ASTM D7559/D7559M-09(2014)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Pressure Decay of Inflatable Restraint Cushions
Standard Test Method for Determining Pressure Decay of Inflatable Restraint Cushions
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method may be used for product development and design, production validation, manufacturing process control, lot acceptance, or for a combination thereof.
5.2 The rate of inflation in this method does not attempt to mimic that of an actual cushion deployment, nor is it intended to subject the cushion to the dynamic loads, stress, and temperatures during such an event. It is also recognized that the compressed air used for this tests may not leak through the cushion at the same rate as the gas or mixture of gasses typically used in cushion inflators. Rather this method is intended to give a relative indication of the pressure holding ability of the cushion.
5.3 The internal volume and internal design of cushions varies greatly. This test method is most useful when comparing data from cushions of the same design and volume. This test method does not provide any data concerning the volume of gas leaking from the bag. At certain higher levels of the initial internal pressure, this test method will irreversibly damage the cushion and change its leakage properties for future testing or for commercial use. The damage to the bag is dependent on the design or shape of a specific bag and the type of coating applied. It is the responsibility of the supplier and / or purchaser to determine if the parameters under which a cushion is tested will be destructive and render the cushion unfit for future use
5.4 Within the limits of variance expressed in Section 12, this test method is useful for design and production validation and may be suitable for incorporation in a cushion specification or for lot acceptance testing of commercial shipments.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended to determine the ability of an inflatable restraint cushion to retain air pressure at elevated pressures for a specified time interval.
1.2 Procedures and apparatus other than those stated in this test method may be used by agreement of purchaser and supplier, provided the specific deviations from the standard acknowledged in the report.
1.3 The results of this test method should not be used to predict the actual internal pressure decay of a cushion during a deployment.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D7559/D7559M −09 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Method for
Determining Pressure Decay of Inflatable Restraint
Cushions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7559/D7559M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
deployment; inflatable restraint.
1.1 This test method is intended to determine the ability of
an inflatable restraint cushion to retain air pressure at elevated 3.2 For all other terms related to textiles, see Terminology
pressures for a specified time interval. D123.
1.2 Procedures and apparatus other than those stated in this
4. Summary of Test Method
test method may be used by agreement of purchaser and
4.1 After inflation with air to a specific initial internal
supplier, provided the specific deviations from the standard
pressure, an inflatable restraint cushion is tested to for its
acknowledged in the report.
abilitytoretainaspecifiedresidualpressure(allowingforsome
1.3 The results of this test method should not be used to
pressure loss) over a specified time period.
predict the actual internal pressure decay of a cushion during a
4.2 An inflatable restraint cushion is mounted onto a test
deployment.
stand that allows for the inflation of the cushion to a specified
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
initial internal pressure. After the air supply is discontinued,
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
instrumentation measures and records internal pressure drop
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
over time.
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
4.3 Cushion internal pressure versus time data is recorded
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
and compared to allowable limits agreed upon by the purchaser
with the standard.
and supplier.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5. Significance and Use
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5.1 This test method may be used for product development
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
and design, production validation, manufacturing process
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
control, lot acceptance, or for a combination thereof.
2. Referenced Documents
5.2 The rate of inflation in this method does not attempt to
2.1 ASTM Standards: mimic that of an actual cushion deployment, nor is it intended
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles to subject the cushion to the dynamic loads, stress, and
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to temperaturesduringsuchanevent.Itisalsorecognizedthatthe
Determine the Precision of a Test Method compressed air used for this tests may not leak through the
cushion at the same rate as the gas or mixture of gasses
D6799 Terminology Relating to Inflatable Restraints
typically used in cushion inflators. Rather this method is
3. Terminology
intended to give a relative indication of the pressure holding
3.1 For all terminology relating to D13.20, Inflatable
ability of the cushion.
restraints, refer to Terminology D6799.
