ASTM C1637-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for the Determination of Impurities in Plutonium Metal: Acid Digestion and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectroscopy (ICP-MS) Analysis
Standard Test Method for the Determination of Impurities in Plutonium Metal: Acid Digestion and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectroscopy (ICP-MS) Analysis
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method may be run together with Test Method C1432 to analyze for trace impurities in Pu metal. Using the technique described in this test method and the technique described in Test Method C1432 will provide the analyst with a more thorough verification of the impurity concentrations contained in the Pu metal sample. In addition, Test Method C1432 can be used to determine impurity concentrations for analytes such as Ca, Fe, Na, and Si, which have not been determined using this test method.
4.2 This test method can be used on Pu matrices in nitrate solutions.
4.3 This test method has been validated for use on materials that meet the specifications described in Specification C757 and Test Methods C758 and C759.
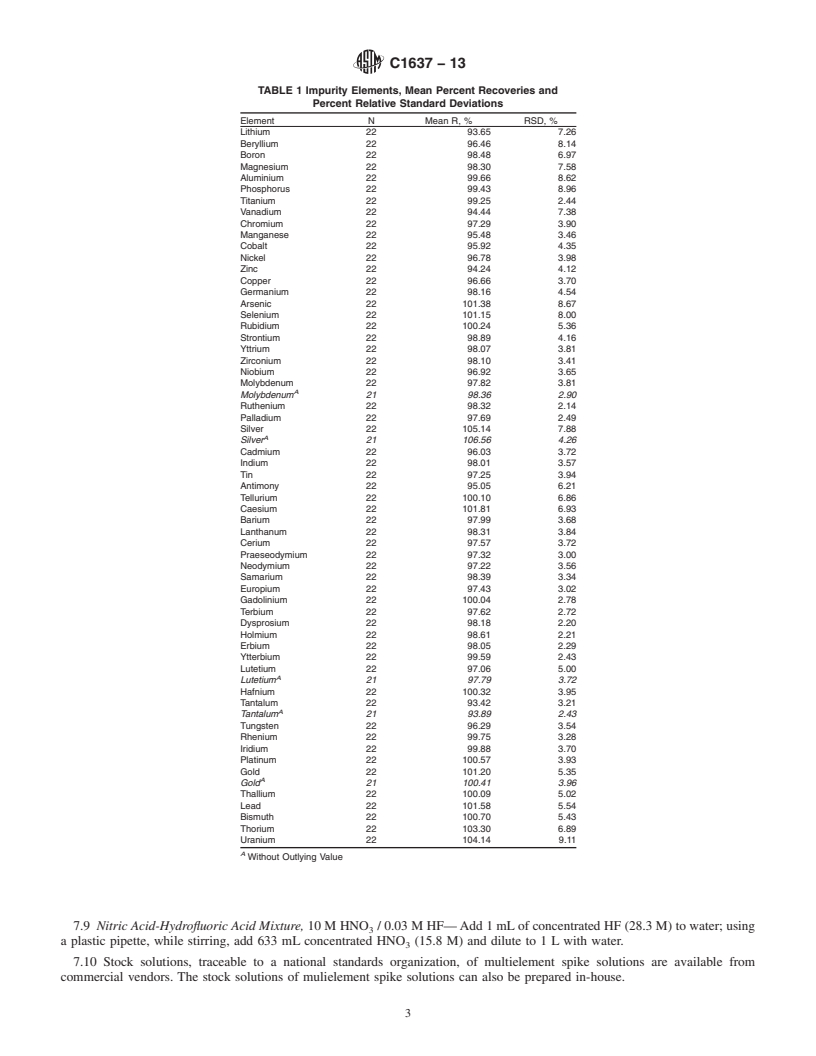
4.4 This test method has been validated for all elements listed in Table 1.TABLE 1 Impurity Elements, Mean Percent Recoveries and Percent Relative Standard Deviations
Element
N
Mean R, %
RSD, %
Lithium
22
93.65
7.26
Beryllium
22
96.46
8.14
Boron
22
98.48
6.97
Magnesium
22
98.30
7.58
Aluminium
22
99.66
8.62
Phosphorus
22
99.43
8.96
Titanium
22
99.25
2.44
Vanadium
22
94.44
7.38
Chromium
22
97.29
3.90
Manganese
22
95.48
3.46
Cobalt
22
95.92
4.35
Nickel
22
96.78
3.98
Zinc
22
94.24
4.12
Copper
22
96.66
3.70
Germanium
22
98.16
4.54
Arsenic
22
101.38
8.67
Selenium
22
101.15
8.00
Rubidium
22
100.24
5.36
Strontium
22
98.89
4.16
Yttrium
22
98.07
3.81
Zirconium
22
98.10
3.41
Niobium
22
96.92
3.65
Molybdenum
22
97.82
3.81
MolybdenumA
21
98.36
2.90
Ruthenium
22
98.32
2.14
Palladium
22
97.69
2.49
Silver
22
105.14
7.88
SilverA
21
106.56
4.26
Cadmium
22
96.03
3.72 ...
