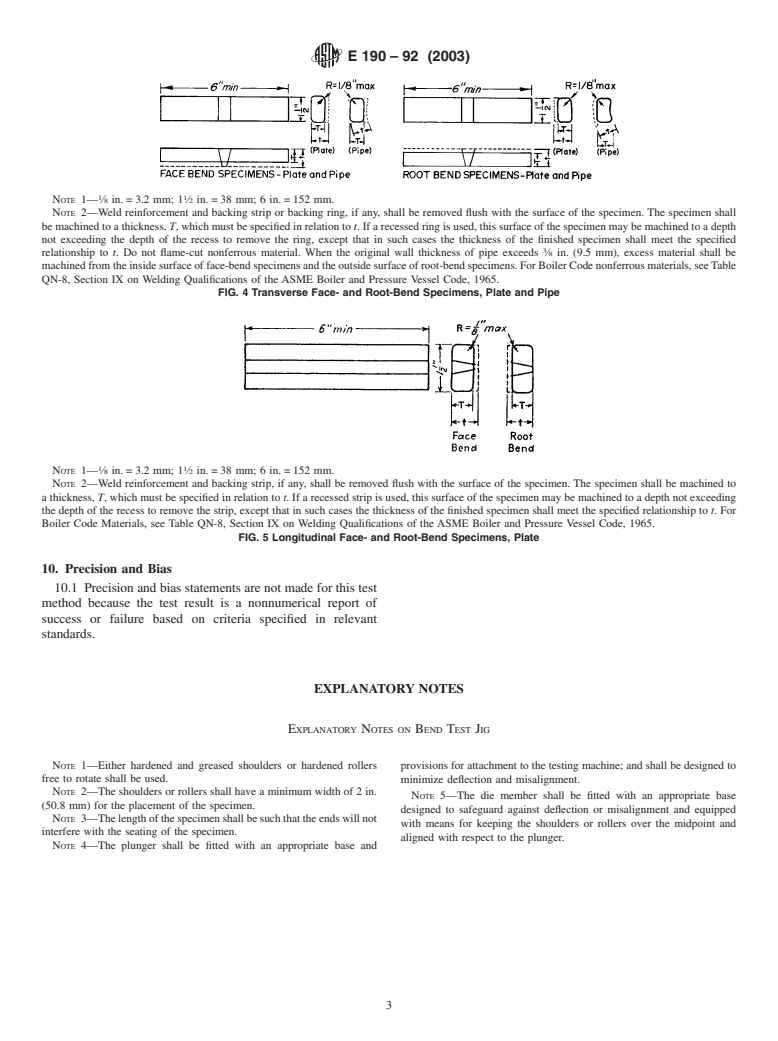
7.1.2 Transverse Face Bend—The weld is transverse to the
3.1 The specimen is bent in a U-shaped die by means of a longitudinalaxisofthespecimenwhichisbentsothattheweld
centrally applied force to the weldment in a flat specimen
face surface becomes the convex surface of the bent specimen
supported at two positions equidistant from the line of force (Fig. 4).
application. The specimen is forced into the die by a plunger
7.1.3 Transverse Root Bend—The weld is transverse to the
longitudinal axis of the specimen which is bent so that the
weld-root surface becomes the convex surface of the bent
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E28 on
specimen (Fig. 4).
Mechanical Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E28.02 on
Ductility and Flexure Testing. 7.1.4 Longitudinal Face Bend—The weld is parallel to the
Current edition approved Aug. 10, 2003. Published September 2003. Originally
longitudinal axis of the specimen which is bent so that the
approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as E 190 – 92 (1997).
weld-face surface becomes the convex surface of the bent
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
specimen (Fig. 5).
Available from The American Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd.,
Miami, FL 33126.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E190–92 (2003)
Thickness of Specimen
A, in. (mm) B, in. (mm) C, in. (mm) D, in. (mm)
in. (mm)
3 1 3 3 3
⁄8 (9.5) 1 ⁄2 (38) ⁄4 (19) 2 ⁄8 (60) 1 ⁄16 (30)
1 1 1 3 3
⁄8 (3.2) 2 ⁄8 (54) 1 ⁄16 (27) 2 ⁄8 (60) 1 ⁄16 (30)
1 1
t 4t 2t 6t + ⁄8 ( + 3.2) 3t + ⁄16(+1.6)
FIG. 1 Guided Bend Test Jig
t, in. (mm) T,in.
3 1
⁄8 to 1 ⁄2 (9.5 to 38) t
>1 ⁄2 See Note
t, in. (mm) T,in.
3 1
⁄8 to 1 ⁄2 (9.5 to 38) t NOTE—For plates over 1 ⁄2 in. (38 mm) thick, cut specimen into
1 3 1
>1 ⁄2 (38) See Note
approximately equal strips between ⁄4 and 1 ⁄2 in. (19 to 38 mm) wide and
test each strip.
NOTE—For plates over 1 ⁄2 in. (38 mm) thick, cut specimen into FIG. 3 Side-Bend Specimen for Nonferrous Materials
3 1
approximately equal strips between ⁄4 and 1 ⁄2 in. (19 and 38 mm) wide
and test each strip.
FIG. 2 Side-Bend Specimen for Ferrous Materials
8.2 Any convenient means may be used for moving the
plunger with relation to the die; but it must be steady and
without any significant lateral motion.Apply the force until the
7.1.5 Longitudinal Root Bend—The weld is
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.