ASTM D257-14
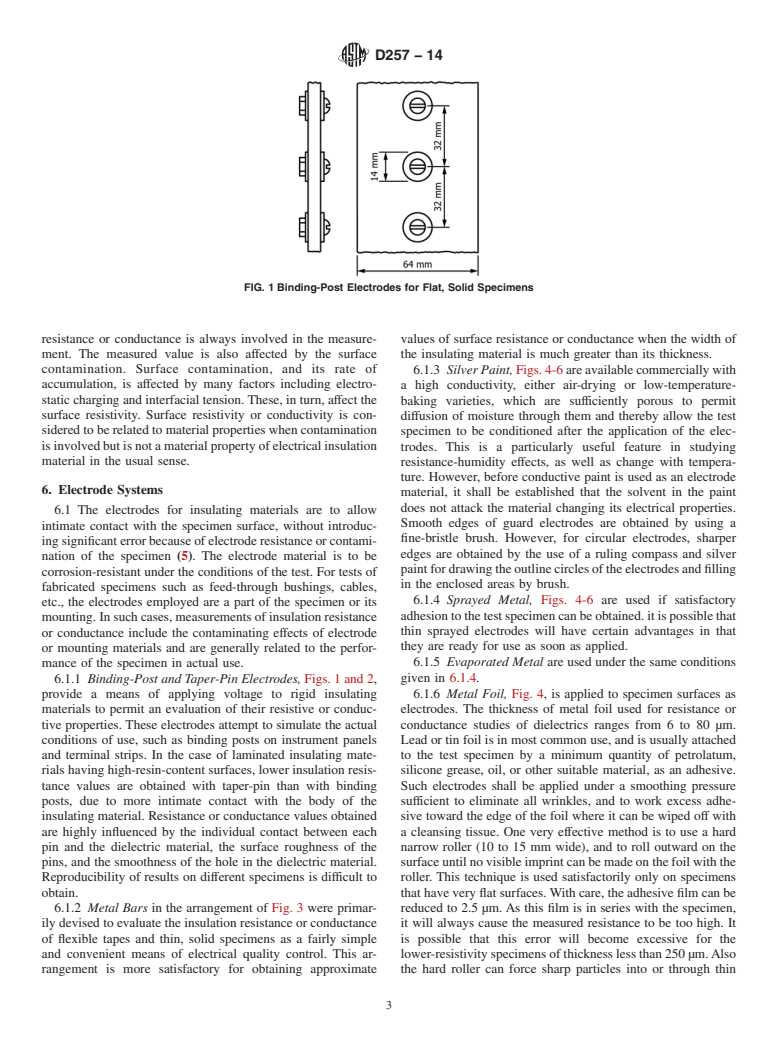
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
Standard Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Insulating materials are used to isolate components of an electrical system from each other and from ground, as well as to provide mechanical support for the components. For this purpose, it is generally desirable to have the insulation resistance as high as possible, consistent with acceptable mechanical, chemical, and heat-resisting properties. Since insulation resistance or conductance combines both volume and surface resistance or conductance, its measured value is most useful when the test specimen and electrodes have the same form as is required in actual use. Surface resistance or conductance changes rapidly with humidity, while volume resistance or conductance changes slowly with the total change being greater in some cases.
5.2 Resistivity or conductivity is used to predict, indirectly, the low-frequency dielectric breakdown and dissipation factor properties of some materials. Resistivity or conductivity is often used as an indirect measure of: moisture content, degree of cure, mechanical continuity, or deterioration of various types. The usefulness of these indirect measurements is dependent on the degree of correlation established by supporting theoretical or experimental investigations. A decrease of surface resistance results either in an increase of the dielectric breakdown voltage because the electric field intensity is reduced, or a decrease of the dielectric breakdown voltage because the area under stress is increased.
5.3 All the dielectric resistances or conductances depend on the length of time of electrification and on the value of applied voltage (in addition to the usual environmental variables). These must be known and reported to make the measured value of resistance or conductance meaningful. Within the electrical insulation materials industry, the adjective “apparent” is generally applied to resistivity values obtained under conditions of arbitrarily selected electrification time. See X1.4.
5.4 Volume resistivity or conductivi...
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover direct-current procedures for the measurement of dc insulation resistance, volume resistance, and surface resistance. From such measurements and the geometric dimensions of specimen and electrodes, both volume and surface resistivity of electrical insulating materials can be calculated, as well as the corresponding conductances and conductivities.
1.2 These test methods are not suitable for use in measuring the electrical resistance/conductance of moderately conductive materials. Use Test Method D4496 to evaluate such materials.
1.3 This standard describes several general alternative methodologies for measuring resistance (or conductance). Specific materials can be tested most appropriately by using standard ASTM test methods applicable to the specific material that define both voltage stress limits and finite electrification times as well as specimen configuration and electrode geometry. These individual specific test methodologies would be better able to define the precision and bias for the determination.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D257 − 14
Standard Test Methods for
1
DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D257; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* D1169 Test Method for Specific Resistance (Resistivity) of
Electrical Insulating Liquids
1.1 These test methods cover direct-current procedures for
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
themeasurementofdcinsulationresistance,volumeresistance,
D4496 Test Method for D-C Resistance or Conductance of
and surface resistance. From such measurements and the
Moderately Conductive Materials
geometric dimensions of specimen and electrodes, both vol-
D5032 Practice for Maintaining Constant Relative Humidity
ume and surface resistivity of electrical insulating materials
by Means of Aqueous Glycerin Solutions
can be calculated, as well as the corresponding conductances
D6054 Practice for Conditioning Electrical Insulating Mate-
and conductivities.
