ASTM D1092-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Apparent Viscosity of Lubricating Greases
Standard Test Method for Measuring Apparent Viscosity of Lubricating Greases
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Apparent viscosity versus shear rate information can be useful in predicting pressure drops in grease distribution systems under steady-state flow conditions at constant temperature.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers measurement, in poises, of the apparent viscosity of lubricating greases in the temperature range from −54 °C to 38 °C (−65 °F to 100 °F). Measurements are limited to the range from 25 P to 100 000 P at 0.1 s−1 and 1 P to 100 P at 15 000 s−1.
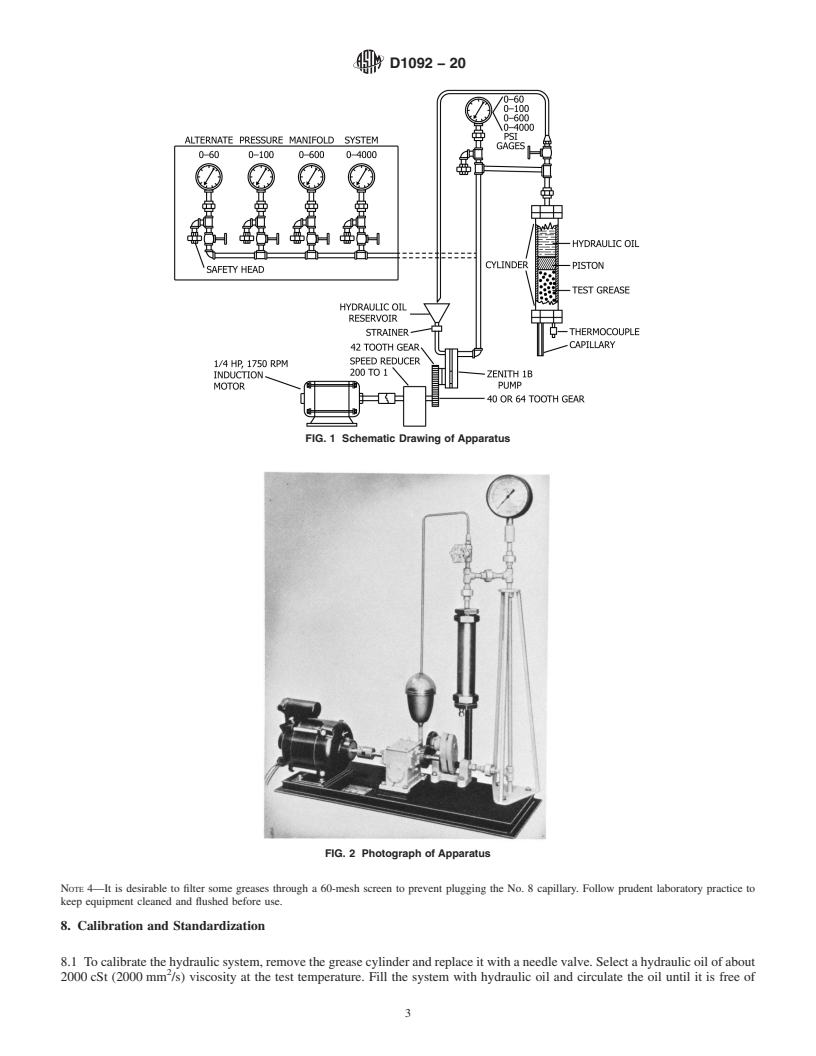
Note 1: At very low temperatures the shear rate range may be reduced because of the great force required to force grease through the smaller capillaries. Precision has not been established below 10 s−1.
1.2 This standard uses inch-pound units as well as SI (acceptable metric) units. The values stated first are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only. The capillary dimensions in SI units in Fig. A1.1 and Fig. A1.2 are standard.
1.3 This test method uses mercury thermometers. WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Use caution when handling mercury and mercury-containing products. See the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional information. The potential exists that selling mercury or mercury-containing products, or both, is prohibited by local or national law. Users must determine legality of sales in their location. The responsible subcommittee, D02.G0, continues to explore alternatives to eventually replace the mercury thermometers.
1.3.1 In addition, temperature measuring devices such as liquid-in-glass thermometers (Specifications E1 and E2251), thermocouples, thermistors, or platinum resistance thermometers that provide equivalent or better accuracy and precision, that cover the temperature range for ASTM thermometer 49C, may be used.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D1092 − 20
Standard Test Method for
1
Measuring Apparent Viscosity of Lubricating Greases
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1092; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.1 This test method covers measurement, in poises, of the
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
apparent viscosity of lubricating greases in the temperature
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
rangefrom−54°Cto38°C(−65°Fto100°F).Measurements
−1 dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
are limited to the range from 25P to 100000P at 0.1s and
−1 ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
1P to 100P at 15000s .
