ASTM D8442-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Cannabinoids in Cannabis Raw Materials and Resin Cannabis Products by Gas Chromatography and Flame Ionization Detection
Standard Test Method for Determination of Cannabinoids in Cannabis Raw Materials and Resin Cannabis Products by Gas Chromatography and Flame Ionization Detection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Gas chromatography and flame ionization detection provides a rapid means to identify and quantify cannabinoids in a variety of samples of interest. This test method allows producers of cannabis products to improve and optimize the quality of their products. For example, hemp extractors can use it to determine the efficiency of extraction processes and to verify that products meet regulatory requirements, ensuring safety and quality of products.
5.2 Cannabinoids, such as CBD and THC can be monitored throughout the production process. The determination of Δ9-THC is often required for regulatory purposes and the determination of other THC isomers is often of interest. The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime provides experimental details and guidance for use of GC to analyze cannabis related samples, including conditions suitable for decarboxylation of cannabinoid acids.3
5.3 Post-decarboxylated methodology is used. In decarboxylation, heat is used to liberate carbon dioxide from carboxylic acid cannabinoids, forming their corresponding neutral cannabinoids, for example, THC from THCA. It should be recognized that the hot temperature of the GC injection port itself is capable of effecting at least some decarboxylation (250 °C – Table 2), and many sample types, such as distillates, require no decarboxylation because it would have occurred during material processing. Therefore, some knowledge of sample properties and material processing is useful. Resulting determinations are for the total cannabinoid content of specific isomers, for example, total Δ9-THC. For those samples requiring decarboxylation, the method is validated per Practice D8282 through the use of reference materials, spike and recovery of knowns, or through comparison with LC results. For example, carrying out the decarboxylation procedure of a standard containing known amounts of CBDA and CBN should yield the correct amounts of CBD and CBN, where CBN is not significantly changed and the mass...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the analysis of cannabinoids in cannabis products by gas chromatography (GC) and flame ionization detection (FID).
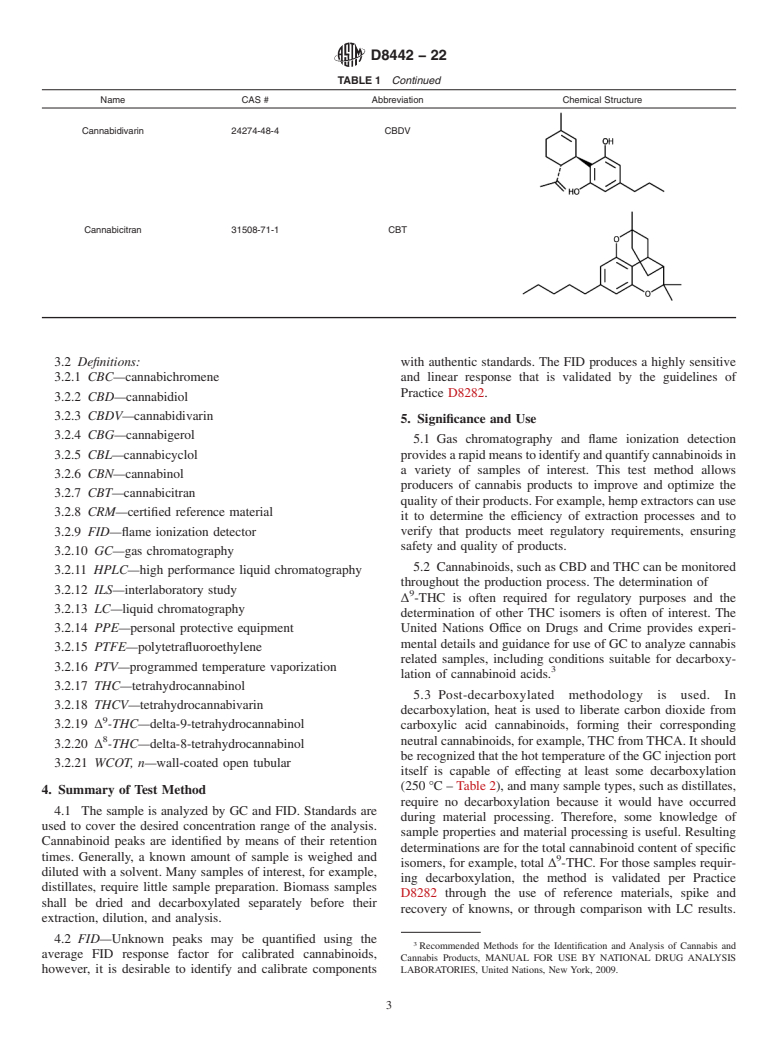
1.2 This test method is applicable to cannabis raw materials and resin cannabis products as defined in Guide D8245, including those from hemp. Such material includes: biomass; plant material; flowers; resins; extracts; distillates; recovered solvents; and other intermediate processing material. The applicable concentration range of analysis will vary to some extent depending on the nature of the sample, for instance measurement of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) for regulatory purposes in hemp would require calibration to lower concentration levels compared to measurement of CBD in its isolate; however, in most cases, the test method is applicable to the determination of major and minor cannabinoids above about 0.1 mass% in concentration. Dilution of sample solutions is used to adjust concentrations to fall within appropriate calibration curves. Particular emphasis is placed on the determination of Δ9-THC for regulatory compliance purposes and control. This test method can measure any cannabinoid that is eluted and detected from a GC column with sufficient resolution from any interfering compounds. Typical cannabinoids of interest that can be determined by this test method are shown in Table 1. Use of an HPLC technique is recommended if individual measurement of acids, such as THCA, is required.