5.3 The internal volume and internal design of cushions
varies greatly. This test method is most useful when comparing
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
data from cushions of the same design and volume. This test
and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.20 on Inflatable Restraints.
method does not provide any data concerning the volume of
Current edition approved July 1, 2014. Published August 2014. Originally
gas leaking from the bag. At certain higher levels of the initial
approved as D7559/D7559M-09. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as
D7559/D7559M-09. DOI: 10.1520/D7559_D7559M-09R14.
internal pressure, this test method will irreversibly damage the
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
cushion and change its leakage properties for future testing or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
for commercial use.The damage to the bag is dependent on the
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. design or shape of a specific bag and the type of coating
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7559/D7559M−09 (2014)
applied. It is the responsibility of the supplier and / or 6.9 Filter requirements, data sampling rate, transducer fre-
purchasertodetermineiftheparametersunderwhichacushion quency response, and amplifier frequency response shall be
is tested will be destructive and render the cushion unfit for such that the overall accuracy of the data acquisition system
future use shall be within 61 %. The significant figures of the recorded
data of time and pressure, along with the timing increment
5.4 Within the limits of variance expressed in Section 12,
should be agreed upon by the purchaser and supplier.
this test method is useful for design and production validation
andmaybesuitableforincorporationinacushionspecification
7. Sampling
or for lot acceptance testing of commercial shipments.
7.1 The Cushion Pressure Decay Test at certain test param-
6. Apparatus
eters and pressures is a destructive test and therefore necessi-
tates sampling procedures if used in conjunction with lot
6.1 Air Supply Source, capable of filling the cushion to the
acceptance.
specified pressure, with a flow rate capable of maintaining the
specified pressure at equilibrium. Typically the pressure used 7.2 The determination of lot size and sampling plan shall be
for testing the cushion will not exceed 200 kPa [29 psi], nor
agreed to by purchaser and supplier.
will the flow exceed 1500 L/min [53 CFM]. The air source
7.3 One cushion assembly is a test specimen.
shouldbeequippedwithaninlinefilter,shutoffvalve,andflow
regulator. Care should be taken to trap out excess moisture or
8. Equipment Calibration
oil from the compressed air source.
8.1 For inflatable restraints, all test equipment used in
6.2 Shut Off Valve, capable of being actuated either manu-
accordance with this test method shall be certified for calibra-
ally or remotely by an electrical signal.
tion annually using gages that are traceable to the National
Institute of Science and Technology (NIST) or other national
6.3 Mounting Fixture, capable of allowing a sealed attach-
standards laboratory. The test parameters of the equipment
ment of the cushion to the air supply source, the shut off valve,
shall be tested within the operating ranges covered in the
and instrumentation to monitor the pressure decay during the
cushion specification or equivalent document.
test. It should contain a pressure pickup tube. It shall be in an
orientation that allows free expansion of the cushion geometry.
9. Conditioning
It should have sufficient safety shielding and isolation for
9.1 Conditioning of specimens and conducting of the testing
operator protection during the test. The clamping device that
in the standard atmosphere for testing textiles is desirable, but
attaches the opening of the cushion to the filling tube fixture
not required. It is recognized that conditions of the air from the
should be designed to properly fit the opening of the cushion,
compressed air source used to inflate the specimen will not be
provide a secure mechanical attachment, and prevent gas
controlled, even though care should be taken to filter the air
leakage.
and trap out any excessive moisture or compressor oils.
6.4 PickupTube,mountedcoaxiallyinsidefillingtubeofthe
9.2 Testing can be conducted in, or specimens conditioned
mounting fixture. One end should extend inside the cushion at
in an environment other that of the standard atmosphere for
minimum of 25 mm [1 in.] beyond the clamping device. The
testing textiles, such as in hot or cold conditions. These
other end should extend through the wall of the filling tube of
conditions will be agreed upon between the purchaser and
the mounting fixture through a sealed joint, and be connected
supplier, or as specified in any relevant customer or supplier
to a pressure transducer or gauge. The end that extends into the
specifications.
cushionshouldbeorientedsuchthatitallowsfreeexpansionof
the cushion geometry.