SCOPE
1.1 This Test Method covers the determination of 58 trace elements in plutonium (Pu) metal. The Pu sample is dissolved in acid, and the concentration of the trace impurities are determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectroscopy (ICP-MS).
1.2 This Test Method is specific for the determination of trace impurities in Pu metal. It may be applied to other types of Pu materials, such as Pu oxides, if the samples are dissolved and oxidized to the Pu(IV) state. However, it is the responsibility of the user to evaluate the performance of other matrices.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this method to establish appropriate safety and health practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use of this standard.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1637 − 13
Standard Test Method for
the Determination of Impurities in Plutonium Metal: Acid
Digestion and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass
1
Spectroscopy (ICP-MS) Analysis
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1637; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope C1168 PracticeforPreparationandDissolutionofPlutonium
Materials for Analysis
1.1 This Test Method covers the determination of 58 trace
C1432 Test Method for Determination of Impurities in
elements in plutonium (Pu) metal. The Pu sample is dissolved
Plutonium: Acid Dissolution, Ion Exchange Matrix
in acid, and the concentration of the trace impurities are
Separation, and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic
determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectros-
Emission Spectroscopic (ICP/AES) Analysis
copy (ICP-MS).
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
1.2 This Test Method is specific for the determination of
traceimpuritiesinPumetal.Itmaybeappliedtoothertypesof
3. Summary of Test Method
Pu materials, such as Pu oxides, if the samples are dissolved
3.1 Asample of Pu metal is dissolved in a small volume of
and oxidized to the Pu(IV) state. However, it is the responsi-
6 M hydrochloric acid (HCl). Then, 10 M nitric acid (HNO )/
3
bility of the user to evaluate the performance of other matrices.
0.03 M hydrofluoric acid (HF) is added to the dissolved Pu to
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
oxidize the Pu to the Pu(IV) state. An aliquot of the original
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
sample is taken and diluted with 1 % HNO by volume to a
3
standard.
prescribed volume. Aliquots from a second dilution of the
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the original sample are used to prepare run batch dilutions that are
3
safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility analyzed for trace impurities by ICP-MS.
of the user of this method to establish appropriate safety and
health practices and to determine the applicability of regula- 4. Significance and Use
tory limitations prior to use of this standard.
4.1 This test method may be run together with Test Method
C1432 to analyze for trace impurities in Pu metal. Using the
2. Referenced Documents
technique described in this test method and the technique
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
described in Test Method C1432 will provide the analyst with
C757 Specification for Nuclear-Grade Plutonium Dioxide
a more thorough verification of the impurity concentrations
Powder, Sinterable
contained in the Pu metal sample. In addition, Test Method
C758 Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric,
C1432 can be used to determine impurity concentrations for
Spectrochemical, Nuclear, and RadiochemicalAnalysis of
analytes such as Ca, Fe, Na, and Si, which have not been
Nuclear-Grade Plutonium Metal
determined using this test method.
C759 Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric,
4.2 This test method can be used on Pu matrices in nitrate
Spectrochemical, Nuclear, and RadiochemicalAnalysis of
solutions.