1.3 The test method does not purport to identify all individual cannabinoids; however, individual users can adapt this test method for specific custom analyses to meet their needs.
1.4 Units—Values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard t...
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D8442 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Cannabinoids in Cannabis Raw Materials
and Resin Cannabis Products by Gas Chromatography and
1
Flame Ionization Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D8442; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This test method covers the analysis of cannabinoids in
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
cannabis products by gas chromatography (GC) and flame
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ionization detection (FID).
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
1.2 This test method is applicable to cannabis raw materials
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
and resin cannabis products as defined in Guide D8245,
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
including those from hemp. Such material includes: biomass;
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
plant material; flowers; resins; extracts; distillates; recovered
2. Referenced Documents
solvents; and other intermediate processing material. The
2
applicable concentration range of analysis will vary to some
2.1 ASTM Standards:
extent depending on the nature of the sample, for instance
D4307Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as
9
measurement of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (∆ -THC) for
Analytical Standards
regulatorypurposesinhempwouldrequirecalibrationtolower
D4626Practice for Calculation of Gas Chromatographic
concentration levels compared to measurement of CBD in its
Response Factors
isolate;however,inmostcases,thetestmethodisapplicableto
D8245Guide for Disposal of Resin-Containing Cannabis
the determination of major and minor cannabinoids above
Raw Materials and Downstream Products
about0.1mass%inconcentration.Dilutionofsamplesolutions
D8270Terminology Relating to Cannabis
is used to adjust concentrations to fall within appropriate
D8282Practice for Laboratory Test Method Validation and
calibration curves. Particular emphasis is placed on the deter-
Method Development
9
mination of ∆ -THC for regulatory compliance purposes and
D8334/D8334MPractice for Sampling of Cannabis/Hemp
control. This test method can measure any cannabinoid that is
Post-Harvest Batches for Laboratory Analyses
eluted and detected from a GC column with sufficient resolu-
D8375Test Method for Determination of Cannabinoid Con-
tion from any interfering compounds. Typical cannabinoids of
centration in Dried Cannabis and Hemp Raw Materials
interest that can be determined by this test method are shown
using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrom-
in Table1. Use of an HPLC technique is recommended if
etry (LC-MS/MS)
individual measurement of acids, such as THCA, is required.
E355PracticeforGasChromatographyTermsandRelation-
1.3 The test method does not purport to identify all indi- ships
E594Practice for Testing Flame Ionization Detectors Used
vidual cannabinoids; however, individual users can adapt this
test method for specific custom analyses to meet their needs. in Gas or Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
E1510Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular
1.4 Units—ValuesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasthe
Capillary Columns in Gas Chromatographs
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
3. Terminology
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1 Definitions:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.1 Refer to Terminology D8270 for guidance on termi-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
nology relating to cannabis.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D37 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Cannabis and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D37.03 on Laboratory. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
CurrenteditionapprovedJuly15,2022.PublishedOctober2022.DOI:10.1520/ Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
D8442-22. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D8442 − 22
TABLE 1 Typical Cannabinoids Measured
Name
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.