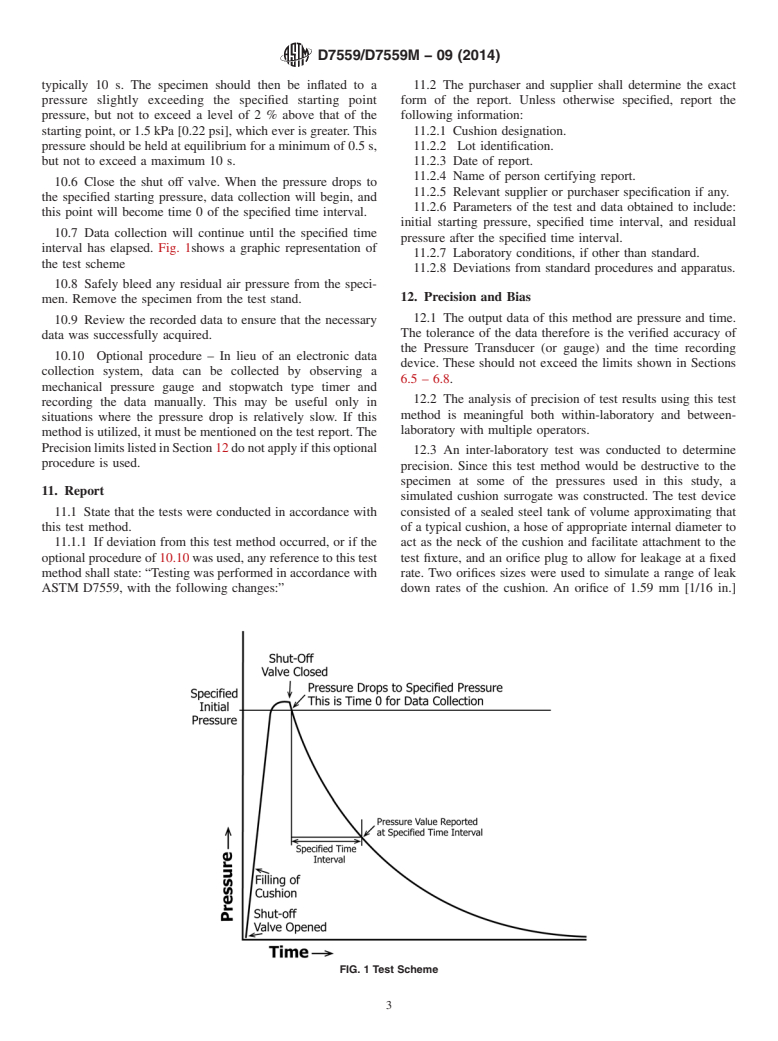
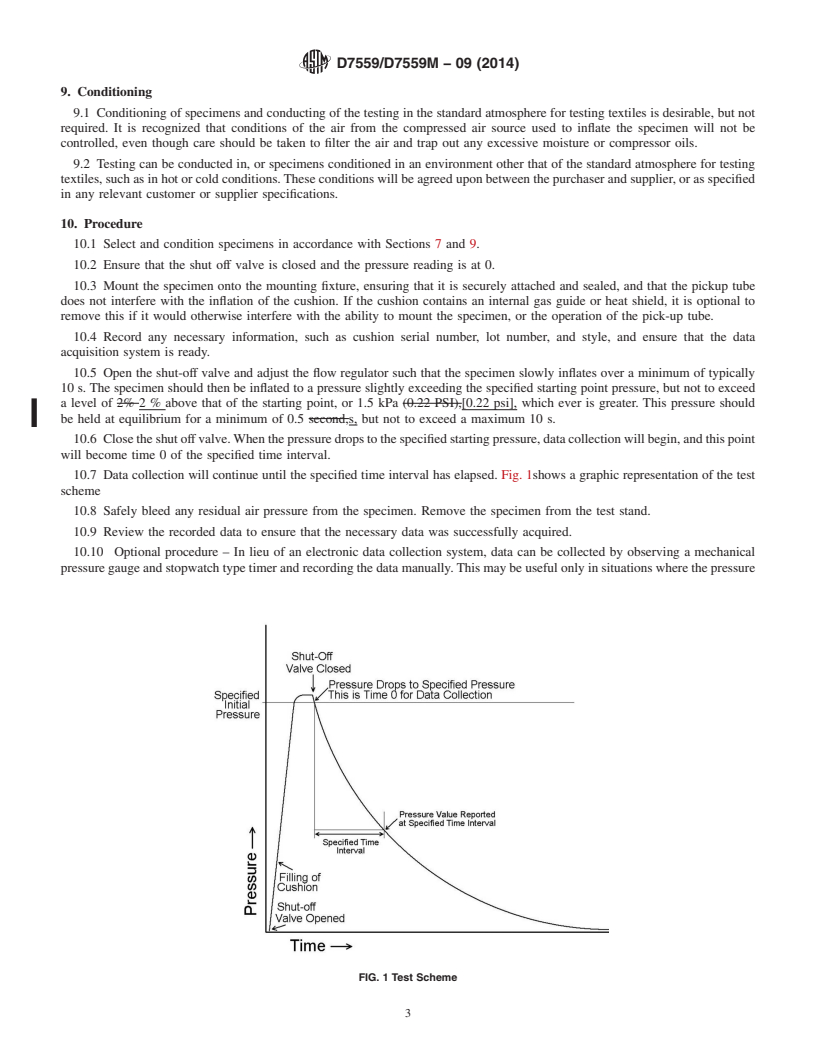
10. Procedure
6.
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7559/D7559M − 09 D7559/D7559M − 09 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Method for
Determining Pressure Decay of Inflatable Restraint
Cushions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7559/D7559M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is intended to determine the ability of an inflatable restraint cushion to retain air pressure at elevated
pressures for a specified time interval.
1.2 Procedures and apparatus other than those stated in this test method may be used by agreement of purchaser and supplier,
provided the specific deviations from the standard acknowledged in the report.
1.3 The results of this test method should not be used to predict the actual internal pressure decay of a cushion during a
deployment.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
D6799 Terminology Relating to Inflatable Restraints
3. Terminology
3.1 For all terminology relating to D13.20, Inflatable restraints, refer to Terminology D6799.
3.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard: deployment; inflatable restraint.
3.2 For all other terms related to textiles, see Terminology D123.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 After inflation with air to a specific initial internal pressure, an inflatable restraint cushion is tested to for its ability to retain
a specified residual pressure (allowing for some pressure loss) over a specified time period.
4.2 An inflatable restraint cushion is mounted onto a test stand that allows for the inflation of the cushion to a specified initial
internal pressure. After the air supply is discontinued, instrumentation measures and records internal pressure drop over time.
4.3 Cushion internal pressure versus time data is recorded and compared to allowable limits agreed upon by the purchaser and
supplier.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method may be used for product development and design, production validation, manufacturing process control,
lot acceptance, or for a combination thereof.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D13 on Textiles and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.20 on Inflatable Restraints.
Current edition approved July 1, 2009July 1, 2014. Published August 2009August 2014. Originally approved as D7559/D7559M-09. Last previous edition approved in
2009 as D7559/D7559M-09. DOI: 10.1520/D7559_D7559M-09.10.1520/D7559_D7559M-09R14.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7559/D7559M − 09 (2014)
5.2 The rate of inflation in this method does not attempt to mimic that of an actual cushion deployment, nor is it intended to
subject the cushion to the dynamic loads, stress, and temperatures during such an event. It is also recognized that the compressed
air used for this tests may not leak through the cushion at the same rate as the gas or mixture of gasses typically used in cushion
inflators. Rather this method is intended to give a relative indication of the pressure holding ability of the cushion.