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
NOTE1—Atverylowtemperaturestheshearraterangemaybereduced
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
because of the great force required to force grease through the smaller
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
−1
capillaries. Precision has not been established below 10s .
1.2 This standard uses inch-pound units as well as SI
2. Referenced Documents
(acceptable metric) units. The values stated first are to be
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for
D88Test Method for Saybolt Viscosity
information only. The capillary dimensions in SI units in Fig.
D217Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating
A1.1 and Fig. A1.2 are standard.
Grease
1.3 This test method uses mercury thermometers.
D3244Practice for Utilization of Test Data to Determine
WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many regula-
Conformance with Specifications
tory agencies as a hazardous substance that can cause serious
E1Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
medicalissues.Mercury,oritsvapor,hasbeendemonstratedto
E2251Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermom-
be hazardous to health and corrosive to materials. Use caution
eters with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
when handling mercury and mercury-containing products. See
3. Terminology
the applicable product Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional
information. The potential exists that selling mercury or
3.1 Definitions:
mercury-containing products, or both, is prohibited by local or
3.1.1 apparent viscosity, n—of a lubricating grease is the
national law. Users must determine legality of sales in their
ratio of shear stress to shear rate calculated from Poiseuille’s
location. The responsible subcommittee, D02.G0, continues to
equation, and is measured in poises (see 10.1).
explore alternatives to eventually replace the mercury ther-
3.1.2 capillary, n—For the purpose of this test method, a
mometers.
capillary is any right cylindrical tube having a length to
1.3.1 In addition, temperature measuring devices such as
diameter ratio of 40 to 1.
liquid-in-glass thermometers (Specifications E1 and E2251),
3.1.3 shear rate, n—the rate at which a series of adjacent
thermocouples, thermistors, or platinum resistance thermom-
layers of grease move with respect to each other; proportional
eters that provide equivalent or better accuracy and precision,
to the linear velocity of flow divided by the capillary radius,
that cover the temperature range forASTM thermometer 49C,
and is thus expressed as reciprocal seconds.
may be used.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Summary of Test Method
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1 The sample is forced through a capillary by means of a
floating piston actuated by the hydraulic system. From the
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee D02.G0.02 on Consistency and Related Rheological Tests. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved June 1, 2020. Published September 2020. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1950. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as D1092–19. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D1092-20. the ASTM website.
*A Summ
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D1092 − 19 D1092 − 20
Standard Test Method for
1
Measuring Apparent Viscosity of Lubricating Greases
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1092; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers measurement, in poises, of the apparent viscosity of lubricating greases in the temperature range from
−1
−54 °C to 38 °C (−65 °F to 100 °F). Measurements are limited to the range from 25 P to 100 000 P at 0.1 s and 1 P to 100 P at
−1
15 000 s .
NOTE 1—At very low temperatures the shear rate range may be reduced because of the great force required to force grease through the smaller capillaries.
−1
Precision has not been established below 10 s .
1.2 This standard uses inch-pound units as well as SI (acceptable metric) units. The values stated first are to be regarded as
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only. The capillary dimensions in SI units in Fig. A1.1 and Fig. A1.2
are standard.
1.3 This test method uses mercury thermometers. WARNING—Mercury has been designated by many regulatory agencies as a
hazardous substance that can cause serious medical issues. Mercury, or its vapor, has been demonstrated to be hazardous to health
and corrosive to materials. Use caution when handling mercury and mercury-containing products. See the applicable product
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for additional information. The potential exists that selling mercury or mercury-containing products, or
both, is prohibited by local or national law. Users must determine legality of sales in their location. The responsible subcommittee,
D02.G0, continues to explore alternatives to eventually replace the mercury thermometers.
1.3.1 In addition, temperature measuring devices such as liquid-in-glass thermometers (Specification(Specifications E1 and
E2251), thermocouples, thermistors, or platinum resistance thermometers that provide equivalent or better accuracy and precision,
that cover the temperature range for ASTM thermometer 49C, may be used.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.G0.02 on Consistency and Related Rheological Tests.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2019June 1, 2020. Published November 2019September 2020. Originally approved in 1950. Last previous edition approved in 20182019
as D1092 – 18.D1092 – 19. DOI: 10.1520/D1092-19.10.1520/D1092-20.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1092 − 20
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D88 Test Method for Saybolt Viscosity
D217 Test Methods for Cone Penetration of Lubricating Grease
D3244 Practice for Utilization of Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E2251 Specification for Liquid-in-Glass ASTM Thermometers with Low-Hazard Precision Liquids
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 apparent viscosity, n—of a lubricating grease is the ratio of shear stress to shear rate calculated from Poiseuille’s equation,
and is measured in poises (see 10.1).
3.1.2 capillary, n—For the purpose of this test method, a capillary is any right cylindrical tube having a length to diameter ratio
of 40 to 1.
3.1.3 shear rate, n—the rate at which a series of adjacent layers of grease move with respect to each other; proportional to the
linear
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.