ASTM F564-02(2006)
(Specification)Standard Specification and Test Methods for Metallic Bone Staples
Standard Specification and Test Methods for Metallic Bone Staples
ABSTRACT
This specification covers characterization of the design and mechanical function of metallic staples used in the internal fixation of the muscular skeletal system. It is not the intention of this specification to describe or specify specific designs for metallic bone staples. Different test methods shall be performed in order to determine the following mechanical properties of metallic bone staples: bending fatigue, pull-out fixation strength, soft tissue fixation strength, and elastic static bending.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers characterization of the design and mechanical function of metallic staples used in the internal fixation of the muscular skeletal system. It is not the intention of this specification to describe or specify specific designs for metallic bone staples.
1.2 This specification includes the following four test methods for measuring mechanical properties of metallic bone staples:
1.2.1 Test Method for Constant Amplitude Bending Fatigue Tests of Metallic Bone Staples—Annex A1.
1.2.2 Test Method for Pull-Out Fixation Strength of Metallic Bone Staples—Annex A2.
1.2.3 Test Method for Soft Tissue Fixation Strength of Metallic Bone Staples—Annex A3.
1.2.4 Test Method for Elastic Static Bending of Metallic Bone Staples—Annex A4.
1.3 Unless otherwise indicated, the values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are given for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F 564 – 02 (Reapproved 2006)
Standard Specification and Test Methods for
1
Metallic Bone Staples
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 564; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E 122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate,
With a Specified Tolerable Error, the Average for a
1.1 This specification covers characterization of the design
Characteristic of a Lot or Process
and mechanical function of metallic staples used in the internal
E 467 Practice for Verification of Constant Amplitude Dy-
fixation of the muscular skeletal system. It is not the intention
namic Forces in an Axial Fatigue Testing System
of this specification to describe or specify specific designs for
F75 Specification for Cobalt-28 Chromium-6 Molybdenum
metallic bone staples.
Alloy Castings and Casting Alloy for Surgical Implants
1.2 This specification includes the following four test meth-
(UNS R30075)
ods for measuring mechanical properties of metallic bone
F86 Practice for Surface Preparation and Marking of Me-
staples:
tallic Surgical Implants
1.2.1 Test Method for ConstantAmplitude Bending Fatigue
F 382 Specification and Test Method for Metallic Bone
Tests of Metallic Bone Staples—Annex A1.
Plates
1.2.2 Test Method for Pull-Out Fixation Strength of Metal-
F 565 Practice for Care and Handling of Orthopedic Im-
lic Bone Staples—Annex A2.
plants and Instruments
1.2.3 Test Method for Soft Tissue Fixation Strength of
F 601 Practice for Fluorescent Penetrant Inspection of Me-
Metallic Bone Staples—Annex A3.
tallic Surgical Implants
1.2.4 Test Method for Elastic Static Bending of Metallic
F 629 Practice for Radiography of Cast Metallic Surgical
Bone Staples—Annex A4.
Implants
1.3 Unless otherwise indicated, the values stated in SI units
are to be regarded as standard.The values given in parentheses
3. Finish
are given for information only.
3.1 Staples conforming to this specification shall be finished
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
and identified in accordance with PracticeF86, as appropriate.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Inspection Practices
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 Staples made in accordance with Specification F75
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
should be inspected in accordance with Practice F 601 or
X-rayed in accordance with Practice F 629.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Care and Handling
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
5.1 Staples should be cared for and handled in accordance
with Practice F 565, as appropriate.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on
Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of
6. Keywords
Subcommittee F04.21 on Osteosynthesis.
6.1 bendingtest;bonefixation;fatiguetest;fixationdevices;
Current edition approved March 1, 2006. Published April 2006. Originally
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as F 564 – 02. metallic bone staples; orthopaedic medical devices; pullout
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
test; soft tissue fixation; surgical implants
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F 564 – 02 (2006)
ANNEXES
(Mandatory Information)
A1. TEST METHOD FOR CONSTANT AMPLITUDE BENDING FATIGUE TESTS OF METALLIC BONE STAPLES
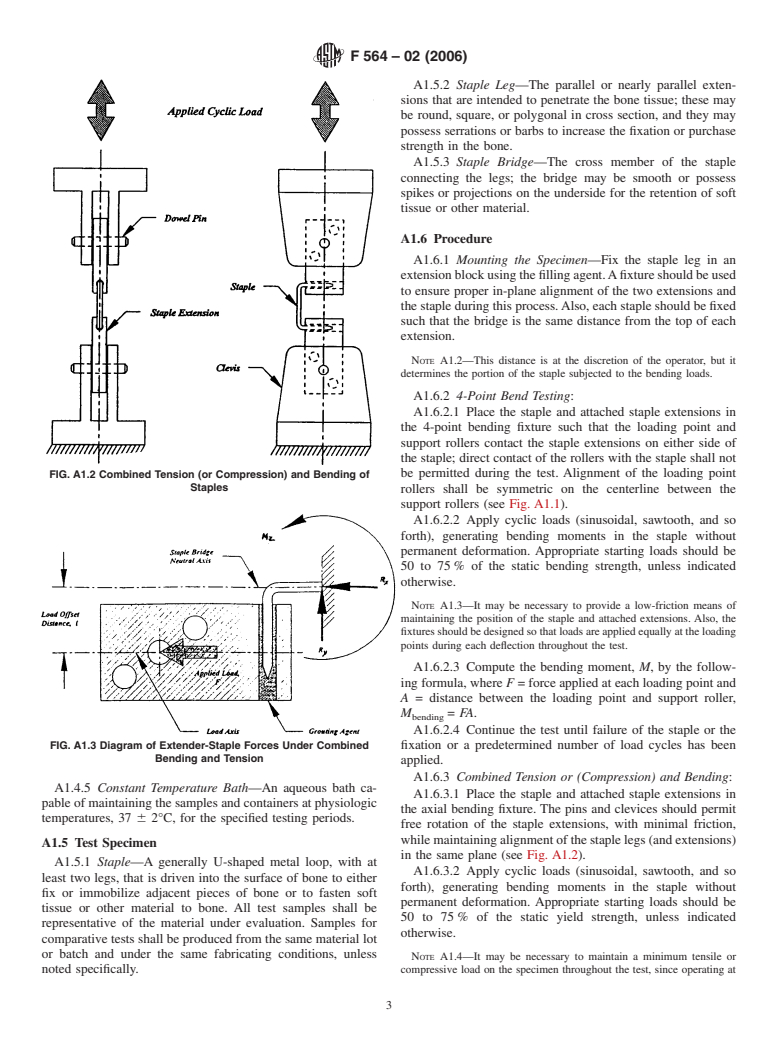
A1.1 Scope clearance to restrict bending of the staple within the hole. The
staple is fixed securely in the block using a moldable filling or
A1.1.1 This test method covers procedures for the perfor-
grouting agent. The extension design should minimize the
mance of constant amplitude fatigue testing of metallic staples
weight to reduce the influence on the staple while maintaining
used in internal fixation of the musculoskeletal system. This
sufficient stiffness to transfer the load to the staple without
test method may be used when testing in air at ambient
undesirable deflection. Holes for pin and clevis fixation are
temperature or in an aqueous or physiological solution.
optional (see Figs. A1.1-A1.3).
A1.1.2 ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasthe
standard.
NOTE A1.1—Variations in fixation hole configuration may be
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.