3
rials for Testing (Withdrawn 2012)
1.2 These test methods are not suitable for use in measuring
E104 Practice for Maintaining Constant Relative Humidity
the electrical resistance/conductance of moderately conductive
by Means of Aqueous Solutions
materials. Use Test Method D4496 to evaluate such materials.
3. Terminology
1.3 This standard describes several general alternative
methodologies for measuring resistance (or conductance).
3.1 Definitions:
Specific materials can be tested most appropriately by using
3.1.1 The following definitions are taken from Terminology
standardASTMtestmethodsapplicabletothespecificmaterial
D1711 and apply to the terms used in the text of this standard.
that define both voltage stress limits and finite electrification
3.1.2 conductance, insulation, n—the ratio of the total
times as well as specimen configuration and electrode geom-
volume and surface current between two electrodes (on or in a
etry. These individual specific test methodologies would be
specimen) to the dc voltage applied to the two electrodes.
better able to define the precision and bias for the determina-
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Insulation conductance is the recipro-
tion.
cal of insulation resistance.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.3 conductance, surface, n—the ratio of the current
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
betweentwoelectrodes(onthesurfaceofaspecimen)tothedc
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
voltage applied to the electrodes.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.3.1 Discussion—(Somevolumeconductanceisunavoid-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ably included in the actual measurement.) Surface conductance
is the reciprocal of surface resistance.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.4 conductance,volume,n—the ratio of the current in the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
volume of a specimen between two electrodes (on or in the
D150 Test Methods forAC Loss Characteristics and Permit-
specimen) to the dc voltage applied to the two electrodes.
tivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
3.1.4.1 Discussion—Volume conductance is the reciprocal
D374 Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insu-
of volume resistance.
lation (Metric) D0374_D0374M
3.1.5 conductivity, surface, n—the surface conductance
multiplied by that ratio of specimen surface dimensions (dis-
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
tance between electrodes divided by the width of electrodes
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and are the direct responsibility of
defining the current path) which transforms the measured
Subcommittee D09.12 on Electrical Tests.
conductance to that obtained if the electrodes had formed the
Current edition approved April 1, 2014. Published May 2014. Originally
approved in 1925. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D257 – 07. DOI: opposite sides of a square.
10.1520/D0257-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
----------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D257 − 07 D257 − 14 An American National Standard
Standard Test Methods for
1
DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D257; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 These test methods cover direct-current procedures for the measurement of dc insulation resistance, volume resistance, and
surface resistance. From such measurements and the geometric dimensions of specimen and electrodes, both volume and surface
resistivity of electrical insulating materials can be calculated, as well as the corresponding conductances and conductivities.
1.2 These test methods are not suitable for use in measuring the electrical resistance/conductance of moderately conductive
materials. Use Test Method D4496 to evaluate such materials.
1.3 This standard describes several general alternative methodologies for measuring resistance (or conductance). Specific
materials can be tested most appropriately by using standard ASTM test methods applicable to the specific material that define both
voltage stress limits and finite electrification times as well as specimen configuration and electrode geometry. These individual
specific test methodologies would be better able to define the precision and bias for the determination.
1.4 The procedures appear in the following sections:
Test Method or Procedure Section
Calculation 13
Choice of Apparatus and Test Method 7
Cleaning Solid Specimens 10.1
Conditioning of Specimens 11
Effective Area of Guarded Electrode Appendix
X2
Electrode Systems 6
Factors Affecting Insulation Resistance or Conductance Appendix
Measurements X1
Humidity Control 11.2
Liquid Specimens and Cells 9.4
Precision and Bias 15
Procedure for the Measurement of Resist- 12
ance or Conductance
Referenced Documents 2
Report 14
Sampling 8
Significance and Use 5
Specimen Mounting 10
Summary of Test Methods 4
Terminology 3
Test Specimens for Insulation, Volume, and Surface 9
Resistance or Conductance Determination
Typical Measurement Methods Appendix
X3
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D09.12 on Electrical Tests.
Current edition approved May 15, 2007April 1, 2014. Published June 2007May 2014. Originally approved in 1925. Last previous edition approved in 20052007 as
D257 – 99D257 – 07.(2005). DOI: 10.1520/D0257-07.10.1520/D0257-14.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D257 − 14
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D150 Test Methods for AC Loss Characteristics and Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
3
D374 Test Methods for Thickness of Solid Electrical Insulation (Withdrawn 2013)
D1169 Test Method for Specific Resistance (Resistivity) of Electrical Insulating Liquids
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
D4496 Test Method for D-C Resistance or Conductance of Moderately Conductive Materials
D5032 Practice for Maintaining Constant Relative Humidity by Means of Aqueous Glycerin Solutions
3
D6054 Practice for Conditioning Electrical Insulating Materials for Testing (Withdrawn 2012)
E104 Practice for Maintaining Constant Relative Humidity by Means of Aqueous Solutions
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 The following definitions are taken from Terminology D1711 and apply to the terms used in the text of this standard.
3.1.2 conductance, insulation, n—the ratio of the total volume and surface current between two electrodes (on or in a specimen)
to the dc voltage applied to the two electrodes.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.