5.3 The internal volume and internal design of cushions varies greatly. This test method is most useful when comparing data
from cushions of the same design and volume. This test method does not provide any data concerning the volume of gas leaking
from the bag. At certain higher levels of the initial internal pressure, this test method will irreversibly damage the cushion and
change its leakage properties for future testing or for commercial use. The damage to the bag is dependent on the design or shape
of a specific bag and the type of coating applied. It is the responsibility of the supplier and / or purchaser to determine if the
parameters under which a cushion is tested will be destructive and render the cushion unfit for future use
5.4 Within the limits of variance expressed in Section 1212,, this test method is useful for design and production validation and
may be suitable for incorporation in a cushion specification or for lot acceptance testing of commercial shipments.
6. Apparatus
6.1 Air Supply Source, capable of filling the cushion to the specified pressure, with a flow rate capable of maintaining the
specified pressure at equilibrium. Typically the pressure used for testing the cushion will not exceed 200 kPa (29 PSI),[29 psi], nor
will the flow exceed 1500 L/min (53 CFM).[53 CFM]. The air source should be equipped with an inline filter, shut off valve, and
flow regulator. Care should be taken to trap out excess moisture or oil from the compressed air source.
6.2 Shut Off Valve, capable of being actuated either manually or remotely by an electrical signal.
6.3 Mounting Fixture, capable of allowing a sealed attachment of the cushion to the air supply source, the shut off valve, and
instrumentation to monitor the pressure decay during the test. It should contain a pressure pickup tube. It shall be in an orientation
that allows free expansion of the cushion geometry. It should have sufficient safety shielding and isolation for operator protection
during the test. The clamping device that attaches the opening of the cushion to the filling tube fixture should be designed to
properly fit the opening of the cushion, provide a secure mechanical attachment, and prevent gas leakage.
6.4 Pickup Tube, mounted coaxially inside filling tube of the mounting fixture. One end should extend inside the cushion at
minimum of 25 mm (1 in.)[1 in.] beyond the clamping device. The other end should extend through the wall of the filling tube
of the mounting fixture through a sealed joint, and be connected to a pressure transducer or gauge. The end that extends into the
cushion should be oriented such that it allows free expansion of the cushion geometry.
6.5 Pressure Transducer, suitable for measuring pressures inside the cushion (via the pickup tube) from 0 to at least 200 kPa
(0[0 to 29 PSI)psi] and maintained to an accuracy of a maximum of +/- 2%.62 %.
6.6 Pressure Gauge, suitable for measuring pressures inside the cushion (via the pickup tube) from 0 to at least 200 kPa (0[0
to 29 PSI)psi] and maintained to an accuracy of a maximum of +/- 2%.62 %.
6.7 Data Acquisition System, suitable for recording the output of the pressure transducer versus elapsed time. The input
amplifier and the time interval at which the data is recorded must have an accuracy of +/- 1%.61 %. It is optional that this system
can initiate the filling of the bag and the closure of the shut-off valve.
6.8 Manual Timer (stopwatch), optional, suitable for manually observing elapsed time. This must have an accuracy of 61%.61
%.
6.9 Filter requirements, data sampling rate, transducer frequency response, and amplifier frequency response shall be such that
the overall accuracy of the data acquisition system shall be within 6 1%.61 %. The significant figures of the recorded data of time
and pressure, along with the timing increment should be agreed upon by the purchaser and supplier.
7. Sampling
7.1 The Cushion Pressure Decay Test at certain test parameters and pressures is a destructive test and therefore necessitates
sampling procedures if used in conjunction with lot acceptance.
7.2 The determination of lot size and sampling plan shall be agreed to by purchaser and supplier.
7.3 One cushion assembly is a test specimen.
8. Equipment Calibration
8.1 For inflatable restraints, all test equipment used in accordance with this test method shall be certified for calibration annually
using gages tha
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.