Nuclear-Grade Plutonium Nitrate Solutions
4.3 This test method has been validated for use on materials
that meet the specifications described in Specification C757
1
and Test Methods C758 and C759.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear
Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of
4.4 This test method has been validated for all elements
Test.
listed in Table 1.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2013. Published January 2013. Originally
approved in 2006. Last previous edition approve in 2006 as D1637 – 06. DOI:
10.1520/C1637-13.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM “Inductively Coupled Plasma – Mass Spectrometry Using the VG Elemental
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Plasma Quad,” Actinide Analytical Chemistry Procedures, Los Alamos National
the ASTM website. Laboratory, ANC102 R.1.2, LA-UR-05-7605, 2004.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1637 − 13
TABLE 1 Impurity Elements, Mean Percent Recoveries and
are observed at 120.5 and 127.5 atomic mass unit (amu), when
Percent Relative Standard Deviations
analyzing plutonium-239.
Element N Mean R, % RSD, %
5.2 Spectral interferences from the argon plasma and the
Lithium 22 93.65 7.26
Beryllium 22 96.46 8.14
aci
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1637 − 06 C1637 − 13
Standard Test Method for
the Determination of Impurities in Plutonium Metal: Acid
Digestion and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass
1
Spectroscopy (ICP-MS) Analysis
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1637; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This Test Method covers the determination of 58 trace elements in plutonium (Pu) metal. The Pu sample is dissolved in acid,
and the concentration of the trace impurities are determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectroscopy (ICP-MS).
1.2 This Test Method is specific for the determination of trace impurities in Pu metal. It may be applied to other types of Pu
materials, such as Pu oxides, if the samples are dissolved and oxidized to the Pu(IV) state. However, it is the responsibility of the
user to evaluate the performance of other matrices.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the
user of this method to establish appropriate safety and health practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory limitations
prior to use of this standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C757 Specification for Nuclear-Grade Plutonium Dioxide Powder, Sinterable
C758 Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric, Spectrochemical, Nuclear, and Radiochemical Analysis of Nuclear-
Grade Plutonium Metal
C759 Test Methods for Chemical, Mass Spectrometric, Spectrochemical, Nuclear, and Radiochemical Analysis of Nuclear-
Grade Plutonium Nitrate Solutions
C1168 Practice for Preparation and Dissolution of Plutonium Materials for Analysis
C1432 Test Method for Determination of Impurities in Plutonium: Acid Dissolution, Ion Exchange Matrix Separation, and
Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectroscopic (ICP/AES) Analysis
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A sample of Pu metal is dissolved in a small volume of 6 M hydrochloric acid (HCl). Then, 10 M nitric acid (HNO )/0.03
3
M hydrofluoric acid (HF) is added to the dissolved Pu to oxidize the Pu to the Pu(IV) state. An aliquot of the original sample is
taken and diluted with 1 % HNO by volume to a prescribed volume. Aliquots from a second dilution of the original sample are
3
3
used to prepare run batch dilutions that are analyzed for trace impurities by ICP-MS.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method may be run together with Test Method C1432 to analyze for trace impurities in Pu metal. Using the
technique described in this test method and the technique described in Test Method C1432 will provide the analyst with a more
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.05 on Methods of Test.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2006Jan. 1, 2013. Published February 2006January 2013. Originally approved in 2006. Last previous edition approve in 2006 as D1637
– 06. DOI: 10.1520/C1637-06.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
“Inductively Coupled Plasma – Mass Spectrometry Using the VG Elemental Plasma Quad,” Actinide Analytical Chemistry Procedures, Los Alamos National Laboratory,
ANC102 R.1.2, LA-UR-05-7605, 2004.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1637 − 13
thorough verification of the impurity concentrations contained in the Pu metal sample. In addition, Test Method C1432 can be used
to determine impurity concentrations for analytes such as Ca, Fe, Na, and Si, which have not been determined using this test
method.
4.2 This test method can be used on Pu matrices in nitrate solutions.
4.3 This test method has been validated for use on materials that meet the specifications described in Specification C757 and
Test Methods C758 and C759.
4.4 This test method has been validated for all element
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.